This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Stathmin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
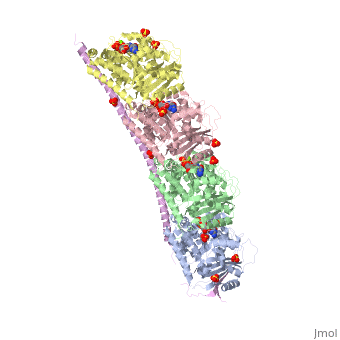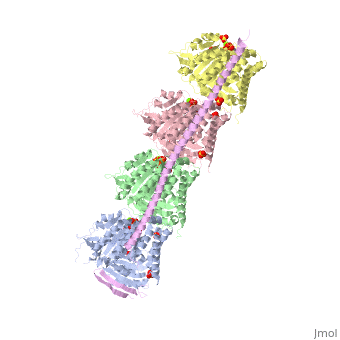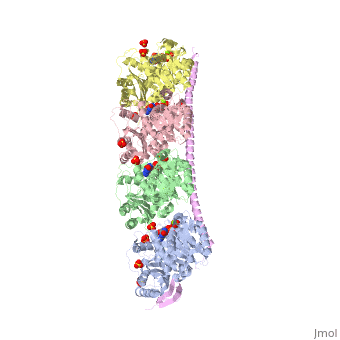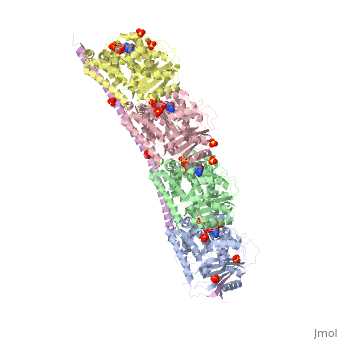
<StructureSection load='3ryf' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat stathmin SLD domain (magenta) complex with tubulin α chain (grey, pink), tubulin β chain (green, yellow), GTP, sulfate and Mg+2 ions (PDB code [[3ryf]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3ryf' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat stathmin SLD domain (magenta) complex with tubulin α chain (grey, pink), tubulin β chain (green, yellow), GTP, sulfate and Mg+2 ions (PDB code [[3ryf]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | '''Stathmin''' (STM) regulates microtubules dynamics. Microtubules undergo continuous assembly and disassembly in the cell’s cytoskeleton. STM binds to tubulin and prevents the latter from polymerization thus preventing microtubule assembly. Phosphorylation of STM weakens the binding of STM to tubulin enabling the microtubule assembly needed for the formation of mitotic spindle. Thus, STM is an oncoprotein. STM contains an SLD ( | + | '''Stathmin''' (STM) regulates microtubules dynamics. Microtubules undergo continuous assembly and disassembly in the cell’s cytoskeleton. STM binds to tubulin and prevents the latter from polymerization thus preventing microtubule assembly. Phosphorylation of STM weakens the binding of STM to tubulin enabling the microtubule assembly needed for the formation of mitotic spindle. Thus, STM is an oncoprotein. STM contains an SLD (Stathmin-Like Domain) domain of 149 residues which binds the tubulin dimer. |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 06:57, 20 July 2015
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of stathmin
Updated on 20-July-2015