Introduction
Connexins are integral transmembrane proteins that form intercellular channels in vertebrates. Connexin 26 is encoded by the GJB2 gene. Six connexins form a hexamerical assembly, known as connexon or hemichannel, which form an intercellular gap junction channel. Gap junctions are specialized membrane regions containing hundreds of intercellular communication channels that allow the passage of molecules such as ions, metabolites, nucleotides and small peptides. Virtually all cells in solid tissues are coupled by gap junctions, thus it is not surprising that mutations in connexin genes have been linked to a variety of Connexin human diseases, including cardiovascular anomalies, peripheral neuropathy, skin disorders, cataracts, and deafness.
Of notice, about half of all cases of human pre-lingual recessive deafness in countries surrounding the Mediterranean have been linked to mutations in the GJB2 gene [1],[2]
[3]
How does connexin 26 biochemically work?
Connexin 26 (CX26) protein is essential for maintaining the high K+ concentration in the endolymph of the inner ear. Sound stimulation of the ossicular chain causes vibrations in the endolymph .K+ ions enter the hair cells under the influence of these vibrations and vibration signal is ultimately converted into a neural signal. The system is regenerated by the release of K+ from the hair cells into the supporting cells. The K+ ions are then passed from cell to cell via gap junctions and are eventually released into the endolymph. Except for sensorineural cells, the CX26 protein is present in gap junctions connecting all cell types in the cochlea, including the spiral limbus, the supporting cells, the spiral ligament and the basal and intermediate cells of the stria vascularis. It is therefore very likely that connexin 26 is involved in K+ recycling in the cochlea.[4]
Phenotypic results of mutations in connexin 26
Mutations in human Connexin 26 (hCx26) can lead to congenital hearing loss (1 child per 1000 frequency) that can be syndromic or non-syndromic. Non-syndromic hearing loss (NSHL) is characterized by sensorineural hearing loss in the absence of other symptoms, while syndromic hearing loss affects other organ systems, primarily the skin. mutations in GJB2 (the gene that encodes for Cx26) account for about half of all congenital and autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss in every population tested . Although the most frequently occurring (NSHL) mutations produce severely truncated proteins due to frameshift or missense, almost 80% of the known deafness mutations are actually single amino acid changes or deletions. These mutations have been found across the entire sequence of Cx26. The majority of NSHL mutations cause either generalized folding problems that result in the failure of Cx26 to traffic to the cell surface, or are permissive for the formation of gap junction plaques, but prevent intercellular channel function.[5]
Structure:
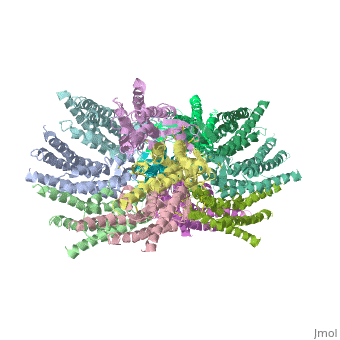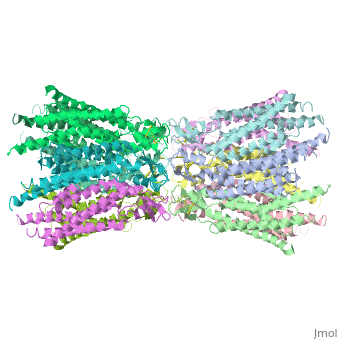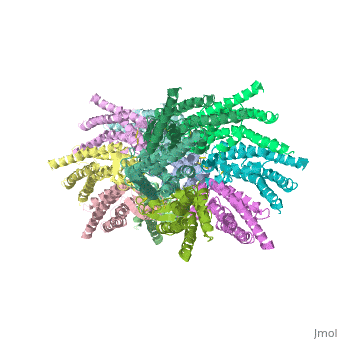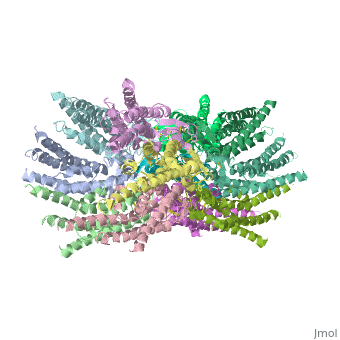
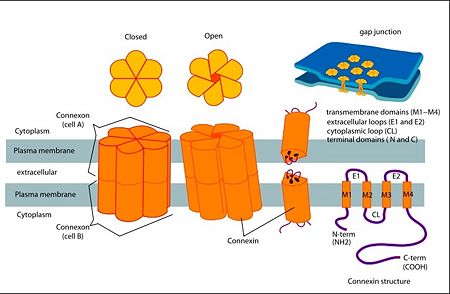
Connexin structure
are integral transmembranal proteins which consist of α-helical domains in the (TM1-TM4) , (E1 and E2), a cytoplasmic loop, an N-terminal helix (NTH), and a C-terminal segment. Each connexin consists of 227 amino acids, and form a hexamerical assembly , known as , or a , which delineates with a minimum diameter of ∼1.2 nm.
When two hemichannels from adjacent cells dock and join, leaving a gap of ∼2–3 nm, they may form a gap junction which spans the two plasma membranes and allows the exchange of cytoplasmic molecules with size up to ∼1 kDa.
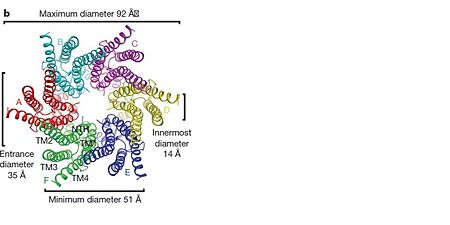
The transmembrane region of the channel is 38Å thick.TM2 extends about 19Å from the membrane surface into the cytoplasm. The extracellular region of the connexon extends 23Å from the membrane surface and interdigitates to the opposite connexon by 6Å, resulting in the intercellular ‘gap’ of 40Å. The extracellular lobes are not protruding so much, as indicated by the structural analyses of split gap junction channels with atomic force microscopy and electron microscopy. The relatively flat lobes could be attributed to the conformational change of the extracellular region induced by the docking of two connexons. The diameter of the connexon is biggest at the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, 92Å , and smallest at the extracellular side, 51Å .
Viewed from the top, the channel looks like a ‘hexagonal nut’ with a pore in the centre .The diameter of the pore is about 40Å at the cytoplasmic side of the channel, narrowing to 14Å near the extracellular membrane surface and then widening to 25Å in the extracellular space.[2]
Structure of the cx26 protomer:
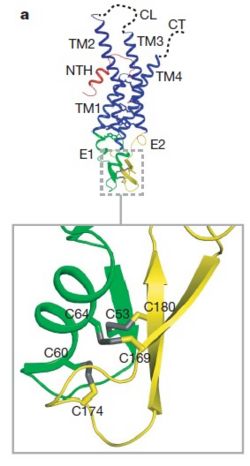
As mentioned before protomer has four transmembrane (TM1–4), two extracellular loops , a cytoplasmic loop, an N-terminal helix (NTH), and a C-terminal segment. Cx26 forms a typical four-helix bundle in which any pair of adjacent helices is antiparallel. The major pore-lining helix TM1 is inclined, so that the pore diameter narrows from the cytoplasmic to the extracellular side of the membrane, and ends in a short 310 helix.
The extracellular loop E1 contains a
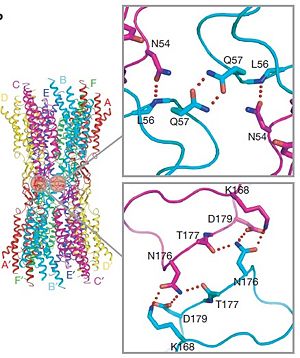
310 helix at the beginning and a short α-helix in its C-terminal. E2, together with E1, contains a short antiparallel β-sheet and stretches over E1, forming the outside of the connexon. Six conserved cysteine residues, three in each loop, form intramolecular disulphide bonds between E1 and E2 Most of the prominent intra-protomer interactions are in the extracellular part of the transmembrane region, The interactions between the two adjoining connexons of the gap junction channel, which involve both E1 and E2 .
The N-terminal half of E2 seems rather flexible and its amino-acid sequence varies greatly among connexins . The C-terminal half of E2 begins with a 310 turn is followed by a conserved Pro-Cys-Pro motif that reverses its direction back to TM4. Most of the prominent intra-protomer interactions are in the extracellular part of the transmembrane region . Arg 32 (TM1) interactswithGln 80 (TM2),Glu 147 (TM3), and Ser 199 (TM4). Two hydrophobic cores around Trp 44 (E1) and Trp 77 (TM2) stabilize the protomer structure. Ala 39 (TM1), Ala 40 (TM1), Val 43 (E1) and Ile 74 (TM2) contribute to the first hydrophobic core around Trp 44, and Phe 154 (TM3) and Met 195 (TM4) form the second core with Trp 77 . In the intracellular part of the transmembrane region, Arg 143 (TM3) forms hydrogen bonds with Asn 206 (TM3) and Ser 139 (TM3) .[2]
Differences between wild type and mutant connexin 26:
In general, single site mutations are spread fairly evenly across the whole protein with TM2 having the highest mutation density (number of amino acids with NHLS mutations divided by the total number of amino acids in the domain) at 67% to M1 and E1 having the lowest density of mutations with their respective domains at 33%. According to this criterion, TM4 has a mutation density of 40%. . Of the four transmembrane helices, M1, M2 and M3 have attracted the most attention, because of the controversies involved in models with different helix assignments, based on lower resolution cryo-electron crystallographic structures and scanning cysteine accessibility mutagenesis . Far less is known about TM4 and how side chains interact with the other helices and with the lipid bilayer. [5]
Electron crystallographic studies yielded a three-dimensional (3D) structure of a C-terminal truncated connexin43 gap junction channel, with each half containing 24 α-helices arranged with a 6-fold symmetry. The 3D structure of a mutant human connexin26 (Cx26M34A) channel shows an unexpected density within the vestibule of each hemichannel compared to the , which is called a "plug". Experiments with this mutant show significantly reduced dye coupling between HeLa cells transiently expressing Cx26M34A gap junctions. [6], two 3D structures of the Cx26M34A gap junctions are available, the first is the [6] and the second is the [6] in which
amino acids 2–7 were deleted.
References
- ↑ Zonta F, Buratto D, Cassini C, Bortolozzi M, Mammano F. Molecular dynamics simulations highlight structural and functional alterations in deafness-related M34T mutation of connexin 26. Front Physiol. 2014 Mar 4;5:85. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00085. eCollection 2014. PMID:24624091 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00085
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Suga M, Maeda S, Nakagawa S, Yamashita E, Tsukihara T. A description of the structural determination procedures of a gap junction channel at 3.5 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009 Aug;65(Pt 8):758-66. Epub 2009, Jul 10. PMID:19622859 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0907444909014711
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Connexin
- ↑ Kikuchi T, Adams JC, Miyabe Y, So E, Kobayashi T. Potassium ion recycling pathway via gap junction systems in the mammalian cochlea and its interruption in hereditary nonsyndromic deafness. Med Electron Microsc. 2000;33(2):51-6. PMID:11810458 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s007950000009
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Ambrosi C, Walker AE, Depriest AD, Cone AC, Lu C, Badger J, Skerrett IM, Sosinsky GE. Analysis of trafficking, stability and function of human connexin 26 gap junction channels with deafness-causing mutations in the fourth transmembrane helix. PLoS One. 2013 Aug 15;8(8):e70916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070916. eCollection, 2013. PMID:23967136 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070916
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Oshima A, Tani K, Toloue MM, Hiroaki Y, Smock A, Inukai S, Cone A, Nicholson BJ, Sosinsky GE, Fujiyoshi Y. Asymmetric Configurations and N-terminal Rearrangements in Connexin26 Gap Junction Channels. J Mol Biol. 2011 Jan 21;405(3):724-35. Epub 2010 Nov 20. PMID:21094651 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.10.032