Introduction
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS). It plays a key role in modulating neuronal activity by binding to specific transmembrane receptors (GABAA,GABAB and GABAC) in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal level.
The mammalian GABAB receptor is a class C G-protein coupled receptor[1]. Its structure is similar to the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR) ligand binding domain. The GABAB receptor is central to inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain and therefor considered as a good candidate for treatments against alcoholism, stress and some brain diseases[2].
The GABAB receptor can stimulate the opening of the K+ (Potassium) channels in the postsynaptic membrane, bringing the neuron closer to the equilibrium potential of K+, producing hyperpolarization. As a result, the Ca+2 (Calcium) channels in the presynaptic terminal close, and neurotransmitter release stops. In addition GABAB receptor function lead to the reduction adenylyl cyclase's activity and decrease the cell’s conductance to Ca+2 .[1].
Structure
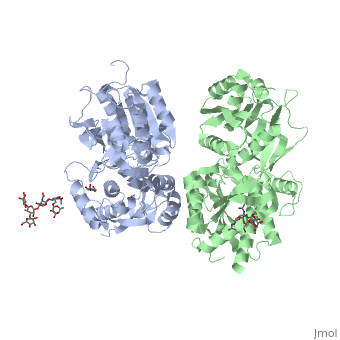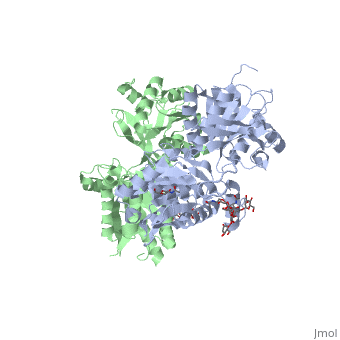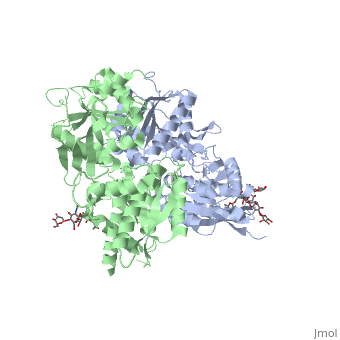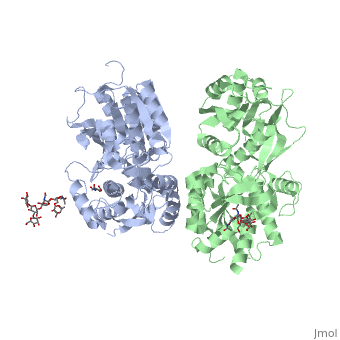
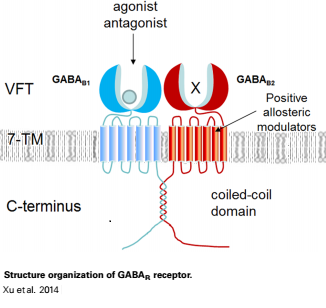
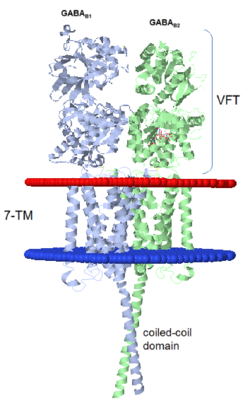
GABAB receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of GABAB1 (GBR1) and GABAB2 (GBR2). GBR1 (blue) is responsible for ligand-binding. GBR2 (green), on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunit. The GABAB receptor is one of the few obligate receptor heterodimer currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete receptor since it has extracellular and inter cellular regions.
Each subunit, GBR1 and GBR2, is a domain of seven-transmembrane helices, composed of a large extracellular domain called venus flytrap, and intercellular domain which important for the dimerzation.
The extracellular domain VFT
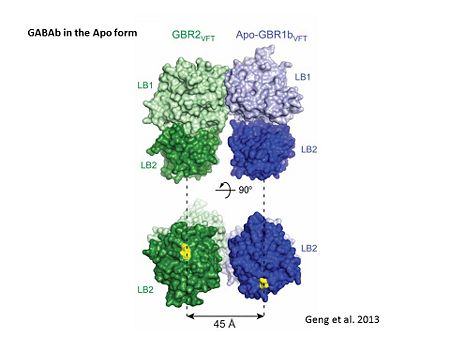
The VFT contains two lobe-shaped domains: LB1 and LB2, which are connected by three short loops.
LB1 and LB2 are [3].
Common subunit-subunit interactions
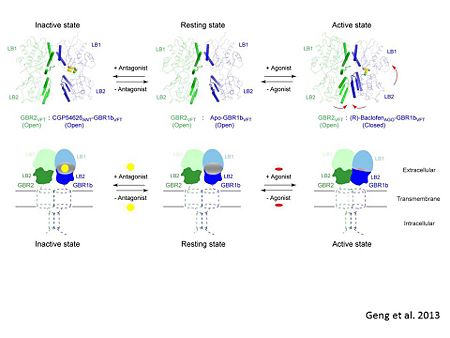
In both the resting (apo form, PDB 4mqe) and active states (the GABAB agonist-bound structures), GBR1bVFT and GBR2VFT interact through their LB1 domains. In the apo and antagonist-bound (inactive state) structures, the subunit association is exclusively facilitated by this LB1-LB1 contact. The heterodimer buries over 1,400 Å2 of solvent accessible surface area and exhibits exceptionally high interfacial shape correlation.
Agonist and antagonist binding
All of the agonists and antagonists bind the extracellular VFT module situated at the crevice between the LB1 and LB2 domains of the GBR1 subunit.
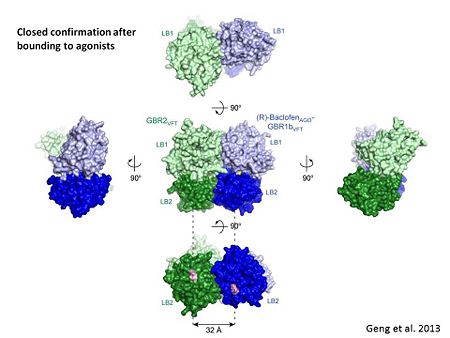
The agonist binding induces the formation of an additional heterodimer interface between the LB2 domains of GBR1bVFT and GBR2VFT subunits. The LB2-LB2 interface buries over 1,300 Å2 of solvent accessible surface area, has poor shape complementarity, and is dominated by polar interactions. The LB2-LB2 interaction is mediated by two strand-loop-helix motifs from each LB2 domain. . (GBR1:LB2 :- strand f-red, strand g-blue, helix F-orange, helix G-darkochid. GBR2:LB2 :- strand f-dimgray, strand g-yellow, helix F-hotpink, helix G-brown).
LB1 and LB2 resdues of GBR1 interact with the GABAB agonsits such as: GABA,baclofen. as a results of this interacting closed conformation will be stabilized when (PDB 4MS3) or (PDB 4MS4) and other agonists.
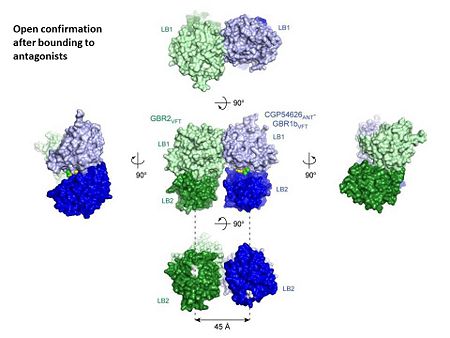
GABAB antgonists such as: saclofen, CGP46381, phaclofen, CGP35348 and CGP54626, mostly intercat with LB1 resduses of GBR1. both ends of the antagonist bind the LB1, which produce open confirmation of GBR1.
it is very easy to notice the open confirmation when :
(PDB 4MQF).
(PDB 4MS1).
(PDB 4MRM).
(PDB 4MR8).
(PDB 4MR7).
In short, the apo and antagonist-bound structures represent the resting state of the receptor; the agonist-bound complex corresponds to the
active state. Both subunits, GBR1 and GBR2 adopt an open conformation at rest, and only GBR1 closes upon agonist-induced receptor activation.
The intercellular dimerization motif
When the GBR1 subunit is expressed alone, it is trapped in vesicles within the cell, whereas the GBR2 alone is expressed on the cell surface, but cannot bind GABA or activate G proteins. When both receptor subunits are expressed in the same cell, the receptor interact through [4][5] (PDB 4PAS) in their carboxyl tails. Then they are expressed on the cell surface, bind GABA and activate G proteins.
This domain is shaped by and is stabilized by [6].
Mutagenesis studies of GBR1 and GBR2 in the extracellular domain VFT
Mutagenesis studies in GBR1 subunit [2]
, , : Abolishes signaling via G-proteins and antagonist binding.
: Slightly decreases signaling via G-proteins.
: Decreases signaling via G-proteins.
: Strongly reduces signaling via G-proteins and abolishes antagonist binding.
: Strongly reduces signaling via G-proteins, no effect on antagonist binding.
Mutagenesis studies in GBR2 subunit [3]
: Decreases signaling via G-proteins.
References
- ↑ Stevens RC, Cherezov V, Katritch V, Abagyan R, Kuhn P, Rosen H, Wuthrich K. The GPCR Network: a large-scale collaboration to determine human GPCR structure and function. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Jan;12(1):25-34. doi: 10.1038/nrd3859. Epub 2012 Dec, 14. PMID:23237917 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd3859
- ↑ Addolorato G, Leggio L, Cardone S, Ferrulli A, Gasbarrini G. Role of the GABA(B) receptor system in alcoholism and stress: focus on clinical studies and treatment perspectives. Alcohol. 2009 Nov;43(7):559-63. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.09.031. PMID:19913201 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.09.031
- ↑ Geng Y, Bush M, Mosyak L, Wang F, Fan QR. Structural mechanism of ligand activation in human GABA(B) receptor. Nature. 2013 Dec 12;504(7479):254-9. doi: 10.1038/nature12725. Epub 2013 Dec 4. PMID:24305054 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature12725
- ↑ Burmakina S, Geng Y, Chen Y, Fan QR. Heterodimeric coiled-coil interactions of human GABAB receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Apr 28. PMID:24778228 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1400081111
- ↑ Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;3(9):639-50. PMID:12209124 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm908
- ↑ Burmakina S, Geng Y, Chen Y, Fan QR. Heterodimeric coiled-coil interactions of human GABAB receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Apr 28. PMID:24778228 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1400081111