We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Rana Saad/The human GABAb receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
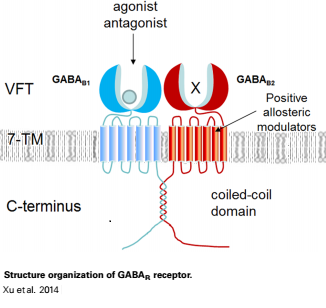
The mammalian '''GABA<sub>B</sub>''' receptor is a class C [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/G_protein-coupled_receptor#3D_Structures_of_G_protein-coupled_receptors G-protein coupled receptor]<ref>PMID:23237917</ref>. Its structure is similar to the [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor|metabotropic glutamate receptors]] (mGluR) ligand binding domain. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is central to inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain and therefor considered as a good candidate for treatments against alcoholism, stress and some brain diseases<ref>PMID:19913201</ref>. | The mammalian '''GABA<sub>B</sub>''' receptor is a class C [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/G_protein-coupled_receptor#3D_Structures_of_G_protein-coupled_receptors G-protein coupled receptor]<ref>PMID:23237917</ref>. Its structure is similar to the [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor|metabotropic glutamate receptors]] (mGluR) ligand binding domain. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is central to inhibitory neurotransmission in the brain and therefor considered as a good candidate for treatments against alcoholism, stress and some brain diseases<ref>PMID:19913201</ref>. | ||
The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor can stimulate the opening of the K<sup>+</sup> (Potassium) channels in the postsynaptic membrane, bringing the neuron closer to the [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4kx9_0YwShE equilibrium potential] of K<sup>+</sup>, producing [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperpolarization_(biology) hyperpolarization]. As a result, the Ca<sup>+2</sup> (Calcium) channels in the presynaptic terminal close, and neurotransmitter release stops. In addition GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor function lead to the reduction adenylyl cyclase's activity and decrease the cell’s conductance to Ca<sup>+2</sup> .[http://physrev.physiology.org/content/84/3/835.short]. | The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor can stimulate the opening of the K<sup>+</sup> (Potassium) channels in the postsynaptic membrane, bringing the neuron closer to the [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4kx9_0YwShE equilibrium potential] of K<sup>+</sup>, producing [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperpolarization_(biology) hyperpolarization]. As a result, the Ca<sup>+2</sup> (Calcium) channels in the presynaptic terminal close, and neurotransmitter release stops. In addition GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor function lead to the reduction adenylyl cyclase's activity and decrease the cell’s conductance to Ca<sup>+2</sup> .[http://physrev.physiology.org/content/84/3/835.short]. | ||
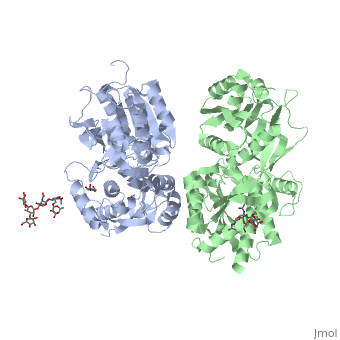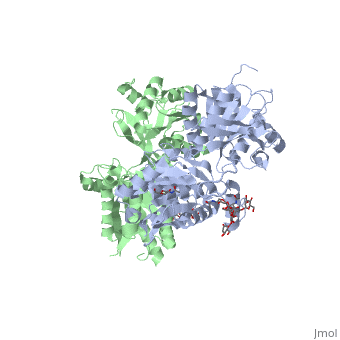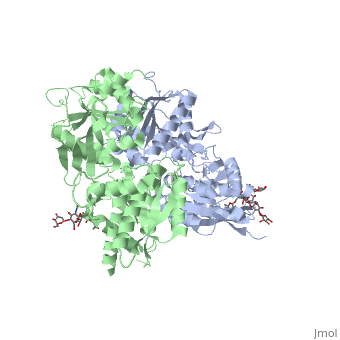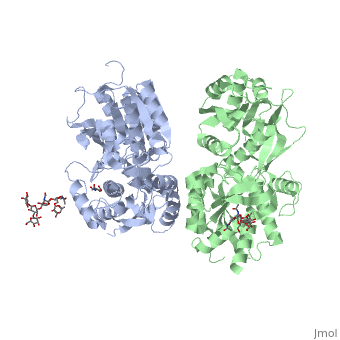
| - | [[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:GABAb.receptor.cartoon2.png|250px|thumb|GABAb receptors are formed from the heterodimerization of two similar 7TM subunits termed GABAB1 and GABAB2 ]] |
=='''''Structure'''''== | =='''''Structure'''''== | ||
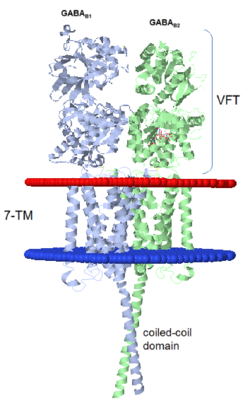
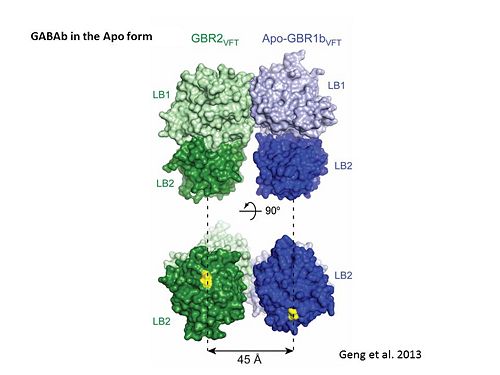
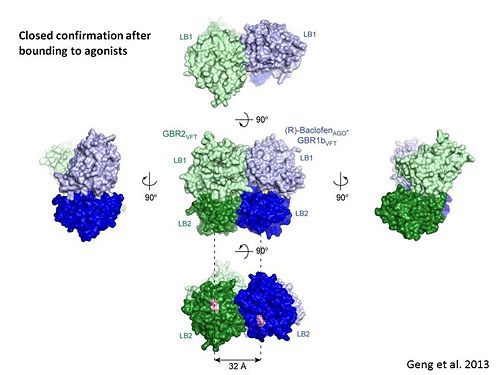
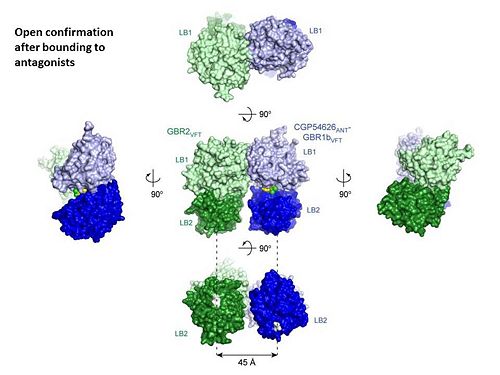
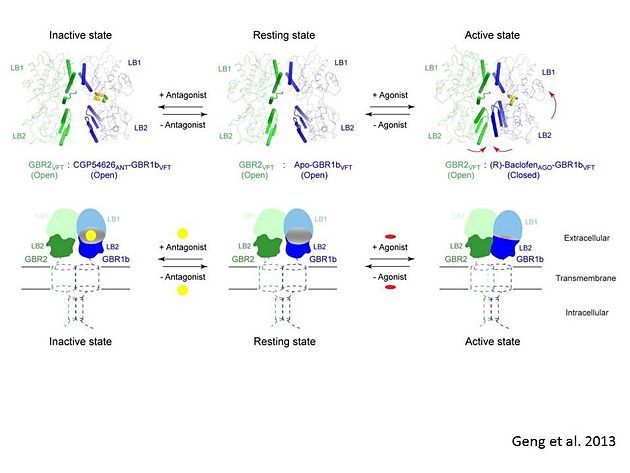
GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of '''GABA<sub>B1</sub>''' (GBR1) and '''GABA<sub>B2</sub>''' (GBR2). '''GBR1''' (blue) is responsible for ligand-binding. '''GBR2''' (green), on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunit. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of the few obligate receptor heterodimer currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete receptor since it has extracellular and inter cellular regions. | GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor functions as an obligatory heterodimer subunit of '''GABA<sub>B1</sub>''' (GBR1) and '''GABA<sub>B2</sub>''' (GBR2). '''GBR1''' (blue) is responsible for ligand-binding. '''GBR2''' (green), on the other hand, is responsible for G protein coupling subunit. The GABA<sub>B</sub> receptor is one of the few obligate receptor heterodimer currently known. There is no crystal or NMR structure of the complete receptor since it has extracellular and inter cellular regions. | ||
Revision as of 13:22, 9 August 2015
| |||||||||||