Quinone reductase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
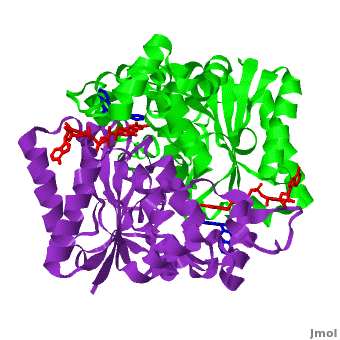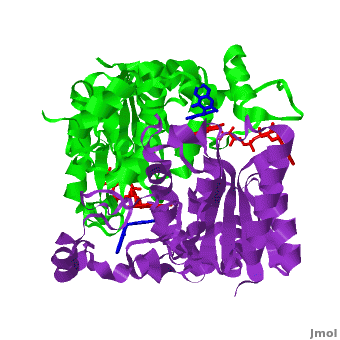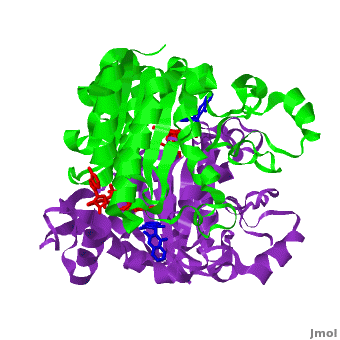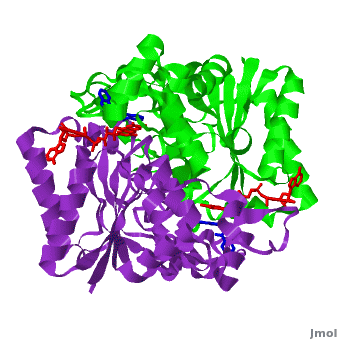
| - | The crystal structure of human NQO1 in complex with dicoumarol was determined at 2.75 Å resolution ([[2f1o]]). NQO1 is a <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/6'>physiological homodimer</scene> composed of two interlocked monomers. <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/7'>Two catalytic sites</scene> are formed and are present at the dimer interface (<font color='red'><b>FAD is colored red</b></font> and <font color='blue'><b>dicoumarol is colored blue</b></font>). Therefore, each from these two <scene name='2f1o/Active_site/3'>dicoumarol-hNQO1 binding sites</scene> is formed by both monomers. <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">Dicoumarol is colored cyan</span>, <span style="color:orange;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">FAD in orange</span>, nitrogens and oxygens are shown in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPK_coloring CPK colors]. NQO1 <font color='blueviolet'><b>chain A is colored blueviolet</b></font> and < | + | The crystal structure of human NQO1 in complex with dicoumarol was determined at 2.75 Å resolution ([[2f1o]]). NQO1 is a <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/6'>physiological homodimer</scene> composed of two interlocked monomers. <scene name='2f1o/Com_view/7'>Two catalytic sites</scene> are formed and are present at the dimer interface (<font color='red'><b>FAD is colored red</b></font> and <font color='blue'><b>dicoumarol is colored blue</b></font>). Therefore, each from these two <scene name='2f1o/Active_site/3'>dicoumarol-hNQO1 binding sites</scene> is formed by both monomers. <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">Dicoumarol is colored cyan</span>, <span style="color:orange;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">FAD in orange</span>, nitrogens and oxygens are shown in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPK_coloring CPK colors]. NQO1 <font color='blueviolet'><b>chain A is colored blueviolet</b></font> and <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">chain C in green</span>. NQO1 residues, participating in ligand interactions, are shown as stick representation and are labeled (A and C refer to the NQO1 chains). H-bonds are shown by dashed lines with their distances. |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
Revision as of 10:35, 9 September 2015
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Quinone reductase
Updated on 09-September-2015
References
- Faig M, Bianchet MA, Talalay P, Chen S, Winski S, Ross D, Amzel LM. Structures of recombinant human and mouse NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductases: species comparison and structural changes with substrate binding and release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 28;97(7):3177-82. PMID:10706635 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.050585797
- Asher G, Dym O, Tsvetkov P, Adler J, Shaul Y. The crystal structure of NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 in complex with its potent inhibitor dicoumarol. Biochemistry. 2006 May 23;45(20):6372-8. PMID:16700548 doi:10.1021/bi0600087