Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
This is a default text for your page '''Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | This is a default text for your page '''Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are two flavors of estrogen receptors. ER - Intracellular receptor and GPER – G protein coupled receptors. ERs are transcription factors while GPER are not transcription factors. ERs are the focus of this page. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Like other steroid hormones estrogen effects the transcription of a large number of genes via its interactions with its intracellular receptors, estrogen receptors. Estrogen receptors are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen (Example of an estrogen; 17β-estradiol). | ||
| + | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 17: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
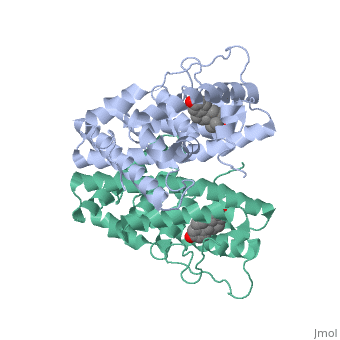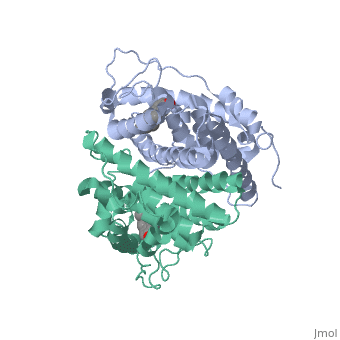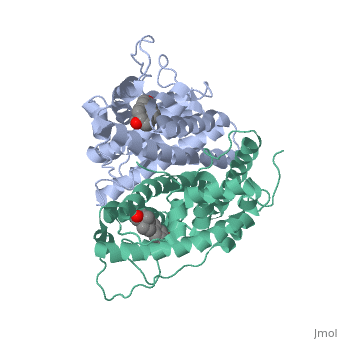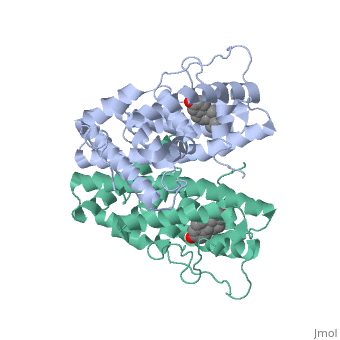
| + | ER is a modular protein composed of a ligand binding domain, a DNA binding domain and a transactivation domain. ER is a DNA-binding transcription factor. Unbound ER normally exists loosly around the nucleus; this is subject to change depending on a multitude of factors including cell type, progress through cell cycle and reception of cellular signals. When estrogen enters the cell and binds ER, ER will trans-locates and undergoes a conformational shift.(1) Ligand bound estrogen receptor associates more tightly with the nucleus. | ||
<scene name='71/714947/Agonist_estradiol_bound_er/1'>Agonist_estradiol_bound_er</scene> | <scene name='71/714947/Agonist_estradiol_bound_er/1'>Agonist_estradiol_bound_er</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='71/714947/Agonist_ferutinine_bound_er/1'>Agonist_ferutinine_bound_er</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='71/714947/Partial_agonist_genistein_er/1'>Partial_Agonist_Genistein_bound_Er</scene> | ||
The specific conformation of this tight loop creates part of the activation signal that will stimulate normal growth, as estradiol is a normal ligand for ER. | The specific conformation of this tight loop creates part of the activation signal that will stimulate normal growth, as estradiol is a normal ligand for ER. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 32: | ||
<scene name='71/714947/Er_bound_to_dna/1'>ER_bound_to_dna</scene> | <scene name='71/714947/Er_bound_to_dna/1'>ER_bound_to_dna</scene> | ||
| - | + | ERα-regulated gene expression involves interactions with cointegrators (ex. p300/CBP, P/CAF) that have the capacity to modify core histone acetyl groups. 2 ER’s DNA binding domain is ordered around two zinc ions that allow the receptors to bind as homodimers to palindromic DNA sequences in such a way that each homodimer links to one half of the palindrome. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
Revision as of 22:05, 9 October 2015
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644