Tyrone Evans Hox Proteins sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(Undo revision 2493298 by Ann Taylor (Talk)) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Interaction with DNA == | == Interaction with DNA == | ||
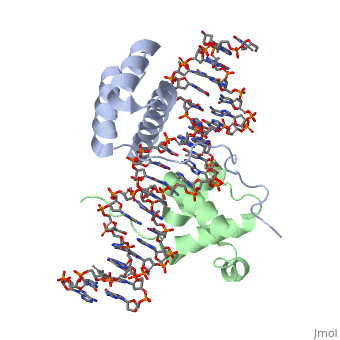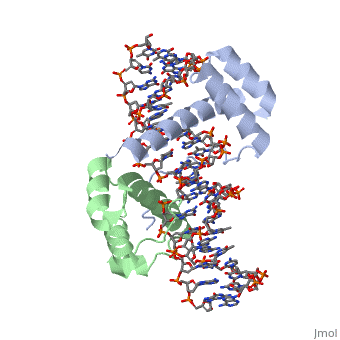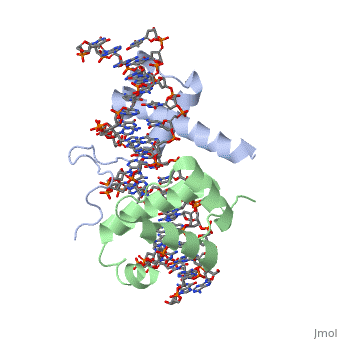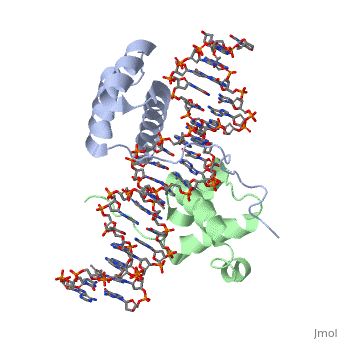
| - | A homeodomain is an essential part that all Hox proteins possess. The homeodomain can be found within the homeobox, a DNA sequence found within genes that are responsible of morphogenesis of living organisms. This sequence codes for homeodomain protein products, 60 amino-acid segments, which have specific folding patterns (helix-turn-helix) that allows them to bind with DNA through a 5’-TAAT-3’ core motif. This domain consist of three helical regions folded into a tight spherical structure (need picture of structure). There are two antiparallel N-terminal helices and one C-terminal helix within this domain. The C-terminal helix binds directly with DNA through the use of hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions between side chains and the outer bases and thymine methyl groups within the major groove of a DNA helix. The <scene name='71/714951/Recognition_helix/1'>Recognition helix</scene> within homeodomain binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_major_groove/1'>major groove</scene> of a DNA helix, while the <scene name='71/714951/Amino-terminal_tail/1'>Amino-Terminal tail</scene> binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_minor_groove/1'>minor groove</scene> of a DNA helix. | + | A homeodomain is an essential part that all Hox proteins possess. The homeodomain can be found within the homeobox, a DNA sequence found within genes that are responsible of morphogenesis of living organisms. This sequence codes for homeodomain protein products, 60 amino-acid segments, which have specific folding patterns (helix-turn-helix) that allows them to bind with DNA through a <scene name='71/714951/Taaat_sequence/1'>5’-TAAT-3’</scene> core motif. This domain consist of three helical regions folded into a tight spherical structure (need picture of structure). There are two antiparallel N-terminal helices and one C-terminal helix within this domain. The C-terminal helix binds directly with DNA through the use of hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions between side chains and the outer bases and thymine methyl groups within the major groove of a DNA helix. The <scene name='71/714951/Recognition_helix/1'>Recognition helix</scene> within homeodomain binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_major_groove/1'>major groove</scene> of a DNA helix, while the <scene name='71/714951/Amino-terminal_tail/1'>Amino-Terminal tail</scene> binds within the <scene name='71/714951/Dna_minor_groove/1'>minor groove</scene> of a DNA helix. |
== Human Hox Genes == | == Human Hox Genes == | ||
Revision as of 13:43, 13 October 2015
Hox Proteins
| |||||||||||