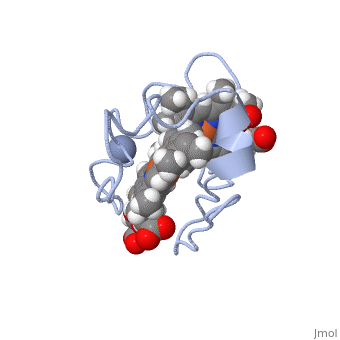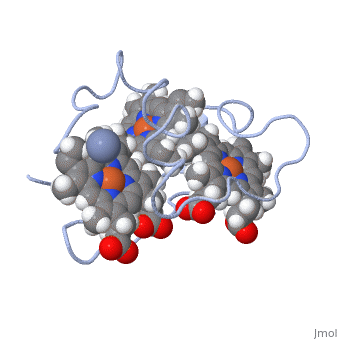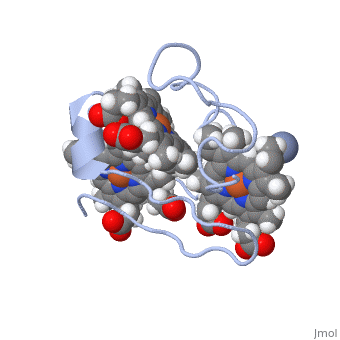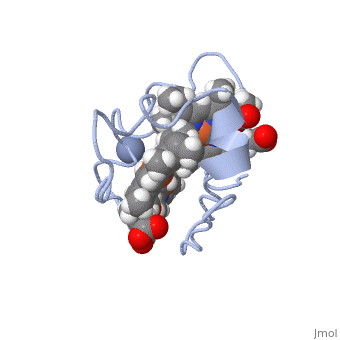We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Cytochrome c 7
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | Cc7 | + | The function of Cc7 was determined by using NMR spectroscopy as a mointoring technique to determine the oxidation levels of the protein as more chromate (-2) |
| + | - <ref></ref>. | ||
| + | - | ||
| + | Chromate (-2) nor chromium are part of Cc7's structure; they are the reactant and the product of the reductase activity of Cc7, respectively. The following steps will elaborate how Cc7 carries out its oxidation. | ||
| - | + | As mentioned previously, Cc7 is a sulfur/metal terminal reductase, an enzyme that reduces a sulfur-containing compounds into a sulfide or reduces heavy metals to generate electrons to be used in electron transport chain | |
| + | - <ref></ref>. | ||
| + | - | ||
| + | To begin thus reaction, Cc7 must be in its resting state (i.e. fully reduced). Chromate(-2) (an oxidized heavy metal) . | ||
The products of the reaction are chromium(III) and the oxidized protein with three iron(III) hemes. | The products of the reaction are chromium(III) and the oxidized protein with three iron(III) hemes. | ||
Revision as of 07:04, 30 November 2015
General
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0065-2164(09)01202-7
- ↑ Pfennig N, Biebl H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. 1976; 110(1): 3-12 DOI: 10.1007/BF00416962
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999
- ↑ Pfennig N, Biebl H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. 1976; 110(1): 3-12 DOI: 10.1007/BF00416962
- ↑ National Service Center for Environmental Publications. [1]