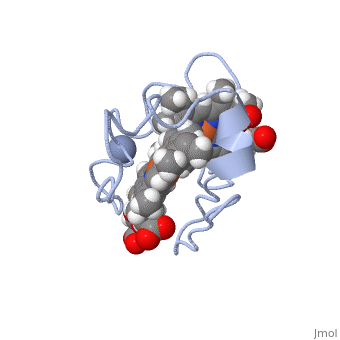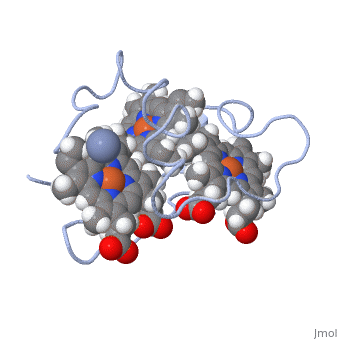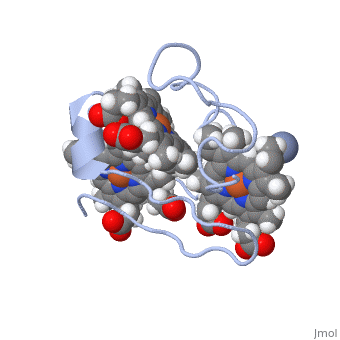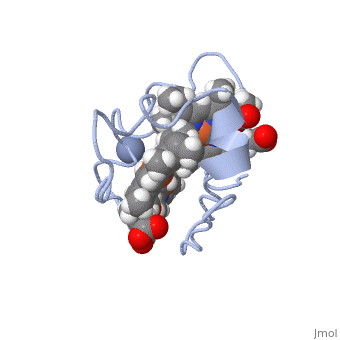We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Cytochrome c 7
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Structural Components== | ==Structural Components== | ||
| - | Cc7 is a single polypeptide chain 68 residues total containing three heme groups. The polypeptide strand has one alpha helix 4 residues in length and two beta strands 2 residues in length. The heme groups are labelled as I, III, and IV. The binding site is located on the distal side of heme group IV where <scene name='71/716635/ | + | Cc7 is a single polypeptide chain 68 residues total containing three heme groups. The polypeptide strand has one alpha helix 4 residues in length and two beta strands 2 residues in length. The heme groups are labelled as I, III, and IV. The binding site is located on the distal side of heme group IV where <scene name='71/716635/Active_site_1/1'>lysine residues 41, 42, 46 and 50</scene> are an interactive component of the active site. The net charge of these residues is positive, thus binding to negatively charge compounds or cations.<ref>Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 '''[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC125002/''' DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999''']'''</ref>. |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 11:07, 30 November 2015
General
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999
- ↑ Barton L, Fauque G. Biochemistry, Physiology and Biotechnology of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Advances in Applied Microbiology. 2009; 68: 41–98. DOI: 10.1016/s0065-2164(09)01202-7
- ↑ Pfennig N, Biebl H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. 1976; 110(1): 3-12 DOI: 10.1007/BF00416962
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999
- ↑ Pfennig N, Biebl H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. 1976; 110(1): 3-12 DOI: 10.1007/BF00416962
- ↑ National Service Center for Environmental Publications. [1]
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999
- ↑ Assfalg M, Bertini I, Bruschi M, Michel C, Turano P. The metal reductase activity of some multiheme cytochromes c: NMR structural characterization of the reduction of chromium(VI) to chromium(III) by cytochrome c(7). 2002; 99(15):9750-4 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.152290999