Acetyl-CoA synthetase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
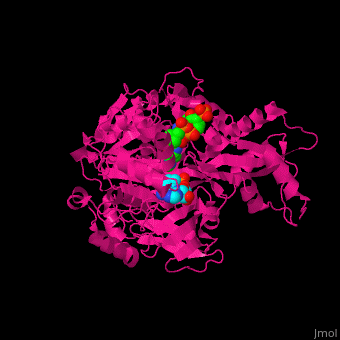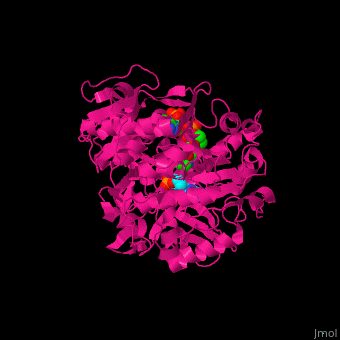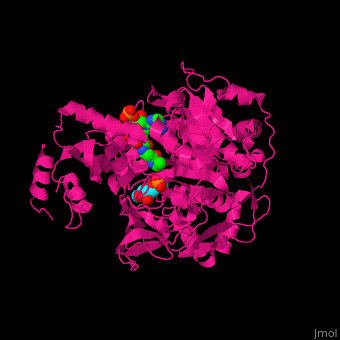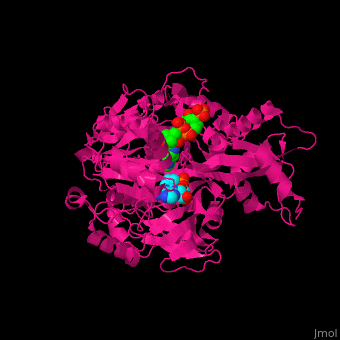
| - | <StructureSection load='2p2j' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='2p2j' size='450' side='right' scene='49/492048/Cv/1' caption='2 monomers of acetyl-CoA synthetase complex with CoA and AMP (PDB code [[2p2j]])'> |
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Acetyl-CoA is used in aerobic respiration to produce energy and electron carriers and for lipid biosynthesis, in histone acetylation which is critical for DNA condensation to chromatin. | Acetyl-CoA is used in aerobic respiration to produce energy and electron carriers and for lipid biosynthesis, in histone acetylation which is critical for DNA condensation to chromatin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural Highlights == | ||
| + | *<scene name='49/492048/Cv/3'>CoA binding site</scene>. | ||
| + | * | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of acetyl-CoA synthetase== | ==3D structures of acetyl-CoA synthetase== | ||
Revision as of 12:56, 1 December 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of acetyl-CoA synthetase
Updated on 01-December-2015
1pg3, 1pg4 – SeACS (mutant) + CoA + AMP – Salmonella enterica
2p20, 2p2m, 2p2q - StACS (mutant) + AMP – Salmonella typhimurium
2p2b, 2p2j - StACS (mutant) + CoA + AMP
2p2f - StACS + CoA + AMP
1ry2 – ACS + AMP - yeast
4u5y – ACS GNAT domain + SeACS C terminal (mutant) – Streptomyces lividans