Acetyl-CoA synthetase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Acetyl-CoA synthetase''' (ACS) catalyzes the ligation of acetate and CoA to form acetyl-CoA with the conversion of ATP to AMP and pyrophosphate. ACS is an ATP-dependent AMP-binding enzyme. Mg+2 is ACS cofactor. ACS participates in the pathway which fixes CO2 under anaerobic conditions. ACS acetylates the response regulator for flagellar movement and for chemotaxis - CheY. | + | '''Acetyl-CoA synthetase''' (ACS) catalyzes the ligation of acetate and CoA to form acetyl-CoA with the conversion of ATP to AMP and pyrophosphate. ACS is an ATP-dependent AMP-binding enzyme. Mg+2 is ACS cofactor. ACS participates in the pathway which fixes CO2 under anaerobic conditions. ACS acetylates the response regulator for flagellar movement and for chemotaxis - CheY. <ref>PMID:14769018</ref> |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Revision as of 13:11, 1 December 2015
| |||||||||||
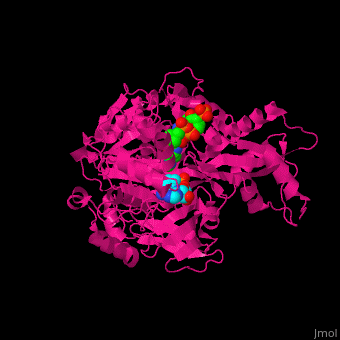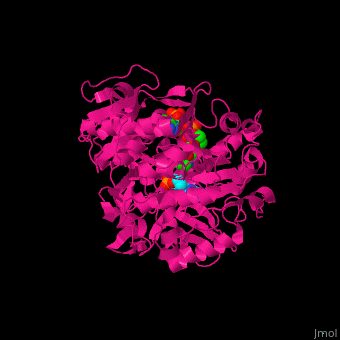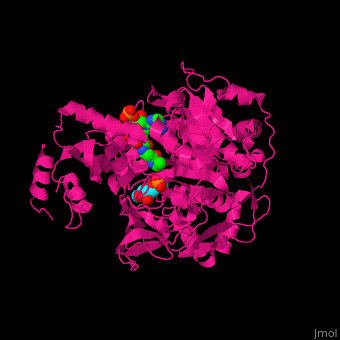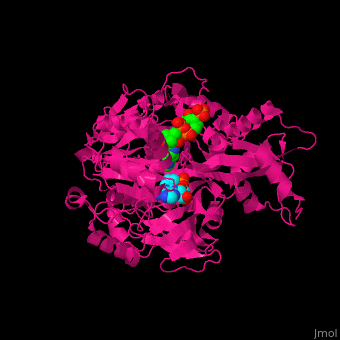
3D structures of acetyl-CoA synthetase
Updated on 01-December-2015
1pg3, 1pg4 – SeACS (mutant) + CoA + AMP – Salmonella enterica
2p20, 2p2m, 2p2q - StACS (mutant) + AMP – Salmonella typhimurium
2p2b, 2p2j - StACS (mutant) + CoA + AMP
2p2f - StACS + CoA + AMP
1ry2 – ACS + AMP - yeast
4u5y – ACS GNAT domain + SeACS C terminal (mutant) – Streptomyces lividans
References
- ↑ Jogl G, Tong L. Crystal structure of yeast acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase in complex with AMP. Biochemistry. 2004 Feb 17;43(6):1425-31. PMID:14769018 doi:10.1021/bi035911a
- ↑ Reger AS, Carney JM, Gulick AM. Biochemical and crystallographic analysis of substrate binding and conformational changes in acetyl-CoA synthetase. Biochemistry. 2007 Jun 5;46(22):6536-46. Epub 2007 May 12. PMID:17497934 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi6026506