We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1122
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
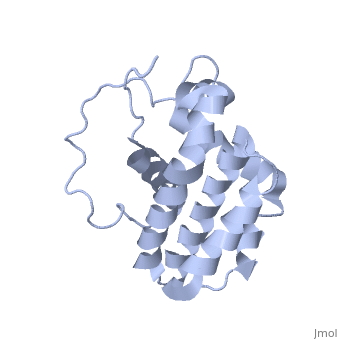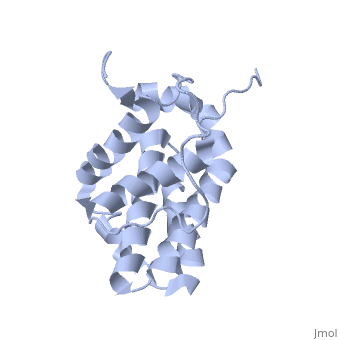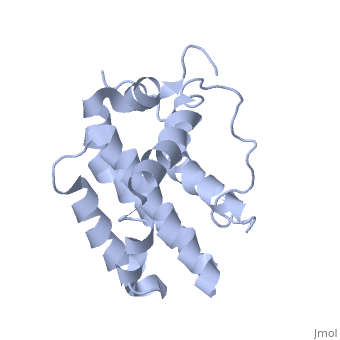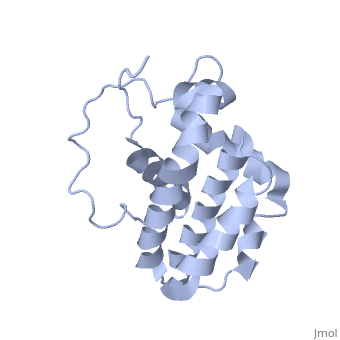
transmembrane domain (218-239) (due to its poor behavior in solution, it has been replaced by a segment of Bcl-xl in the presented 3D structure). It organizes as eight alpha-helices: from 11 to 25 (1) , from 93 to 107 (2), from 109 to 118 (3), from 126 to 137 (4), from 144-163 (5), from 169 to 184 (6), from 186 to 191 (7) and from 194 to 202(8). Helices 5 and 6 are mostly hydrophobic and they are surrounded by four other helices characterized by their amphipathic properties. There are also 3 turns (32-34, 123-125, 138-140). The <scene name='71/719863/Bcl2helix/1'>3rd alpha-helix</scene> is a 3(10) helix, whereas BCL-XL 3rd helix is a normal alpha-helix. | transmembrane domain (218-239) (due to its poor behavior in solution, it has been replaced by a segment of Bcl-xl in the presented 3D structure). It organizes as eight alpha-helices: from 11 to 25 (1) , from 93 to 107 (2), from 109 to 118 (3), from 126 to 137 (4), from 144-163 (5), from 169 to 184 (6), from 186 to 191 (7) and from 194 to 202(8). Helices 5 and 6 are mostly hydrophobic and they are surrounded by four other helices characterized by their amphipathic properties. There are also 3 turns (32-34, 123-125, 138-140). The <scene name='71/719863/Bcl2helix/1'>3rd alpha-helix</scene> is a 3(10) helix, whereas BCL-XL 3rd helix is a normal alpha-helix. | ||
| + | The transmembrane domain of Bcl-2 is made of 21 aminoacids and is located at the carboxy-terminal tail of the protein. It allows the docking of Bcl-2 in the mitochondrial outer membrane where the protein interacts with other effectors. | ||
Bcl-2 contains a hydrophobic groove on its surface that allows dimerization with other members of the Bcl-2 family. This region needs to be highly conserved to keep the ability of interacting with proapoptotic protein of the family, in fact, it has been shown that a mutation in this structure leads to the silencing of the dimerization thus may inhibit the activity of Bcl-2. | Bcl-2 contains a hydrophobic groove on its surface that allows dimerization with other members of the Bcl-2 family. This region needs to be highly conserved to keep the ability of interacting with proapoptotic protein of the family, in fact, it has been shown that a mutation in this structure leads to the silencing of the dimerization thus may inhibit the activity of Bcl-2. | ||
The isoform 1 and 2 differs from two amino acid in the hydrophobic groove but this difference doesn’t induce any change in the conformation of this protein. | The isoform 1 and 2 differs from two amino acid in the hydrophobic groove but this difference doesn’t induce any change in the conformation of this protein. | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 28 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
HUMAN BCL-2, ISOFORM1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Solution structure of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2
- ↑ Alpha-Helical Destabilization of the Bcl-2-BH4-Domain Peptide Abolishes Its Ability to Inhibit the IP3 Receptor
- ↑ BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax
- ↑ Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family
- ↑ Differential Targeting of Prosurvival Bcl-2 Proteins by Their BH3-Only Ligands Allows Complementary Apoptotic Function
- ↑ Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics
- ↑ The Release of Cytochrome c from Mitochondria: A Primary Site for Bcl-2 Regulation of Apoptosis
- ↑ Prevention of Apoptosis by Bcl-2: Release of Cytochrome c from Mitochondria Blocked
- ↑ Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL Regulate Proinflammatory Caspase-1 Activation by Interaction with NALP1