We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1136
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS_2015}} | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS_2015}} | ||
==Structure and Functional aspects of Sucrose Synthase from ''Arabidopsis thaliana''== | ==Structure and Functional aspects of Sucrose Synthase from ''Arabidopsis thaliana''== | ||
| - | Sucrose Synthase 1 (EC:2.4.1.13), also known as the Sucrose-UDP glucolsyltransferase 1 or simply Susy, is a reversible enzyme allowing the synthesis or the degradation of Sucrose in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. It belongs to the Glycosyltransferase | + | Sucrose Synthase 1 (EC:2.4.1.13), also known as the Sucrose-UDP glucolsyltransferase 1 or simply Susy, is a reversible enzyme allowing the synthesis or the degradation of Sucrose in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. It belongs to the Glycosyltransferase subfamily 4 (GT4). |
| - | <StructureSection scene=' | + | <StructureSection scene='' size='340' side='right' caption='X-ray crystal structures of AtSus1, as a complex with UDP-glucose at 2.8-Å resolution and as a complex with UDP and fructose at 2.85-Å resolution'> |
| + | |||
| + | 71/719877/Susy/3 | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
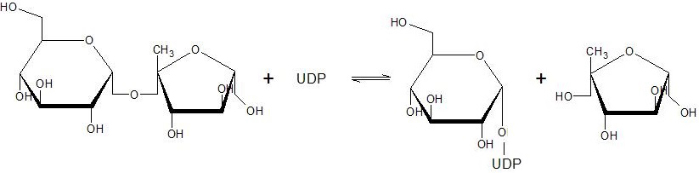
The Sucrose Synthase is able to catalyse the following reaction in both directions: | The Sucrose Synthase is able to catalyse the following reaction in both directions: | ||
| - | '''sucrose = glucose + fructose''' | ||
[[Image:Susy_reaction.jpg]] | [[Image:Susy_reaction.jpg]] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
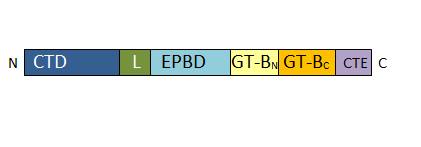
• 1-127: N-Terminal regulatory domain involved in targeting <ref>Determination of structural requirements and probable regulatory effectors for membrane association of maize sucrose synthase 1. Hardin SC, Duncan KA, Huber SC. Plant Physiol. 2006</ref>. On this sequence, two serines can be phosphorylated, which enable a control of enzyme location <ref>Phosphorylation of sucrose synthase at serine 170: occurrence and possible role as a signal for proteolysis. Hardin SC, Tang GQ, Scholz A, Holtgraewe D, Winter H, Huber SC. Plant J. 2003</ref>. | • 1-127: N-Terminal regulatory domain involved in targeting <ref>Determination of structural requirements and probable regulatory effectors for membrane association of maize sucrose synthase 1. Hardin SC, Duncan KA, Huber SC. Plant Physiol. 2006</ref>. On this sequence, two serines can be phosphorylated, which enable a control of enzyme location <ref>Phosphorylation of sucrose synthase at serine 170: occurrence and possible role as a signal for proteolysis. Hardin SC, Tang GQ, Scholz A, Holtgraewe D, Winter H, Huber SC. Plant J. 2003</ref>. | ||
| - | • | + | • 1-127: CTD: Cellular targeting domain |
| - | • | + | • 157-276: EPBD: ENOD40 peptide-binding domain. This domain has a role in the regulation of the enzyme. |
| - | • 776-808 : C-terminal | + | • 277-776 : GT-B glycosyltransferase domain. It contains the catlytic site. |
| + | |||
| + | • 776-808 : C-terminal extension. The length of this domain is variable depending of the SUS isoform. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Monomer_structure.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 11:53, 30 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Structure and Functional aspects of Sucrose Synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana
Sucrose Synthase 1 (EC:2.4.1.13), also known as the Sucrose-UDP glucolsyltransferase 1 or simply Susy, is a reversible enzyme allowing the synthesis or the degradation of Sucrose in Arabidopsis thaliana. It belongs to the Glycosyltransferase subfamily 4 (GT4).
| |||||||||||
References
• UniProt entry: P49040
• Brenda entry : 2.4.1.13
- ↑ Salerno GL, Curatti L Origin of sucrose metabolism in higher plants: when, how and why? Trends Plant Sci. 2003 Feb
- ↑ Baroja-Fernández, E., Muñoz, F.J., Saikusa, T., Rodríguez-López, M., Akazawa, T. and Pozueta-Romero, J. Sucrose synthase catalyzes the de novo production of ADPglucose linked to starch biosynthesis in heterotrophic tissues of plants. Plant Cell Physiol.
- ↑ Salerno GL, Curatti L. Origin of sucrose metabolism in higher plants: when, how and why? Trends Plant Sci. 2003 Feb
- ↑ Determination of structural requirements and probable regulatory effectors for membrane association of maize sucrose synthase 1. Hardin SC, Duncan KA, Huber SC. Plant Physiol. 2006
- ↑ Phosphorylation of sucrose synthase at serine 170: occurrence and possible role as a signal for proteolysis. Hardin SC, Tang GQ, Scholz A, Holtgraewe D, Winter H, Huber SC. Plant J. 2003