We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1126
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
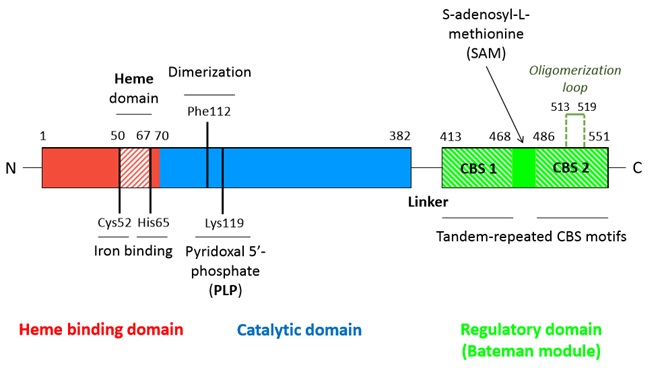
A CBS monomer is natively a 63 kDa protein made of 551 amino-acids and each of them binds two cofactors (the iron heme and the pyridoxal phosphate), as well as two substrates (homocysteine and serine). Hence, a CBS monomer contains (from N-terminal to C-terminal): <br/> | A CBS monomer is natively a 63 kDa protein made of 551 amino-acids and each of them binds two cofactors (the iron heme and the pyridoxal phosphate), as well as two substrates (homocysteine and serine). Hence, a CBS monomer contains (from N-terminal to C-terminal): <br/> | ||
| - | - a <scene name='71/719867/Scene_4/2'>heme iron</scene> binding site located in a hydrophobic pocket (residues 50-67) <br/> | + | - a <scene name='71/719867/Scene_4/2'>heme iron</scene> binding site located in a hydrophobic pocket (residues 50-67), <br/> |
| - | - a pyridoxal phosphate = <scene name='71/719867/Scene_4/1'>PLP</scene> (covalently linked to Lysine 119 amino group) situated in a <scene name='71/719867/Scene_1/1'>highly conserved catalytic domain</scene> (residues 70-382)<br/> | + | - a pyridoxal phosphate = <scene name='71/719867/Scene_4/1'>PLP</scene> (covalently linked to Lysine 119 amino group) situated in a <scene name='71/719867/Scene_1/1'>highly conserved catalytic domain</scene> (residues 70-382), <br/> |
| - | - a <scene name='71/719867/Scene_2/1'>C-terminal regulatory domain</scene> called Bateman module composed of two CBS domains (CBS1 and CBS2) | + | - a <scene name='71/719867/Scene_2/1'>C-terminal regulatory domain</scene> called Bateman module composed of two CBS domains (CBS1 and CBS2). |
[[Image:Linear_structure_CBS_monomer.jpg]] | [[Image:Linear_structure_CBS_monomer.jpg]] | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
The Bateman modules natively prevent the access of the substrates to the catalytic site (PLP cavity) through: <br/> | The Bateman modules natively prevent the access of the substrates to the catalytic site (PLP cavity) through: <br/> | ||
| - | - hydrophobic interactions between residues I537, L540, A544 of the CBS1 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues I166, V189, V206, L210, I214 of the catalytic core of the other monomer <br/> | + | - hydrophobic interactions between residues I537, L540, A544 of the CBS1 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues I166, V189, V206, L210, I214 of the catalytic core of the other monomer, <br/> |
| - | - hydrogen bounds between residues T460, N463, S466, Y484 of the CBS2 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues E201, N194, R196, D198 of the loop 191-202 of the catalytic core of the other monomer <br/><br/> | + | - hydrogen bounds between residues T460, N463, S466, Y484 of the CBS2 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues E201, N194, R196, D198 of the loop 191-202 of the catalytic core of the other monomer. <br/><br/> |
These hydrophobic interactions combined with the hydrogen bounds network anchor the Bateman module of one monomer to the entrance of the catalytic core of the other monomer, thus making it impossible for any substrate to access it. | These hydrophobic interactions combined with the hydrogen bounds network anchor the Bateman module of one monomer to the entrance of the catalytic core of the other monomer, thus making it impossible for any substrate to access it. | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 29 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Human cystathionine β-synthase (hCBS)
| |||||||||||