We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1136
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS_2015}} | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS_2015}} | ||
| - | ==Structure and Functional aspects of Sucrose Synthase from ''Arabidopsis thaliana''== | + | ==Structure and Functional aspects of Sucrose Synthase 1 from ''Arabidopsis thaliana''== |
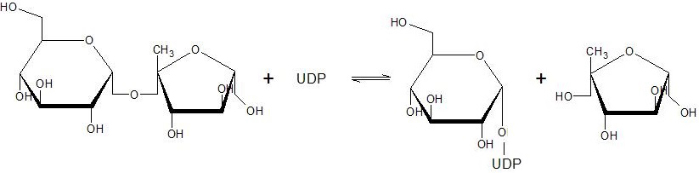
Sucrose Synthase 1 (EC:2.4.1.13), also known as the Sucrose-UDP glucolsyltransferase 1, is a reversible enzyme allowing the synthesis or the degradation of Sucrose in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. It is a 360 kDa tetramer and belongs to the Glycosyltransferase subfamily 4 (GT4). | Sucrose Synthase 1 (EC:2.4.1.13), also known as the Sucrose-UDP glucolsyltransferase 1, is a reversible enzyme allowing the synthesis or the degradation of Sucrose in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. It is a 360 kDa tetramer and belongs to the Glycosyltransferase subfamily 4 (GT4). | ||
| - | <StructureSection scene='' size='340' side='right' caption='X-ray crystal structures of AtSus1, as a complex with UDP-glucose at 2.8-Å resolution and as a complex with UDP and fructose at 2.85-Å resolution'> | + | <StructureSection scene='71/719877/Susy/3' size='340' side='right' caption='X-ray crystal structures of AtSus1, as a complex with UDP-glucose at 2.8-Å resolution and as a complex with UDP and fructose at 2.85-Å resolution'> |
| - | |||
| - | 71/719877/Susy/3 | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The Sucrose Synthase is able to catalyse the following reaction in both directions: | The Sucrose Synthase is able to catalyse the following reaction in both directions: | ||
| Line 53: | Line 51: | ||
== Regulation == | == Regulation == | ||
Sucrose synthase regulation is not well known, but here are some of the supposed mechanisms. | Sucrose synthase regulation is not well known, but here are some of the supposed mechanisms. | ||
| + | |||
• ENOD40-A is a small hormon-like peptide able to specifically thiolates the Cys-266 of AtSUS1. It also inhibit the phosphorylation of Ser-167. | • ENOD40-A is a small hormon-like peptide able to specifically thiolates the Cys-266 of AtSUS1. It also inhibit the phosphorylation of Ser-167. | ||
| + | |||
• In Arabidopsis, SUS1 gene is probably regulated by both by sucrose and D-Glucose. | • In Arabidopsis, SUS1 gene is probably regulated by both by sucrose and D-Glucose. | ||
| + | |||
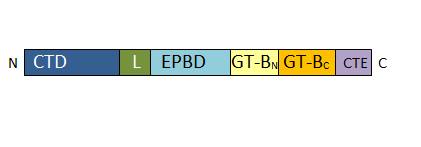
• Conformational changes of the EPBD may change the active site activity through distortions of an α helix. | • Conformational changes of the EPBD may change the active site activity through distortions of an α helix. | ||
| + | |||
• The CTD can possibly interact with actin and other cellular target, which can regulate sucrose synthase activity. | • The CTD can possibly interact with actin and other cellular target, which can regulate sucrose synthase activity. | ||
| + | |||
• In other organisms, it has been shown that the sucrose synthase is active into its dimer form, it is supposed to be the same phenomenon in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', though it has not been prouved. | • In other organisms, it has been shown that the sucrose synthase is active into its dimer form, it is supposed to be the same phenomenon in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', though it has not been prouved. | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 30 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Structure and Functional aspects of Sucrose Synthase 1 from Arabidopsis thaliana
Sucrose Synthase 1 (EC:2.4.1.13), also known as the Sucrose-UDP glucolsyltransferase 1, is a reversible enzyme allowing the synthesis or the degradation of Sucrose in Arabidopsis thaliana. It is a 360 kDa tetramer and belongs to the Glycosyltransferase subfamily 4 (GT4).
| |||||||||||
References
• UniProt entry: P49040
• Brenda entry : 2.4.1.13
- ↑ Salerno GL, Curatti L Origin of sucrose metabolism in higher plants: when, how and why? Trends Plant Sci. 2003 Feb
- ↑ Baroja-Fernández, E., Muñoz, F.J., Saikusa, T., Rodríguez-López, M., Akazawa, T. and Pozueta-Romero, J. Sucrose synthase catalyzes the de novo production of ADPglucose linked to starch biosynthesis in heterotrophic tissues of plants. Plant Cell Physiol.
- ↑ 11 Juan Gabriel Angeles N_U ~Nez. Study of sucrose synthase in arabdopsis seed : lacalization, regulation and function. Sciences of the U.
- ↑ Sucrose synthase oligomerization and F-actin association are regulated by sucrose concentration and phosphorylation. Duncan KA, Huber SC. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007 Nov; 48(11):1612-23.
- ↑ Salerno GL, Curatti L. Origin of sucrose metabolism in higher plants: when, how and why? Trends Plant Sci. 2003 Feb
- ↑ Determination of structural requirements and probable regulatory effectors for membrane association of maize sucrose synthase 1. Hardin SC, Duncan KA, Huber SC. Plant Physiol. 2006
- ↑ Phosphorylation of sucrose synthase at serine 170: occurrence and possible role as a signal for proteolysis. Hardin SC, Tang GQ, Scholz A, Holtgraewe D, Winter H, Huber SC. Plant J. 2003
- ↑ Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms. Lairson LL, Henrissat B, Davies GJ, Withers SG. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008