We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Lysin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ||
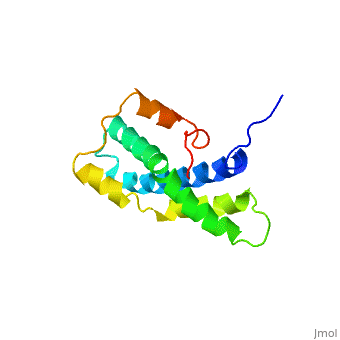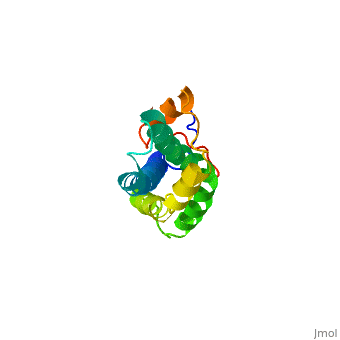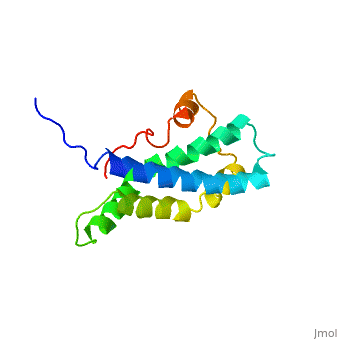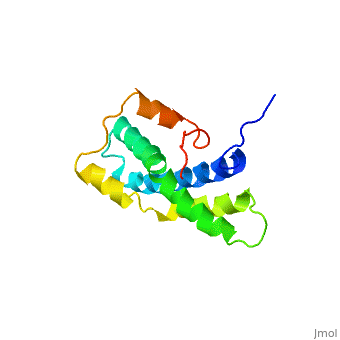
<StructureSection load='1lis' size='340' side='right' caption='Abalone lysin (PDB code [[1lis]])' scene='60/607850/Lysin_fertilization_protein/1'> | <StructureSection load='1lis' size='340' side='right' caption='Abalone lysin (PDB code [[1lis]])' scene='60/607850/Lysin_fertilization_protein/1'> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | Egg Lysin, a protein from abalone sperm, creates a hole in the envelope of the egg, permitting the sperm to pass through the envelope and fuse with the egg. | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | '''Lysin''' (Lys) is a protein which cleaves cell walls. Egg Lysin, a protein from abalone sperm, creates a hole in the envelope of the egg, permitting the sperm to pass through the envelope and fuse with the egg. | |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | The structure of lysin, refined at 1.9 angstroms resolution, reveals an alpha-helical, amphipathic molecule<scene name='60/607850/Alpha_helixes/1'>To see alpha helixes press here</scene>. you can see the alpha helixes in pink. <scene name='60/607850/Surface/1'>the surface of the protein</scene> exhibits three features: two tracks of basic residues that span the length of the molecule, a solvent-exposed cluster of <scene name='60/607850/Aromatic_and_aliphatic/1'>aromatic and aliphatic amino acids</scene>,(in green) and an extended amino-terminal hypervariable domain that is species-specific. The structure suggests possible mechanisms of action. | + | The structure of lysin, refined at 1.9 angstroms resolution, reveals an alpha-helical, amphipathic molecule<scene name='60/607850/Alpha_helixes/1'>To see alpha helixes press here</scene>. you can see the alpha helixes in pink. <scene name='60/607850/Surface/1'>the surface of the protein</scene> exhibits three features: two tracks of basic residues that span the length of the molecule, a solvent-exposed cluster of <scene name='60/607850/Aromatic_and_aliphatic/1'>aromatic and aliphatic amino acids</scene>,(in green) and an extended amino-terminal hypervariable domain that is species-specific. The structure suggests possible mechanisms of action<ref>PMID:6266073</ref>. |
| Line 17: | Line 12: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | The crystal structure of lysin, a fertilization protein. | ||
| - | Shaw A1, McRee DE, Vacquier VD, Stout CD. | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 31 January 2016
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Sumi T, Kishino Y. Histochemical and ultracytochemical detection of pyridoxal and pyridoxamine phosphate hydrolase in rat tissues. Tokushima J Exp Med. 1980 Dec;27(3-4):57-62. PMID:6266073
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Carmit Ginesin, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky