From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | <StructureSection load='1qha' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Hexokinase I complex with ATP analog, glucose, glucose-phosphate and Mg+2 ion (PDB code [[1qha]])'> | | <StructureSection load='1qha' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Hexokinase I complex with ATP analog, glucose, glucose-phosphate and Mg+2 ion (PDB code [[1qha]])'> |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | + | == Function == |
| | '''Hexokinase''' is an enzyme that phosphorylates a six-carbon sugar, a hexose, to a hexose phosphate. In most tissues and organisms, glucose is the most important substrate of hexokinases, and glucose 6-phosphate the most important product. Hexokinases have been found in every organism checked, ranging from bacteria, yeast, and plants, to humans and other vertebrates. They are categorized as actin fold proteins, sharing a common ATP binding site core surrounded by more variable sequences that determine substrate affinities and other properties. Several hexokinase isoforms or isozymes providing different functions can occur in a single species. See [[Glycolysis Enzymes]]. | | '''Hexokinase''' is an enzyme that phosphorylates a six-carbon sugar, a hexose, to a hexose phosphate. In most tissues and organisms, glucose is the most important substrate of hexokinases, and glucose 6-phosphate the most important product. Hexokinases have been found in every organism checked, ranging from bacteria, yeast, and plants, to humans and other vertebrates. They are categorized as actin fold proteins, sharing a common ATP binding site core surrounded by more variable sequences that determine substrate affinities and other properties. Several hexokinase isoforms or isozymes providing different functions can occur in a single species. See [[Glycolysis Enzymes]]. |
| | | | |
Revision as of 11:02, 21 March 2016
|
Function
Hexokinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates a six-carbon sugar, a hexose, to a hexose phosphate. In most tissues and organisms, glucose is the most important substrate of hexokinases, and glucose 6-phosphate the most important product. Hexokinases have been found in every organism checked, ranging from bacteria, yeast, and plants, to humans and other vertebrates. They are categorized as actin fold proteins, sharing a common ATP binding site core surrounded by more variable sequences that determine substrate affinities and other properties. Several hexokinase isoforms or isozymes providing different functions can occur in a single species. See Glycolysis Enzymes.
- Hexokinase I/A is found in all mammalian tissues, and is considered a "housekeeping enzyme," unaffected by most physiological, hormonal, and metabolic changes. More details in Hexokinase Type 1.
- Hexokinase II/B constitutes the principal regulated isoform in many cell types and is increased in many cancers.
- Hexokinase III/C is substrate-inhibited by glucose at physiologic concentrations. Little is known about the regulatory characteristics of this isoform.
- Hexokinase IV/D is also known as glucokinase.
Additional details in The Structure and Mechanism of Hexokinase.
Structure of Hexokinase
Hexokinase is composed of an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal catalytic domain. These two domains are . The molecular weights of hexokinases are around 100 kD. Each domain weighs about 50kD and contains a . But, only in hexokinase II do both halves have functional active sites. The tertiary structure of hexokinase includes an open alpha/beta sheet. There is a large amount of variation associated with this structure. The ATP-binding domain is composed of . In this open alph/beta sheet four of the beta sheets are parallel and one is in the anitparallel directions. The alpha helices and beta loops connect the beta sheets to produce this open alpha/beta sheet.
Mechanism of Hexokinase
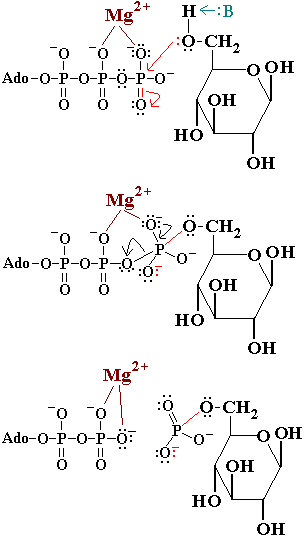
In the first reaction of glycolysis, the gamma-phosphoryl group of an ATP molecule is transferred to the oxygen at the C-6 of glucose. Hexokinase catalyzes this phosphoryl group transfer. To start this reaction, ATP forms a complex with magnesium (II) ion and glucose binds to hexokinase. The magnesium-ATP complex then binds with the hexokinase-glucose complex and forms an intermediate (Zeng, et al. present a picture showing the interctions of brain hexokinase with ATP). are thought to be involved in binding the magnesium ion in the magnesium-ATP complex [4]. The hydroxyl group on the terminal phosphoryl group of the ATP molecule nucleophilically attacks carbon 6 on glucose. This produces glucose-6-phosphate still bound to hexokinase and ADP still in complex with magnesium ion [5]. Glucose-6-phosphate and the magnesium-ADP complex leave hexokinase. Glucose-6-phosphate and ADP are the products of this reaction. Hexokinase undergoes an induced-fit conformational change when it binds to glucose, which ultimately prevents the hydrolysis of ATP. It also experiences potent allosteric inhibition under physiological concentrations by its immediate products, glucose-6-phosphate [4]. This is a mechanism by which the influx of substrate into the glycolytic pathway is controlled.
Kinetics and Inhibition of Hexokinase
Hexokinase activates glycoloysis by phosphorylating glucose. Since the phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate is the rate limiting step of glucose metabolism, hexokinase has a very important role in regulating healthy glucose levels in the human body [7]. Hexokinase has high affinity, thus a low Km, for glucose. Tissues where hexokinase is present use glucose at low blood serum levels.
G6P inhibits hexokinase by binding to the N-terminal domain(this is simple feedback inhibition). It competitively inhibits the binding of ATP [8]. If the cell is not using the G6P that it is making, then it stops making it. In this way, hexokinase can also slow down glycolysis. Hexokinase I is thought to be the "pacemaker" of glycolysis in brain tissue and red blood cells [4]. Inorganic phosphate allosterically relieves hexokinase of inhibition by G6P [8].
|
3D structures of hexokinase
Updated on 21-March-2016
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
1.↑ Pollard-Knight D, Cornish-Bowden A. Mechanism of liver glucokinase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Apr 30;44(2):71-80. PMID:7048063
2.↑ 2.0 2.1 Kamata K, Mitsuya M, Nishimura T, Eiki J, Nagata Y. Structural basis for allosteric regulation of the monomeric allosteric enzyme human glucokinase. Structure. 2004 Mar;12(3):429-38. PMID:15016359 doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.02.005
3.↑ Postic C, Shiota M, Magnuson MA. Cell-specific roles of glucokinase in glucose homeostasis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:195-217. PMID:11237213
4.↑ Zeng C, Aleshin A, Hardie J, Harrison R, Fromm H. ATP-Binding site of Human Brain Hexokinase as Studied by Molecular Modeling and Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Biochem. 1996 Aug 6;35:13157-13164.
5.↑ hammes G, and Kochavi D. Studies of the Enzyme Hexokinase: Kinetic Inhibition by Products. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1961 Oct 5.
6.↑ Ralph E, Thomson J, Almaden J, Sun S. Glucose Modulation fo Glucokinase Activation by Small Molecules. Biochem. 2008 Feb 15;47:5028-5036.
7.↑ Pal P, and Miller B. Activating Mutations in the Human Glucokinase Gene Revealed by Genetic Selection. Biochem. 2008 Dec 3;48:814-816.
8.↑ Aleshin A, Malfois M, Liu X, Kim C, Fromm H, Honzatko R, Koch M, Svergun D. Nonaggregating Mutant of Recombinant Human Hexokinase I Exhibits Wild-Type Kinetics and Rod-like Conformations in Solution. Biochem. 1999 Apr 29;38:8359-8366.
Seth Bawel and Kyle_Schroering created this page in Che 361 at Wabash College.