We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1175
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<scene name='72/721546/Lpa-helices/1'>Helices</scene> | <scene name='72/721546/Lpa-helices/1'>Helices</scene> | ||
===Comparison of S1P and LPA=== | ===Comparison of S1P and LPA=== | ||
| - | + | Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors (LPA) are part of a larger family known as lysophospholipid receptor family (EDG family). Within this family there is a structure called S1P1. Since only the structures for LPA1 and S1P1 are known in the EDG family, comparisons are made between the two structures. | |
| + | There is a difference in binding paths between these two receptors. The binding path in the LPA1 is located in the extracellular milieu. While in the S1P1 the ligands are able to have access to the membrane so that the binding can occur. There is a difference in the shape of the electron density from the binding pocket. In S1P1 the binding pocket has more of an oval shape. For the LPA1 receptor the binding pocket has a spherical shape. Since the binding pocket is more spherical it gives LPA1 the ability to be able to recognize a larger group of chemical species. In particular the ability to bind with acyl chains of varying lengths. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:LPA1vs. SAP1.png|200px|left|thumb|A comparison of the binding pockets of LPA1 vs. S1P1]] | [[Image:LPA1vs. SAP1.png|200px|left|thumb|A comparison of the binding pockets of LPA1 vs. S1P1]] | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 22 March 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
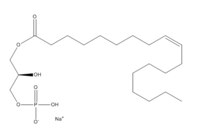
Human Lysophosphatodic Acid Receptor 1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Chrencik JE, Roth CB, Terakado M, Kurata H, Omi R, Kihara Y, Warshaviak D, Nakade S, Asmar-Rovira G, Mileni M, Mizuno H, Griffith MT, Rodgers C, Han GW, Velasquez J, Chun J, Stevens RC, Hanson MA. Crystal Structure of Antagonist Bound Human Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1. Cell. 2015 Jun 18;161(7):1633-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002. PMID:26091040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002
- ↑ Tager AM, LaCamera P, Shea BS, Campanella GS, Selman M, Zhao Z, Polosukhin V, Wain J, Karimi-Shah BA, Kim ND, Hart WK, Pardo A, Blackwell TS, Xu Y, Chun J, Luster AD. The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak. Nat Med. 2008 Jan;14(1):45-54. Epub 2007 Dec 9. PMID:18066075 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm1685