Sandbox Reserved 1160
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The mGlu family of receptors was the first of the Class C GPCR to be extensively studied<ref name="Wu" />. The first regions of the protein crystallized and studied were the Venus fly trap domain and the cystiene-rich domain on the extracellular region of the receptor. The hydrophobic nature and flexibility of the transmembrane domain made it difficult to crystallize. Recently, the human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain was crystallized and a structure elucidated. There were several modifications that had to be made to the TMD for it to successfully crystallize. The protein was thermostabilized and flexible domains were removed. In total residue 2-568 and residues 837-1153 were excised from the structure. Also, a T4 -<scene name='72/721531/Protien_lys/1'>Lysozyme</scene> was inserted into ICL-2. | The mGlu family of receptors was the first of the Class C GPCR to be extensively studied<ref name="Wu" />. The first regions of the protein crystallized and studied were the Venus fly trap domain and the cystiene-rich domain on the extracellular region of the receptor. The hydrophobic nature and flexibility of the transmembrane domain made it difficult to crystallize. Recently, the human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain was crystallized and a structure elucidated. There were several modifications that had to be made to the TMD for it to successfully crystallize. The protein was thermostabilized and flexible domains were removed. In total residue 2-568 and residues 837-1153 were excised from the structure. Also, a T4 -<scene name='72/721531/Protien_lys/1'>Lysozyme</scene> was inserted into ICL-2. | ||
== Structure== | == Structure== | ||
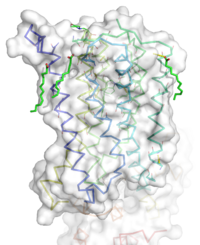
| - | [[Image:STR.png|200 px|left|thumb|Overall Structure of the TMD. The polar heads on the | + | [[Image:STR.png|200 px|left|thumb|Overall Structure of the TMD. The polar heads on the Oliec acids orient the protein with the top of the image being the extracellular portion of the protein,the middle portion inserted into the membrane, and the lower portion located inside of the cell. ]] |
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
The mGlu5 TMD contains 7 <scene name='72/721531/Protien_7_helices/2'> alpha helices</scene> that span the membrane. The protein was crystallized with Oleic acid and MES. On the superior portion of the protein there are several critical extracellular loops.The binding pocket can be found near the middle of the protein.Inserted into the biding pocket is the negative allosteric modulator Mavoglurant. It is important to note that the TMD as illustrated is in an inactive conformation. On the intracellular portion of the protein there exist several ionic locks whose positions will determine the activity of the protein. | The mGlu5 TMD contains 7 <scene name='72/721531/Protien_7_helices/2'> alpha helices</scene> that span the membrane. The protein was crystallized with Oleic acid and MES. On the superior portion of the protein there are several critical extracellular loops.The binding pocket can be found near the middle of the protein.Inserted into the biding pocket is the negative allosteric modulator Mavoglurant. It is important to note that the TMD as illustrated is in an inactive conformation. On the intracellular portion of the protein there exist several ionic locks whose positions will determine the activity of the protein. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
=== Fragile X === | === Fragile X === | ||
| - | + | Fragile X syndrome is the most common genetic cause of mental disabilty, and is a member of the Autism spectrum disorder family<ref name="Bailey" />. The severity of intellectual disability can vary from patient to patient, but symptoms stem from a misregulation of the mGlu1 and MGlu5 pathways<ref name="Bailey" />. This leads to over potentiation in neural cells. Mavoglurant and other allosteric regulators like fenobam have shown promise in treating Fragile X.One positive characteristic of ligands that target the TMD is they tend to be more specific, thus interacting less with brain proteins<ref name="Feng" />. Mavoglurant would act to down regulate glutamate signaling in an attempt to decrease potentiation. Unfortunately, recent Phase 2 clinical trials have proven mavoglurant ineffective <ref name="Bailey" />. Novartis the company who developed the drug has stopped clinical trials of mavoglurant <ref name="Bailey" />. However, modulators of mGlu5 TMD are still be researched to treat Parkinson's, Alzheimer's disease, and various addictions<ref name="Niswender" />. | |
| - | One positive characteristic of ligands that target the TMD is they tend to be more specific, thus interacting less with brain proteins<ref name="Feng" />. | + | |
| - | However, modulators of mGlu5 TMD | + | |
=== Parkinsons === | === Parkinsons === | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 46: | Line 44: | ||
<ref name="Niswender">PMID: 20055706</ref> | <ref name="Niswender">PMID: 20055706</ref> | ||
<ref name="Feng">PMID: 25762450</ref> | <ref name="Feng">PMID: 25762450</ref> | ||
| - | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="Bailey">PMID: 26855682</ref> |
<references/> | <references/> | ||
== External Resources == | == External Resources == | ||
Revision as of 01:51, 30 March 2016
Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dore AS, Okrasa K, Patel JC, Serrano-Vega M, Bennett K, Cooke RM, Errey JC, Jazayeri A, Khan S, Tehan B, Weir M, Wiggin GR, Marshall FH. Structure of class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain. Nature. 2014 Jul 31;511(7511):557-62. doi: 10.1038/nature13396. Epub 2014 Jul 6. PMID:25042998 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13396
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Niswender CM, Conn PJ. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:295-322. doi:, 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145533. PMID:20055706 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145533
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Wu H, Wang C, Gregory KJ, Han GW, Cho HP, Xia Y, Niswender CM, Katritch V, Meiler J, Cherezov V, Conn PJ, Stevens RC. Structure of a class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 bound to an allosteric modulator. Science. 2014 Apr 4;344(6179):58-64. doi: 10.1126/science.1249489. Epub 2014 Mar , 6. PMID:24603153 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1249489
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Bailey DB Jr, Berry-Kravis E, Wheeler A, Raspa M, Merrien F, Ricart J, Koumaras B, Rosenkranz G, Tomlinson M, von Raison F, Apostol G. Mavoglurant in adolescents with fragile X syndrome: analysis of Clinical Global Impression-Improvement source data from a double-blind therapeutic study followed by an open-label, long-term extension study. J Neurodev Disord. 2016;8:1. doi: 10.1186/s11689-015-9134-5. Epub 2015 Dec 15. PMID:26855682 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s11689-015-9134-5
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Feng Z, Ma S, Hu G, Xie XQ. Allosteric Binding Site and Activation Mechanism of Class C G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Family. AAPS J. 2015 May;17(3):737-53. doi: 10.1208/s12248-015-9742-8. Epub 2015 Mar 12. PMID:25762450 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9742-8