User:Giavanna Verdi/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
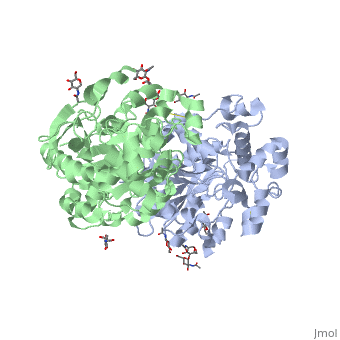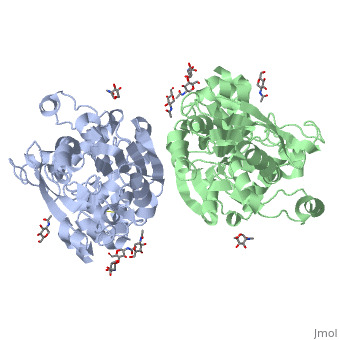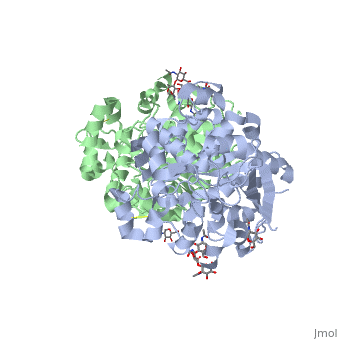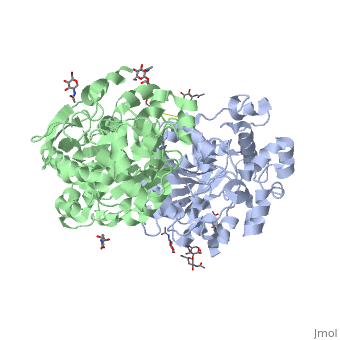
<Structure load='1HLG' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Regions of Human Gastric Lipase' scene='72/727839/Hydrophobic_and_polar_regions/1' /> | <Structure load='1HLG' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Regions of Human Gastric Lipase' scene='72/727839/Hydrophobic_and_polar_regions/1' /> | ||
<Structure load='1HLG' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Secondary Structure of Human Gastric Lipase' scene='72/727839/Secondary_structure/1' /> | <Structure load='1HLG' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Secondary Structure of Human Gastric Lipase' scene='72/727839/Secondary_structure/1' /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | This is a default text for your page '''Giavanna Verdi/Sandbox1'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
| - | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| - | Human gastric lipase (HGL, E.C. 3.1.1.3) (PBD ID: 1hlg) is a type of [[hydrolase]] (an enzyme class that includes [[lipase]]) that is responsible for initiating the digestion of dietary fats in the stomach <ref name="armand">PMID:7598069</ref>. This enzyme is secreted by the fundic chief cells of the human stomach and catalyzes 10-20% of total lipolytic processes (i.e., those involving fat breakdown) in healthy adults <ref name="armand" />. HGL specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol in order to produce diacylglycerol and a carboxylate byproduct <ref name="roussel">PMID:10358049</ref>. | + | Human gastric lipase (HGL, E.C. 3.1.1.3) (PBD ID: 1hlg) is a type of [[hydrolase]] (an enzyme class that includes [[lipase]]) that is responsible for initiating the digestion of dietary fats in the stomach <ref name="armand">PMID:7598069</ref>. This enzyme is secreted by the fundic chief cells of the human stomach and catalyzes 10-20% of total lipolytic processes (i.e., those involving fat breakdown) in healthy adults <ref name="armand" />. HGL specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol in order to produce diacylglycerol and a carboxylate byproduct <ref name="roussel">PMID:10358049</ref>, a process through which subsequent hydrolysis performed by pancreatic lipase is facilitated <ref name="dogs">PMID:20965171</ref>. |
| Line 24: | Line 19: | ||
HGL, a 379 amino acid residue-long lipase enzyme, possesses a catalytic arm consisting of residues Ser-153, His-353, and Asp-324 <ref name="roussel" />. | HGL, a 379 amino acid residue-long lipase enzyme, possesses a catalytic arm consisting of residues Ser-153, His-353, and Asp-324 <ref name="roussel" />. | ||
| - | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
| - | |||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 21:30, 8 April 2016
|
|
|
Contents |
Introduction
Human gastric lipase (HGL, E.C. 3.1.1.3) (PBD ID: 1hlg) is a type of hydrolase (an enzyme class that includes lipase) that is responsible for initiating the digestion of dietary fats in the stomach [1]. This enzyme is secreted by the fundic chief cells of the human stomach and catalyzes 10-20% of total lipolytic processes (i.e., those involving fat breakdown) in healthy adults [1]. HGL specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of triacylglycerol in order to produce diacylglycerol and a carboxylate byproduct [2], a process through which subsequent hydrolysis performed by pancreatic lipase is facilitated [3].
Function
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
HGL, a 379 amino acid residue-long lipase enzyme, possesses a catalytic arm consisting of residues Ser-153, His-353, and Asp-324 [2].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Armand M, Hamosh M, DiPalma JS, Gallagher J, Benjamin SB, Philpott JR, Lairon D, Hamosh P. Dietary fat modulates gastric lipase activity in healthy humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995 Jul;62(1):74-80. PMID:7598069
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Roussel A, Canaan S, Egloff MP, Riviere M, Dupuis L, Verger R, Cambillau C. Crystal structure of human gastric lipase and model of lysosomal acid lipase, two lipolytic enzymes of medical interest. J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 11;274(24):16995-7002. PMID:10358049
- ↑ Selvan A, Seniya C, Chandrasekaran SN, Siddharth N, Anishetty S, Pennathur G. Molecular dynamics simulations of human and dog gastric lipases: insights into domain movements. FEBS Lett. 2010 Nov 19;584(22):4599-605. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.10.021. Epub, 2010 Oct 20. PMID:20965171 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2010.10.021