Introduction
Rickets is a disease resulting from prolonged vitamin D deficiency. As vitamin D is vital for the absorption of phosphorus and calcium, a deficiency would cause weakening of bones. Rickets also causes muscle weakness, skeletal deformities, dental problems, inhibition of growth, and muscle spasms. In some cases, rickets can be inherited due to mutations in genes responsible for coding for human CYP2R1.
In the human body, CYP2R1, a member of the cytochrome P450 family, is responsible for the first steps of the conversion of vitamin D into a bioavailable form within the liver. CYP2R1 is also known as Vitamin D 25-hydroxylase as it hydroxylates vitamin D3 into calcidiol, the bioavailable form of the vitamin, which would then be converted to calcitriol via the enzyme 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1-alpha-hydroxylase, as seen in figure 1.
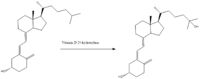
Fig. 1, the conversion of vitamin D3 into calcidiol via Vitamin D 25-hydroxylase
is shown with amino acids in teal and the heme center shown as a space filling model, with the nitrogen shown in blue, carbon in gray, oxygen in red, and the iron center shown in orange
Overall Structure
Cytochrome P450 is an , which means the protein is made of two subunits that are structurally very similar to one another, but not identical. Each dimeric subunit contain 12 α-helices (labeled A-L) along with some β-sheets that are localized to one side of the molecule. Helices F and G from each of the units form the dimer interface of cytochrome P450, and are involved in the formation of the active site. This dimeric interface of the protein is stabilized by between residues from the G helix of one the units with residues located on the the F helix of the second unit, and vice versa. Two molecules of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin are also found near the dimer interface. The cyclodextrins are believed to help further stabilize the protein, and also shield the hydrophobic part of the F-G helix transition loop from the solvent by . Cytochrome P450 has an apparent mass of ~120 kDa.
Binding Interactions
CYP2R1 binds vitamin D3 at an extended binding site that orients the bound molecule to bring its side chain close to the heme and allow for hydroxylation. The binding site is located at the channel between the G and I helices and the B' helix/B-C loop. The active site has non-polar residues which allows for nonpolar interactions with D3. In the you can see the residues that interact to bind Vitamin D3 and the channel between. Once bound, the D3 molecule is submerged into the protein, with only its 3-OH group showing.
The B' helix is one of the substrate recognition sites and has a flexible C terminus which unwinds outward to allow entrance of the substrate into the active site channel. Due to the stabilizing interactions of B' with the F-G loop, binding of the substrate causes the protein to adopt a closed conformation which closes the access channel.
Additional Features
Cytochrome P450 has a central iron-bound heme, which, combined with its structural conformation, allows for hydroxylation with the attached substrate. Cytochrome P450 has specific vitamin D 25-hydroxylase activity, which does not function properly when a person has rickets. Rickets is caused by a lack of sufficient vitamin D in their system, which is often caused by a vitamin D-25 hydroxylation defect. Leu99Pro is an evolutionarily conserved mutation in the beta helix which contributes to the hydroxylation defect. Leu99 does not inhibit substrate binding; however, Leu99Pro disturbs hydrogen binding around the heme and interferes with the helix steric properties, causing protein instability. When Leu99 does not have the proline mutation, its carboxyl group forms hydrogen bonds with Arg445, which are both located around the central heme and allows for hydroxylation of vitamin D.
Quiz Question 1
1A) Why is Proline so poorly suited for inclusion in Alpha Helices?
A) It cannot hydrogen bond due to the position of its amide
B) The residue is incapable of forming the correct phi and psi angles in a helix
C) The steric hindrance of its sidechain
D) A and C
E) All of the above
1B) This protein being a dimer, has symmetry between its two large sections, from where most of the molecule has been cut away for simplicity, you can see where one half (in green) comes within close proximity of the other half (in blue). These 2 pairs of helices help hold the dimer together via electrostatic interactions. If the black residue is Arg, and the white residue is Asp, what is most likely to be on the opposite helix
(Arg match, Asp match)
A) Asp, His
B) Gly, Val
C) Met, Lys
See Also
Credits
Introduction - Sami Kriksceonaitis
Overall Structure - Kati Johnson
Binding Interactions - Isabel Hand
Additional Features - Elizabeth Humble
Quiz Question 1 - Matthew Tiller
References
- ↑ Strushkevich N, Usanov SA, Plotnikov AN, Jones G, Park HW. Structural analysis of CYP2R1 in complex with vitamin D3. J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 27;380(1):95-106. Epub 2008 Apr 8. PMID:18511070 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.065

