Receiving and responding to extracellular messages is critical to the proper function of the nervous system. Glutamate is the primary excitory neurotransmitter of the Central Nervous System (CNS), and metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a key member of the glutamate signaling pathway[1]. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a homodimeric GPCR that resides in the cellular membrane [1]. mGlu5 is a member of the Class C GPCR family and can further be categorized into the Group I subgroup[2].
The functionality of the mGlu5 receptor is determined by conformational changes throughout multiple domains. mGlu5 will bind glutamate through its extracellular Venus flytrap domain and the signal will be transduced across the membrane to a heterotrimeric G protein, which will ultimately lead to calcium release and the activation of PKC[2]. The signal is relayed through a Gq/11 pathway[1]. Activated PKC will elicit a excitory post-synaptic response and modulate long term potentiation[2].
Human mGlu5 is found throughout the central nervous system. Areas containing high concentrations of mGlu5 are often involved in emotional processing and higher cognition[3]. The localization of mGlu5 in the CNS and the presence of multiple domains makes mGlu5 an excellent target for treating neurological conditions including: schizophrenia,Fragile X, depression, anxiety, and Alzheimer's disease[2].
Discovery
The mGlu family of receptors was the first of the Class C GPCR to be extensively studied[2]. The first regions of the protein crystallized and studied were the Venus Fly Trap domain and the cystiene -rich domain on the extracellular region of the receptor[1].The Venus Flytrap domain is a large extracellular domain that will selectively bind to glutamate[2]. The CRD is a somewhat smaller domain composed of many ß sheets and cystiene residues [2]. The CRD acts as a signal mediator between the Venus Flytrap domain and the TMD of mGlu5, by linking to each domain with disulfide bonds[2]. The hydrophobic nature and flexibility of the transmembrane domain made it difficult to crystallize. Recently, the human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain (TMD) was crystallized and a structure elucidated[1]. Several modifications made to the TMD for successful crystallization. The protein was thermostabilized and flexible domains were removed[1]. In total residue 2-568 and residues 837-1153 were excised from the structure. The structure of the alpha helices are shown in green, and the negative allosteric modulator mavoglurant shown in yellow. Also in orange, a T4 - was inserted into intracellular loop 2 to add stability[1].
Structure
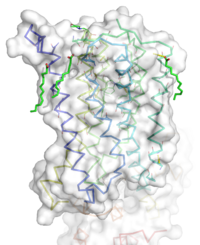
Figure 1: Overall Structure of the mGlu5 TMD. The polar heads on the Oliec acids orient the image with the top oriented extracellularly, the middle portion inserted into the membrane, and the lower portion oriented intracellularly. The white exterior represents the surface of the protien, and the multicolored lines interior to the surface represent the backbones 7 transmembrane alpha helices.
Overview
The mGlu5 TMD contains 7 that spans the membrane. The protein was crystallized with shown in red. On the top portion of the protein several critical extracellular loops connect the TMD to the CRD. The binding pocket can be found near the middle of the protein, and is mainly comprised of hydrophobic amino acids with more polar amino acids found in the upper and lower portions of the binding site. Inserted into the biding pocket is the negative allosteric modulator mavoglurant. The TMD is in an inactive conformation, since mavoglurant is bound. Also, the deletion of the flexible domains leaves the mGlu5 receptor unable to bind to its GPCR. The inactive state is maintained by multiple ionic locks whose positions determine the active versus inactive conformation.
Extracellular Domain
These are the with extracellular loops (ECLs) 1, 2, and 3 highlighted in purple. Additionally in the ECL domain, a is attached to both Helix 3 and the amino acid chain between Helix 5 and the N-terminus. Helix 3 and Helix 5 are colored in teal and red respectively. N-terminus is represented in blue. The disulfide bond is highlighted in yellow, and it is conserved in all classes of glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domains[2] ECLs and the Helices are also factors that dictate how mavolgarent fits in the binding pocket (citations. The position of these factors can change the size of the binding pocket through tightening or widening.
Binding Pocket

Figure 2. Mavolugarent in its binding pocket of the 7TM region of mGLu5 Class C receptor. The binding pocket's surface is clipped in black with the substrate, mavolugarent, in red. The rest of the protein is colored in green. The binding pocket is present in the 7 Helix Transmembrane Domain that would be present in the phosolipid bilayer appearing as an intergral protein. The presence of mavolugarent inhibits the function of the metabotropic glutamate receptor.
The binding pocket, not to be confused with the glutamate binding site, represents an useful source of regulatory control. The binding pocket is only accessible by a relatively narrow (7 Å) . This small entrance severely restricts the access of both positive and negative allosteric regulators. One such regulator, , is a relatively small molecule that can travel through the entrance and fit between the helices of the mGlu5 receptor. Mavoglurant acts as a negative allosteric modulator of the mGlu5 receptor. Mavoglurant is a relatively hydrophobic molecule, which compliments the largely hydrophobic nature of the interior of mGlu5. The carbamate tail and hydroxyl group of mavoglurant will also interact with several key amino acids in the binding site of mGlu5.
Important Amino Acids[1]:
- 747 forms a hydrogen bond network with the main chain carbonyl of Glycine 652 and the carbamate portion of mavoglurant.
- Bicyclic ring of mavoglurant surrounded by . Hydrophobic regions of the mGlu5 receptor are shown in purple and the rest of the helices are shown in grey. Mavoglurant is represented by spheres.
- 2 Catalytic residues H-bond to the hydroxyl oxygen of our ligand.
- A inside of the binding pocket helps stabilize the inactive state.
Upon mavoglurant’s diffusion into the mGlu5 receptor binding pocket, the ordered water cage found in the center of mGlu5 is displaced. Favorable interactions between the hydrophobic regions of the binding pocket and the bicyclic ring and the 3-methylphenyl ring of mavoglurant help increase the strength and energetic favorability of mavoglurant binding via the hydrophobic effect. In the binding pocket mavoglurant can hydrogen bond with Asp 747 and that hydrogen bond will be further stabilized by an extended hydrogen bond network with Gly 652. The hydroxyl group of mavoglurant will also form another hydrogen bond with Ser 805 and Ser 809. Multiple hydrogen bonds make the binding of mavoglurant to the mGlu5 receptor favorable and specific. Once bound to mavoglurant, transmembrane helix 7 undergoes a conformational change[1]. The shifting of TM7 will lead to a more global conformational change, which inactivates the receptor[1]. Variation can be seen in positioning of alpha helices across receptor class. Class C receptors have seemingly less space for mavoglurant to enter as compared to Class A and F receptors[2]. The position of the ligand binding site is also varied between different classes of mGlu receptors[1].
Ionic Locks
Another important structural feature is the series of on the intracellular side of the protein. Interactions between these five amino acids will form a salt bridge, which will stabilize the inactive conformation[1]. The primary ionic lock forms between Glu770, Lys665, and Ser613[1]. A secondary ionic lock occurs between Ser614 and Arg668[1]. The purpose of these ionic locks is analogous to the ionic interactions that stabilize the T state in Hemoglobin. In the case of the TMD of mGlu5, the ionic lock is formed when the NAM mavoglurant is bound. This ionic lock stabilizes the inactive state, where the intracellular loops are stabilized facing inwards[2]. This conformational change will effectively block the crevice that is involved in binding the G-protein[2]. Models have suggested that, even in a glutamate bound state, the mavoglurant bound receptor would be dimerized but incapable of signaling[2]. This signaling incapable mGlu5 dimer will help maintain the readiness of the pathway, while still decreasing signal response.
Pathway
It all begins with glutamate binding to the Venus flytrap domain. The signal is transduced across the cystine-rich domain to the TMD[3]. Next, the dimerization of the TMD occurs. This activates the Gq/11 pathway, which activates phospholipase Cβ[3]. The active phospholipase Cβ hydrolyzes phosphotinositides and generates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacyl-glycerol[4]. This results in calcium mobilization and activation of PKC[3].
Disease
Fragile X
Fragile X syndrome is the most common genetic cause of mental disability, and is a member of the Autism spectrum disorder family[5]. The severity of intellectual disability can vary from patient to patient, but symptoms commonly stem from a misregulation of the mGlu1 and MGlu5 pathways[5]. Misregulation of these pathways leads to over potentiation in neural cells. Mavoglurant and other allosteric regulators like fenobam have shown promise in treating Fragile X. One positive characteristic of ligands that target the TMD of mGlu5 is they tend to be more specific, thus interacting less with nonspecific brain proteins[6]. Mavoglurant down regulates glutamate signaling in an attempt to decrease potentiation. Unfortunately, recent Phase 2 clinical trials have proven mavoglurant ineffective [5]. However, modulators of mGlu5 TMD are still being investigated as treatment for to Parkinson's, Alzheimer's disease, and various addictions[3].
References
[1]
[2]
[3]
[6]
[5]
[4]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 Dore AS, Okrasa K, Patel JC, Serrano-Vega M, Bennett K, Cooke RM, Errey JC, Jazayeri A, Khan S, Tehan B, Weir M, Wiggin GR, Marshall FH. Structure of class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain. Nature. 2014 Jul 31;511(7511):557-62. doi: 10.1038/nature13396. Epub 2014 Jul 6. PMID:25042998 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13396
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 Wu H, Wang C, Gregory KJ, Han GW, Cho HP, Xia Y, Niswender CM, Katritch V, Meiler J, Cherezov V, Conn PJ, Stevens RC. Structure of a class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 bound to an allosteric modulator. Science. 2014 Apr 4;344(6179):58-64. doi: 10.1126/science.1249489. Epub 2014 Mar , 6. PMID:24603153 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1249489
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Niswender CM, Conn PJ. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:295-322. doi:, 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145533. PMID:20055706 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145533
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Woodcock EA, Kistler PM, Ju YK. Phosphoinositide signalling and cardiac arrhythmias. Cardiovasc Res. 2009 May 1;82(2):286-95. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn283. Epub 2008 Oct, 20. PMID:18940816 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvn283
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Bailey DB Jr, Berry-Kravis E, Wheeler A, Raspa M, Merrien F, Ricart J, Koumaras B, Rosenkranz G, Tomlinson M, von Raison F, Apostol G. Mavoglurant in adolescents with fragile X syndrome: analysis of Clinical Global Impression-Improvement source data from a double-blind therapeutic study followed by an open-label, long-term extension study. J Neurodev Disord. 2016;8:1. doi: 10.1186/s11689-015-9134-5. Epub 2015 Dec 15. PMID:26855682 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s11689-015-9134-5
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Feng Z, Ma S, Hu G, Xie XQ. Allosteric Binding Site and Activation Mechanism of Class C G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Family. AAPS J. 2015 May;17(3):737-53. doi: 10.1208/s12248-015-9742-8. Epub 2015 Mar 12. PMID:25762450 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9742-8
External Resources
Novartis Fragile X trials
[1]


