This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
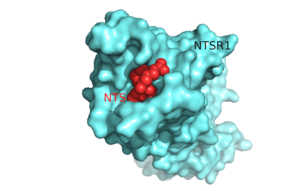
Sandbox Reserved 1176
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
====Glu166==== | ====Glu166==== | ||
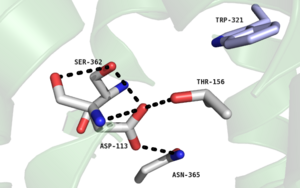
| - | Although the role of <scene name='72/721548/E166/4'>Glu166</scene> in G-protein activity is not quite as clear as it is for <scene name='72/721548/L310/3'>Leu310</scene> or <scene name='72/721547/Hydrophobic_binding_pocket/5'>Phe358</scene>, substituting this residue for an alanine significantly reduced '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Active_site catalytic]''' G-protein activity <ref name="SPGP"/>. Glu166 is part of a <scene name='72/721548/Dery_motif/2'>D/ERY motif</scene> that is highly conserved in class A GPCRs and includes Arg167 and Tyr168. To determine a role for Glu166, other class A GPCRs were structurally analyzed. It's hypothesized <ref name="SPGP"/> that E166 in NTSR1 interacts with Val102, Thr101,and | + | Although the role of <scene name='72/721548/E166/4'>Glu166</scene> in G-protein activity is not quite as clear as it is for <scene name='72/721548/L310/3'>Leu310</scene> or <scene name='72/721547/Hydrophobic_binding_pocket/5'>Phe358</scene>, substituting this residue for an alanine significantly reduced '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Active_site catalytic]''' G-protein activity <ref name="SPGP"/>. Glu166 is part of a <scene name='72/721548/Dery_motif/2'>D/ERY motif</scene> that is highly conserved in class A GPCRs and includes Arg167 and Tyr168. To determine a role for Glu166, other class A GPCRs were structurally analyzed. It's hypothesized <ref name="SPGP"/> that E166 in NTSR1 interacts with Val102, Thr101,and His105 to stabilize the G protein. The possibility of an important connection between the D/ERY motif and intracellular loop 2, which plays a role in the dissociation of the receptor-G protein complex with GTP present has also been noted.<ref name="SPGP"/> M181 is believed to link the D/ERY motif and ICL2. <ref name="SPGP"/> |
Revision as of 02:10, 22 April 2016
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 Krumm BE, White JF, Shah P, Grisshammer R. Structural prerequisites for G-protein activation by the neurotensin receptor. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 24;6:7895. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8895. PMID:26205105 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8895
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 White JF, Noinaj N, Shibata Y, Love J, Kloss B, Xu F, Gvozdenovic-Jeremic J, Shah P, Shiloach J, Tate CG, Grisshammer R. Structure of the agonist-bound neurotensin receptor. Nature. 2012 Oct 25;490(7421):508-13. doi: 10.1038/nature11558. Epub 2012 Oct 10. PMID:23051748 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11558
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Liang Y, Boules M, Li Z, Williams K, Miura T, Oliveros A, Richelson E. Hyperactivity of the dopaminergic system in NTS1 and NTS2 null mice. Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jun;58(8):1199-205. doi:, 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.02.015. Epub 2010 Mar 6. PMID:20211191 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.02.015
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Carraway RE, Plona AM. Involvement of neurotensin in cancer growth: evidence, mechanisms and development of diagnostic tools. Peptides. 2006 Oct;27(10):2445-60. Epub 2006 Aug 2. PMID:16887236 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2006.04.030
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Griebel G, Holsboer F. Neuropeptide receptor ligands as drugs for psychiatric diseases: the end of the beginning? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 May 18;11(6):462-78. doi: 10.1038/nrd3702. PMID:22596253 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd3702