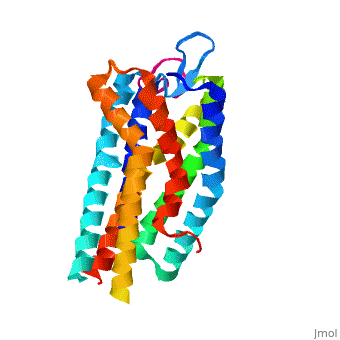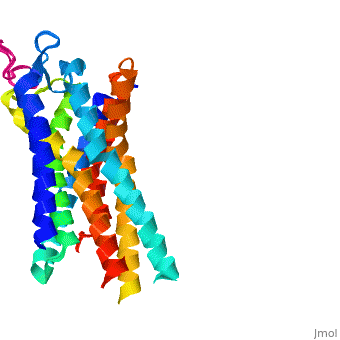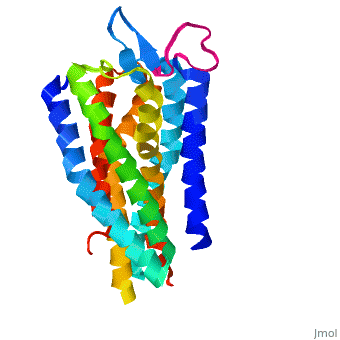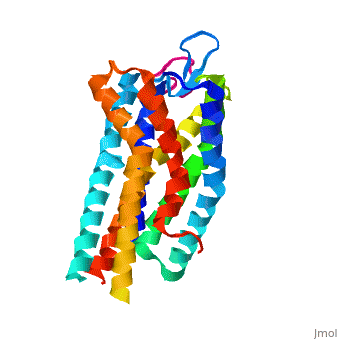
Background
Human G-protein coupled receptor 40 (hGPR40), also known as free fatty acid 1 receptor (FFAR1), is a seven helical transmembrane domain receptor that recognizes long-chain free fatty acids and induces insulin secretion.[1] Some known fatty acid substrates of hGPR40 include linoleic acid, oleic acid, eicosatrienoic acid, and palmitoleic acid[2]. hGPR40 is highly expressed in human pancreatic β cells, brain, and endocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract.[3] hGPR40 is of particular interest because the triggering of insulin secrection is glucose dependent.This glucose-dependence for hGPR40 signaling makes it a target for the treatment of type-2 diabetes as agonists could increase glycemic control and lower the risk of hypoglycemia.[1] GPR40 is a member of a group of homologous GPCRs all located on chromosome 19q13.1 including GPCR41, 42, and 43.[4]
Function
GPR40 is most prevalent in pancreatic β-cells where free fatty acids (FFAs) have pleiotropic effects [5]. While acute intake of FFAs stimulates insulin release, chronic exposure to high levels of FFAs results in the impairment of β-cell function and insulin secretory response [5]. GPR40 mediates the effect of both acute and chronic levels of FFAs. FFAs amplify glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells by activating GPR40. When GPR40 is inhibited, insulin secretion no longer increases in response to fatty acid stimulation [5]. This decreased activity of GPR40 leads to a decreased risk of hyperinsulinemia, fatty liver disease, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperglycemia, and glucose tolerance in obese patients [5]. On the contrary, overexpression of GPR40 leads to impaired β-cell function, hyperinsulinemia, and diabetes [5]. These results suggest that GPR40 plays an important role in the mechanism that links obesity and type 2 diabetes and thus is a popular drug target.
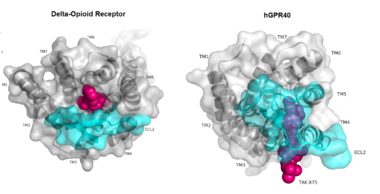
Figure 1:Comparison of Delta-opioid receptor to human free-fatty acid receptor (hGPR40) both of which are G-protein coupled receptors. The binding pocket of the delta-opioid receptor is solvent exposed allowing ligands to enter directly from the extracellular space while the binding pocket of hGPR40 is covered by the extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) preventing entry from the extracellular space (ECL2 represented in cyan). The Delta-opioid displays the canonical binding site typical of most GPCRs while ligands of hGPR40 bind to a noncanonical pocket represented in pink.
Structure
Like most G-protein coupled receptors, hGPR40 contains (). To obtain a crystal structure of the protein, four (, , , ) were made to increase the expression and thermal stability of the protein. These mutations did not significantly impact the enzyme's binding affinity with a known agonist, TAK-875.[1] (shown in crimson) was also added to intracellular loop 3 to aid in the formation of crystals. T4 Lysozyme had little effect on TAK-875 binding.[1] For clarity, lysozyme is removed in all further renderings of hGPR40. hGPR40 also contains an extracellular loop that is conserved among most G-protein coupled receptors (ECL2). This loop has two subsections and is involved in the permeability of the binding site.
While there is relatively low sequence identity between hGPR40 and peptide-binding and opioid GPCRs, they do share structural similarities such as a conserved motif on (ECL2).[1] In addition, a conserved is formed between transmembrane helix 3 (Cys 79) and the C-terminus of ECL2 (Cys170).[1] Compared to peptide-binding and opioid GPCRs, which have distinctive β-sheets spanning from transmembrane helix 4 to 5, hGPR40 possesses a shorter B-sheet-like region, which has low B-factors.[1] This reflects the low mobility of the region that limits the overall flexibility of the adjacent portion of ECL2 between Leu171 and Asp175.[1] A unique feature of hGPR40 is the presence of an additional 13 residues (Pro147 to Gly159) on ECL2, which is absent on all the other peptide/opioid receptors.[1] These extra residues form a separate between the B-sheet-like region and transmembrane 4. Together, the auxiliary loop and ECL2 of hGPR40 function as a over the canonical binding site covering it from the central extracellular region.[1]
The canonical binding pocket for many other GPCRs is solvent exposed and centrally located between the transmembrane helices allowing ligands to directly bind from the extracellular space.[1] However, because acts as a roof to this canonical binding site, it inhibits ligands from entering directly from the extracellular region. Instead, the highly lipophilic nature of hGPRC40’s ligands allow it to enter a between TM3 and TM4 by moving through the lipid bilayer.[1]
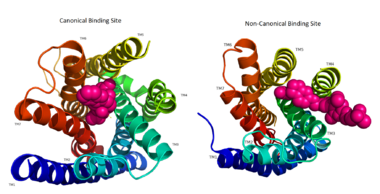
Figure 2: Comparison of the canonical binding site represented in pink of most opioid/peptide binding GPCRs (left) compared to the noncanonical binding site of ligands with hGPR40 (right).
Binding Sites
GPR40’s natural substrate are FFAs in which a free carboxyl group is required to bind. However, GPR40 can be activated by a wide variety of fatty acids with chain lengths ranging from saturated fatty acids with 8 carbons to 23 carbons. In addition, various mono (i.e. palmitoleic (C16:1) and oleic (C18:1) acids) and poly-unsaturated fatty acids (i.e.linoleic (C18:2) and eicosatrienoic (C20:3) acids) can activate GPR40.[2] The agonists potency varies according to the carbon-chain length however. The activity of GPR40 increases when the chain is increased from C6 to C15 but then decreased when the chain was extended beyond C15. One explanation for this is that as alkyl chain increased, so did the hydrophobic interactions with the protein within the binding pocket. However, for FFAs with carbon chains longer than C15, the molecular size is too large for the binding pocket. This causes the alkyl chain to extend beyond the binding pocket and destabilize the binding.[3]
FFAs bind to hGPR40 by coordinating its free carboxyl group to three amino acids, , which are located close to the of hGPR40 on TM5, 6 and 7. Because of the close proximity of these residues to the extracellular domain and the dominantly hydrophobic nature of FFA’s, it is likely that ligand binding occurs close to the plane of the membrane.[2]
Radioligand binding studies identified multiple binding sites in hGPR40.[1] Full agonists and partial agonists were shown to bind in separate sites with positive cooperativity.[6] The has been identified, but other binding sites were hypothesized. TAK-875 binds between transmembrane helices 3, 4, and 5 and underneath ECL2. By visual inspection, a second possible binding site was proposed between transmembrane helices 3, 4, and 5 on the intracellular side of the transmembrane helices. The location of this binding site with respect to the membrane proposes that substrates would gain entry to the membrane by binding in this site. Also by visual inspection, a third possible binding site was proposed between transmembrane helices 1, 2, and 7 on the extracellular side of hGPR40, close to the TAK-875 binding site.[1] These binding sites could potentially serve as regulation points for hGPR40. Many proteins that exhibit cooperativity are regulated by the binding of inhibitors.
Charge Network
hGPR40 has a distinct binding pocket that is established by : , , , , , , , and (all individual residues shown in chartreuse). The importance of these residues for agonist binding was determined by alanine mutagenesis studies. Each of these residues have either a charged or polar R-group that creates a charge network that keeps these residues in a stable, unbound state until exposed to a substrate. When the substrate (an agonist) enters the binding pocket, four of the eight interact directly with the carboxylate moiety of the agonist by hydrogen bonding to it. These residues include two key arginines in the binding pocket, Arg183 and Arg258,[7][8] and two key tyrosine residues, Tyr91 and Tyr240. Tyr240 is especially important for binding, as mutation of Tyr240 caused an eight fold reduction in the binding affinity of TAK-875 and had a significant effect on the binding affinity (KD) of the protein.[1]
ECL2
hGPR40 contains a highly conserved hairpin extracellular loop. This extracellular loop () is the longest and most divergent of the extracellular loops found in proteins (). The loop is accompanied by a disulfide bond () that forms between transmembrane helix 4 and the C-terminus of the ECL2 loop. In hGPR40, ECL2 has two sections: a beta sheet and an auxiliary loop. The beta sheet spans helices 4 and 5 and is shorter in hGPR40 than in other GPCRs. The ECL2 of hGPR40 also differs from that of other proteins because it contains an auxiliary loop of 13 extra residues. The entire extracellular loop has low mobility and flexibility, which allows it to act as a cap for the binding pocket. The only exception to the low flexibility is the tip of the auxiliary loop, which corresponds to residues Asp152-Asn155. This area of greater mobility allows for substrates to enter the binding site.[1]
Function
hGPR40 functions as a free fatty acid receptor that participates in insulin signaling to regulate blood glucose concentrations. The actual mechanisms by which insulin signaling occurs are unknown, but multiple theoretical mechanisms have been posited for how hGPR40 participates in the regulation of glucose uptake.[1]
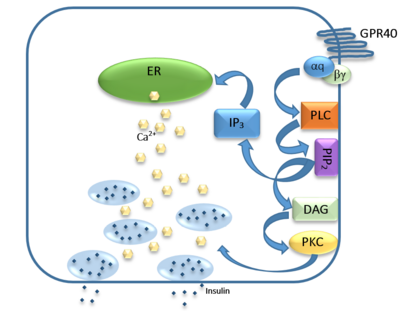
Figure 3: Signaling pathway mediated by GPR40 in pancreatic β-cells. The 𝝰q subunit represents the Gq unit that is coupled to hGPR40. This subunit breaks off to activate phospholipase C (PLC), resulting in the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate (PIP
2). PIP
2 goes on to create diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3). The DAG activates protein kinase c (PKC), triggering secretion of insulin. Activated IP3 diffuses to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), releasing the stored Ca
2+, which aids in insulin secretion.
The natural substrate of hGPR40 is free fatty acids (FFAs) which bind to the G-protein and enhance glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.[2] FFAs bind to GPR40 which then couples with the G-protein Gq leading to increased phospholipase C (PLC) activity.[2] PLC catalyzes the hydrolysis of the phospholipid phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate (PIP2) resulting in the formation of diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3).[2] DAG can then activate protein kinase C (PKC) to enhance insulin secretion.[2] IP3 on the other hand is soluble and diffuses to the endoplasmic reticulum where it binds a ligand-gated Ca2+ channel.[2] This binding triggers the opening of the channel causing stored Ca2+ to be released into the cytoplasm.[2] This large increase in intracellular free Ca2+ produces a proportional increase in glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suggesting that insulin release can be contributed in part to the changes in Ca2+ concentration resulting from activated GPR40.[2]
Clinical Relevance
By signaling predominantly through Gaq/11, hGPR40 increases intracellular calcium and activates phospholipases to generate diacylglycerols resulting in increased insulin secretion. Synthetic small-molecule agonists of hGPR40 enhance insulin secretion in a glucose dependent manner in vitro and in vivo with a mechanism similar to that found with fatty acids. hGPR40 agonists have shown efficacy in increasing insulin secretion and lowering blood glucose in rodent models of type 2 diabetes.[4]
is a partial agonist of GPR40 and tested for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The binding of TAK-875 to hGPR40 occurs by the ligand entering the binding site through the membrane bilayer. This membrane insertion is performed via a method similar to ligand binding to sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1, retinal loading of GPCR opsin, and the entry of anandamide in cannabinoid receptors, in which the block the binding from the extracellular matrix [9]. The binding mechanism through the bilayer may be selectively favoring the free fatty acid because of the non-polar regions of the ligand (Figure 5).
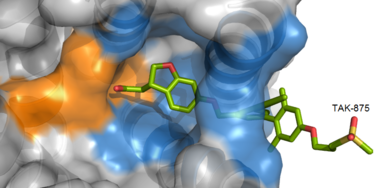
Figure 4: TAK-875 buries its polar head group within a very hydrophobic region and coordinate within the polar charge network of hGPR40.
TAK-875 binds to the created between transmembrane (TM) domains 3-5 and the extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) of hGPR40. The ECL2 and auxiliary loop form a roof causing TAK-875 to enter through TM3 and TM4, first passing through the lipid bilayer. The carboxylate of TAK-875 is buried within a very hydrophobic region and in a complex complex involving Glu172, Ser187, Asn241, and Asn 244 from hGPR40 forming ionic and polar interactions by coordinating TAK-875 with Arg183, Arg258, Tyr91, and Tyr240.
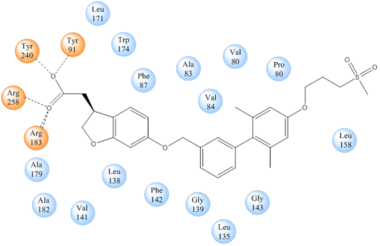
Figure 5: Stabilizing binding interactions between TAK-875 and hGPR40. Amino acids denoted in orange coordinate with the polar head of TAK-875 by polar/ionic interactions while blue amino acids stabilize the binding through hydrophobic interactions.
Other Potential Inhibitors
TAK-875 had the most promising outlooks of any current known agonists of hGPR40, but clinical trials were discontinued. Some other agonists tested in clinical trials include AMG-837 and AM-1638. When coadministered, AMG-837 and AM-1638 enhanced glucose tolerance, but they were found to be toxic in the human trials. Some other agonsits are currently being examined as well. One compound, LY 2881835 (Eli Lilly & Company, Indianapolis, IN), has undergone clinical trials, but the results are unknown. In addition to the above-mentioned compound, other orally bioavailable GPR40-specific agonists are currently in preclinical or clinical development. As of 2015, TUG-770 and CNX-011-67 (Connexios Life Sciences, Karnataka, India) were in preclinical trials and JTT-851 (Japan Tobacco, Toyko, Japan), and P11187 (Piramal, Mumbai, India) were in clinical trails.[10]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 Srivastava A, Yano J, Hirozane Y, Kefala G, Gruswitz F, Snell G, Lane W, Ivetac A, Aertgeerts K, Nguyen J, Jennings A, Okada K. High-resolution structure of the human GPR40 receptor bound to allosteric agonist TAK-875. Nature. 2014 Jul 20. doi: 10.1038/nature13494. PMID:25043059 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13494
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 Morgan NG, Dhayal S. G-protein coupled receptors mediating long chain fatty acid signalling in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 15;78(12):1419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020., Epub 2009 Aug 4. PMID:19660440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ren XM, Cao LY, Zhang J, Qin WP, Yang Y, Wan B, Guo LH. Investigation of the Binding Interaction of Fatty Acids with Human G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Using a Site-Specific Fluorescence Probe by Flow Cytometry. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 17. PMID:26974599 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00079
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Burant CF. Activation of GPR40 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013 Aug;36 Suppl 2:S175-9. doi: 10.2337/dcS13-2037. PMID:23882043 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dcS13-2037
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Ichimura A, Hirasawa A, Hara T, Tsujimoto G. Free fatty acid receptors act as nutrient sensors to regulate energy homeostasis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2009 Sep;89(3-4):82-8. doi:, 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 May 19. PMID:19460454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.05.003
- ↑ Lin DC, Guo Q, Luo J, Zhang J, Nguyen K, Chen M, Tran T, Dransfield PJ, Brown SP, Houze J, Vimolratana M, Jiao XY, Wang Y, Birdsall NJ, Swaminath G. Identification and pharmacological characterization of multiple allosteric binding sites on the free fatty acid 1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;82(5):843-59. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.079640. Epub 2012 Aug , 2. PMID:22859723 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/mol.112.079640
- ↑ Sum CS, Tikhonova IG, Neumann S, Engel S, Raaka BM, Costanzi S, Gershengorn MC. Identification of residues important for agonist recognition and activation in GPR40. J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29248-55. Epub 2007 Aug 15. PMID:17699519 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705077200
- ↑ Sum CS, Tikhonova IG, Costanzi S, Gershengorn MC. Two arginine-glutamate ionic locks near the extracellular surface of FFAR1 gate receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3529-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806987200. Epub 2008, Dec 8. PMID:19068482 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M806987200
- ↑ Hanson MA, Roth CB, Jo E, Griffith MT, Scott FL, Reinhart G, Desale H, Clemons B, Cahalan SM, Schuerer SC, Sanna MG, Han GW, Kuhn P, Rosen H, Stevens RC. Crystal structure of a lipid G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 2012 Feb 17;335(6070):851-5. PMID:22344443 doi:10.1126/science.1215904
- ↑ Mancini AD, Poitout V. GPR40 agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: life after 'TAKing' a hit. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Jul;17(7):622-9. doi: 10.1111/dom.12442. Epub 2015 Feb , 24. PMID:25604916 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dom.12442
Proteopedia Resources
Category:GPR40
Butler University Proteopedia Pages