Regulator of G protein signaling
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
On the other side, Gα subunits participate in a range of interactions with a variety of other proteins. Therefore, they have interfaces that interact selectively with receptors, effector subfamilies and RGS proteins. However, <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4_interface/4'>Gα residues</scene> from Gα<sub>i</sub> subfamily members that interact specifically with RGS proteins are highly conserved (red spheres). These Gα Residues located on Gα switch regions interact with Significant & Conserved RGS residues because of the pivotal role of the switch regions in GTP hydrolysis that is catalyzed by RGS proteins. On the other hand, Gα residues located in switch regions II and III and multiple residues in the Gα all-helical domain interact with Modulatory RGS residues.<ref name="Mickey2011" /> For example, one important conserved RGS4 residue that projects into the active site of Gα<sub>i</sub> is <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4-asn128/2'>Asn-128</scene> shown as blue sticks, which contacts the side chains of three Gα residues: Lys-180, Gln-204, and Glu-207 shown as green, magenta, and red sticks respectively.<ref name="Tesmer97" /> A unique modulatory RGS4 residue that interacts with Gα<sub>i</sub> is <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4_arg166/6'>Arg-166</scene> shown as blue sticks which forms salt bridge with the positively charged side chain of Glu-116 shown as magenta sticks located in the helical domain of Gα subunit. | On the other side, Gα subunits participate in a range of interactions with a variety of other proteins. Therefore, they have interfaces that interact selectively with receptors, effector subfamilies and RGS proteins. However, <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4_interface/4'>Gα residues</scene> from Gα<sub>i</sub> subfamily members that interact specifically with RGS proteins are highly conserved (red spheres). These Gα Residues located on Gα switch regions interact with Significant & Conserved RGS residues because of the pivotal role of the switch regions in GTP hydrolysis that is catalyzed by RGS proteins. On the other hand, Gα residues located in switch regions II and III and multiple residues in the Gα all-helical domain interact with Modulatory RGS residues.<ref name="Mickey2011" /> For example, one important conserved RGS4 residue that projects into the active site of Gα<sub>i</sub> is <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4-asn128/2'>Asn-128</scene> shown as blue sticks, which contacts the side chains of three Gα residues: Lys-180, Gln-204, and Glu-207 shown as green, magenta, and red sticks respectively.<ref name="Tesmer97" /> A unique modulatory RGS4 residue that interacts with Gα<sub>i</sub> is <scene name='70/701447/Gi-rgs4_arg166/6'>Arg-166</scene> shown as blue sticks which forms salt bridge with the positively charged side chain of Glu-116 shown as magenta sticks located in the helical domain of Gα subunit. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | ==3D structures of regulator of G-protein | + | ==3D structures of regulator of G-protein signaling== |
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 1 | |
| - | * Regulator of G-protein | + | |
**[[2bv1]] – hRGS1 – human<br /> | **[[2bv1]] – hRGS1 – human<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4pni]] – bRGS1 – bovine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2gtp]] – hRGS1 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α1 <br /> | ||
| - | * Regulator of G-protein | + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 2 |
| + | |||
| + | **[[2af0]] – hRGS2<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4ekc]], [[4ekd]] – hRGS2 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2v4z]] – hRGS2 (mutant) + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | ||
| + | **[[3v5w]] – hRGS2 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit β1 and γ2 <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 3 | ||
**[[2f5y]] – hRGS3 PDZ domain<br /> | **[[2f5y]] – hRGS3 PDZ domain<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2oj4]] – hRGS3<br /> | ||
| - | * Regulator of G-protein | + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 4 |
| - | **[[1agr]] – | + | **[[1agr]] – rRGS4 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α – rat <br /> |
| + | **[[1ezt]], [[1ezy]] – rRGS4 - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | * Regulator of G-protein | + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 5 |
| + | |||
| + | **[[2crp]] – hRGS5 - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 6 | ||
**[[2es0]] – hRGS6<br /> | **[[2es0]] – hRGS6<br /> | ||
| - | * Regulator of G-protein | + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 7 |
**[[2a72]] – hRGS7<br /> | **[[2a72]] – hRGS7<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[2d9j]] – hRGS7 - NMR<br /> |
| - | * Regulator of G-protein | + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 8 |
| + | **[[2ihd]] – hRGS8<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5do9]] – mRGS8 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α – mouse <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2ode]] – hRGS8 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 9 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1fqi]] – bRGS9<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2pbi]] – mRGS9 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit β5 <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1fqj]] – bRGS9 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α + phosphodiesterase subunit γ <br /> | ||
| + | **[[1fqk]] – bRGS9 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2i59]], [[2dlr]] – hRGS10 - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2ihb]] – hRGS10 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | **[[2ihb]] – hRGS10 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | ||
| - | * Regulator of G-protein | + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 12 |
| + | |||
| + | **[[2ebz]] – hRGS12 - NMR <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 14 | ||
**[[2om2]] – hRGS14 GOLOCO motif + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | **[[2om2]] – hRGS14 GOLOCO motif + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | ||
| + | **[[2jnu]] – hRGS14 - NMR <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 16 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2bt2]] – hRGS16<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3c7k]], [[3c7l]], [[2ik8]] – hRGS16 + guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit α <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 17 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[1zv4]] – hRGS17<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Regulator of G-protein signaling 18 | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2dlv]], [[2owi]], [[2jm5]] – hRGS18 - NMR <br /> | ||
}} | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 06:36, 4 August 2016
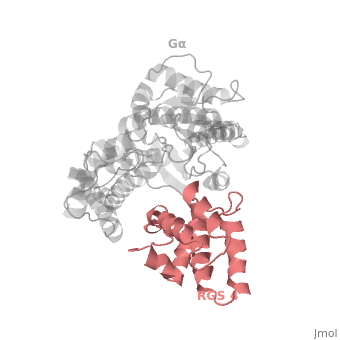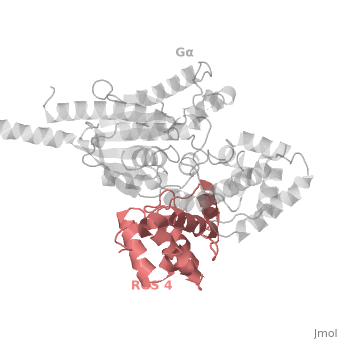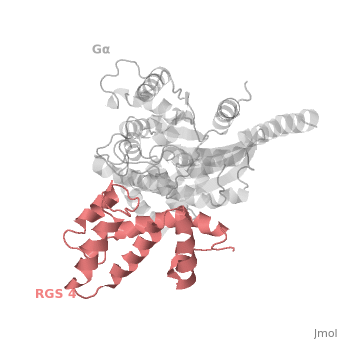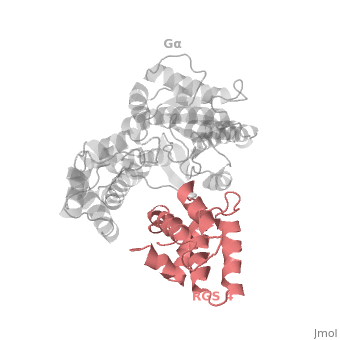
Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) interactions with G proteins – RGS4-Gαi as a model structure.
| |||||||||||
3D structures of regulator of G-protein signaling
Updated on 04-August-2016
References
- ↑ Milligan G, Kostenis E. Heterotrimeric G-proteins: a short history. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147 Suppl 1:S46-55. PMID:16402120 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706405
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Kosloff M, Travis AM, Bosch DE, Siderovski DP, Arshavsky VY. Integrating energy calculations with functional assays to decipher the specificity of G protein-RGS protein interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 19;18(7):846-53. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2068. PMID:21685921 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2068
- ↑ Gibbons DL, Abeler-Dorner L, Raine T, Hwang IY, Jandke A, Wencker M, Deban L, Rudd CE, Irving PM, Kehrl JH, Hayday AC. Cutting Edge: Regulator of G protein signaling-1 selectively regulates gut T cell trafficking and colitic potential. J Immunol. 2011 Sep 1;187(5):2067-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100833. Epub 2011, Jul 27. PMID:21795595 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1100833
- ↑ Tatenhorst L, Senner V, Puttmann S, Paulus W. Regulators of G-protein signaling 3 and 4 (RGS3, RGS4) are associated with glioma cell motility. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2004 Mar;63(3):210-22. PMID:15055445
- ↑ Chen X, Dunham C, Kendler S, Wang X, O'Neill FA, Walsh D, Kendler KS. Regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) gene is associated with schizophrenia in Irish high density families. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2004 Aug 15;129B(1):23-6. PMID:15274033 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.30078
- ↑ Stewart A, Maity B, Wunsch AM, Meng F, Wu Q, Wemmie JA, Fisher RA. Regulator of G-protein signaling 6 (RGS6) promotes anxiety and depression by attenuating serotonin-mediated activation of the 5-HT(1A) receptor-adenylyl cyclase axis. FASEB J. 2014 Apr;28(4):1735-44. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-235648. Epub 2014 Jan 13. PMID:24421401 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-235648
- ↑ Miao R, Lu Y, Xing X, Li Y, Huang Z, Zhong H, Huang Y, Chen AF, Tang X, Li H, Cai J, Yuan H. Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 10 Negatively Regulates Cardiac Remodeling by Blocking Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinase 1/2 Signaling. Hypertension. 2016 Jan;67(1):86-98. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05957. Epub , 2015 Nov 16. PMID:26573707 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05957
- ↑ Willard FS, Willard MD, Kimple AJ, Soundararajan M, Oestreich EA, Li X, Sowa NA, Kimple RJ, Doyle DA, Der CJ, Zylka MJ, Snider WD, Siderovski DP. Regulator of G-protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is a selective H-Ras effector. PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004884. Epub 2009 Mar 25. PMID:19319189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004884
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Tesmer JJ, Berman DM, Gilman AG, Sprang SR. Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF4--activated G(i alpha1): stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell. 1997 Apr 18;89(2):251-61. PMID:9108480
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Ali Asli, Denise Salem, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky