This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Ribozyme
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m (add more types) |
m |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*[[:Category:Ribozyme|Ribozyme]] | *[[:Category:Ribozyme|Ribozyme]] | ||
*[[:Category:Catalytic rna|Catalytic RNA]] | *[[:Category:Catalytic rna|Catalytic RNA]] | ||
| - | *[[:Category:glmS| | + | *[[:Category:glmS|GlmS]] |
*[[:Category:Hammerhead|Hammerhead]] | *[[:Category:Hammerhead|Hammerhead]] | ||
*[[:Category:Hairpin|Hairpin]] | *[[:Category:Hairpin|Hairpin]] | ||
Revision as of 17:10, 22 August 2016
|
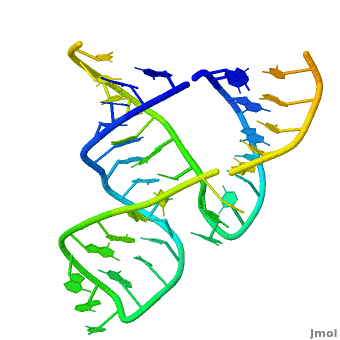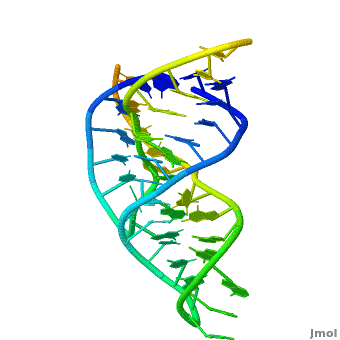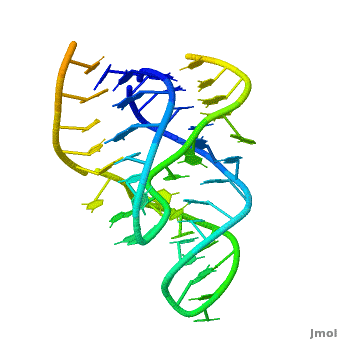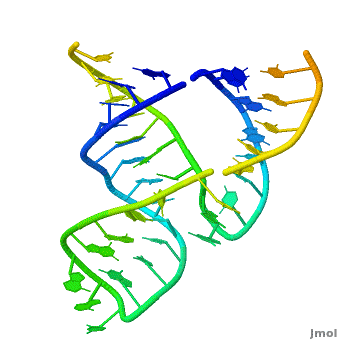
Ribozyme (RZ) is an RNA molecule which catalyzes a chemical reaction[1].
- Glucosamine-6-phosphate activated RZ (glmS RZ) is a RZ and a riboswitch which regulates genes in response to metabolites.
- Leadzyme is a small, artificially-made RZ which can cleave RNA in the presence of lead. For more details on leadzyme see Student Projects for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2012-10.
- Hairpin RZ and hammerhead RZ are named based on their shape[2].
- Group I intron catalyzes its own selfish splicing[3].
Articles in Proteopedia concerning ribozymes include:
- Azoarcus group I intron
- Kink-turn motif
- Ribosome
- The Large Ribosomal Subunit
- Hairpin Ribozyme
- Human CPEB3 ribozyme's P4 domain
To view automatically seeded indices concerning ribozymes, see:
- Ribozyme
- Catalytic RNA
- GlmS
- Hammerhead
- Hairpin
- Hepatitis delta virus
- Twister
- Twister sister
- Hatchet
- Pistol
- Group I intron
- Varkud satellite
3D Structures of Ribozymes
Updated on 22-August-2016
References
- ↑ Tang J, Breaker RR. Rational design of allosteric ribozymes. Chem Biol. 1997 Jun;4(6):453-9. PMID:9224568
- ↑ Amarzguioui M, Prydz H. Hammerhead ribozyme design and application. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998 Nov;54(11):1175-202. PMID:9849614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s000180050247
- ↑ Cech TR. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543-68. PMID:2197983 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Wayne Decatur, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky