T-box proteins
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
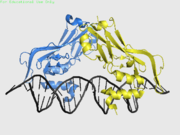
| - | + | <StructureSection load='4a04' size='400' side='right' scene='' caption='Human TBX1 complex with DNA, [[4a04]]> | |
[[Image:TBX3.png|thumb|right|alt=TBX3 dimer on DNA|TBX3, a T-box protein, binds to palindromic DNA as a dimer.]] | [[Image:TBX3.png|thumb|right|alt=TBX3 dimer on DNA|TBX3, a T-box protein, binds to palindromic DNA as a dimer.]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
T-box proteins are expressed in specific organs or in only particular cell types, and are involved in decisions about early cell fate. Mutant alleles typically show haploinsufficiency (T-box proteins tend to be dosage-specific). When mutations occur, developmental disorders arise such as the ulnar-mammary syndrome caused by mutations in TBX3, and some aspects of DiGeorge syndrome implicated by mutations in TBX1. | T-box proteins are expressed in specific organs or in only particular cell types, and are involved in decisions about early cell fate. Mutant alleles typically show haploinsufficiency (T-box proteins tend to be dosage-specific). When mutations occur, developmental disorders arise such as the ulnar-mammary syndrome caused by mutations in TBX3, and some aspects of DiGeorge syndrome implicated by mutations in TBX1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
Genes involved in limb bud formation and development are a subset of T-box proteins: [[T]], TBX2, [[TBX3]], [[TBX5]], [[TBX15]] and TBX18. | Genes involved in limb bud formation and development are a subset of T-box proteins: [[T]], TBX2, [[TBX3]], [[TBX5]], [[TBX15]] and TBX18. | ||
Revision as of 13:17, 21 June 2017
| |||||||||||
Genes involved in limb bud formation and development are a subset of T-box proteins: T, TBX2, TBX3, TBX5, TBX15 and TBX18.
Contents |
T-box family members in Homo sapiens
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| T | Crystal structure solved | |
| TBX19 |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX1 | Crystal structure solved (4a04) | DiGeorge syndrome |
| TBX10 | ||
| TBX15 | Cousin syndrome | |
| TBX18 | ||
| TBX20 | ||
| TBX22 | Truncated T-box domain predicted not to bind DNA | Cleft palate with ankyloglossia |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX2 | Mutation of Arg122 destroys DNA binding. Acts as a repressor. TRP-1 promoter is a possible binding site. | Amplified in certain types of breast cancer. |
| TBX3 | Crystal structure solved | Ulnar-mammary syndrome |
| TBX4 | Small patella syndrome | |
| TBX5 | Crystal structure solved | Holt-Oram syndrome |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX6 | ||
| MGA | Also contains leucine zipper domain |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBR1 | ||
| EOMES | ||
| TBX21 |
3D structures of T-box protein
4a04 – hTBX1 T-box domain + DNA - human
1h6f - hTBX3 T-box domain + DNA
2x6u, 5bqd – hTBX5 T-box domain
2x6v – hTBX5 T-box domain + DNA
4s0h, 5flv - hTBX5 T-box domain + homebox protein + DNA
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Transcription and RNA Processing
References
- Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 1997, 7:474-480;
- Gene 258 (2000) 15–29;
- American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 140A:1407–1413 (2006);
- Genome Biology 2002, 3(6):reviews3008.1–3008.7;
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Helen Ginn, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman