Palmitoyl protein thioesterase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(adding BAMBED ref) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
===Hydrophobic Groove === | ===Hydrophobic Groove === | ||
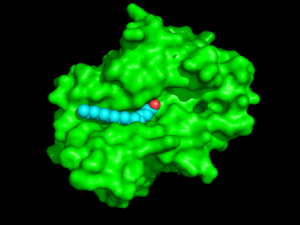
| - | The <scene name='57/573128/3/1'>hydrophobic binding groove</scene> is located in the second domain of PPT1, where palmitate mainly binds. The fact that palmitate has to <scene name='57/573128/6/1'>bend</scene> to fit into the binding pocket suggests that this pocket is designed to bind an unsaturated fatty acid, with a possible cis-double bond between C4 and C5 (Figure 1)<ref name="RSCB"/>. The top portion of the groove is formed by the residues from α2 to α3. The acid binds in a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gauche_effect gauche conformation] creating a <scene name='58/580839/Kink_in_acid/1'>kink </scene> in the acid chain. This bending suggests that PPT-1 was originally designed to react with an unsaturated fatty acid with cis-double bonds. Several residues that are present near the active site create the rest of the groove, including <scene name='57/573128/10/1'>Ile235, Val236, Gln116, Gly40, and Met41</scene><ref name="RSCB"/>. | + | The <scene name='57/573128/3/1'>hydrophobic binding groove</scene> is located in the second domain of PPT1, where palmitate mainly binds. (Shown in <scene name='48/489312/Binding_groove/1'>the orientation</scene> as the static figure on the left). The fact that palmitate has to <scene name='57/573128/6/1'>bend</scene> to fit into the binding pocket suggests that this pocket is designed to bind an unsaturated fatty acid, with a possible cis-double bond between C4 and C5 (Figure 1)<ref name="RSCB"/>. The top portion of the groove is formed by the residues from α2 to α3. The acid binds in a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gauche_effect gauche conformation] creating a <scene name='58/580839/Kink_in_acid/1'>kink </scene> in the acid chain. This bending suggests that PPT-1 was originally designed to react with an unsaturated fatty acid with cis-double bonds. Several residues that are present near the active site create the rest of the groove, including <scene name='57/573128/10/1'>Ile235, Val236, Gln116, Gly40, and Met41</scene><ref name="RSCB"/>. |
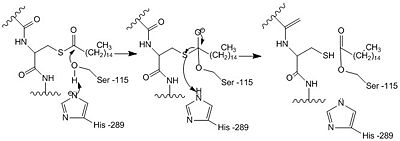
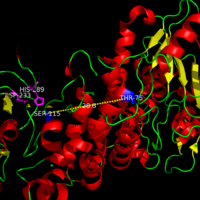
==Catalytic Triad== | ==Catalytic Triad== | ||
Revision as of 03:54, 28 December 2018
This page, as it appeared on May 3, 2014, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wang R, Borazjani A, Matthews AT, Mangum LC, Edelmann MJ, Ross MK. Identification of palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 in human THP1 monocytes and macrophages and characterization of unique biochemical activities for this enzyme. Biochemistry. 2013 Oct 29;52(43):7559-74. doi: 10.1021/bi401138s. Epub 2013 Oct, 18. PMID:24083319 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi401138s
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Bellizzi JJ 3rd, Widom J, Kemp C, Lu JY, Das AK, Hofmann SL, Clardy J. The crystal structure of palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 and the molecular basis of infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 25;97(9):4573-8. PMID:10781062 doi:10.1073/pnas.080508097
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Simonati A, Tessa A, Bernardina BD, Biancheri R, Veneselli E, Tozzi G, Bonsignore M, Grosso S, Piemonte F, Santorelli FM. Variant late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis because of CLN1 mutations. Pediatr Neurol. 2009 Apr;40(4):271-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2008.10.018. PMID:19302939 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2008.10.018
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Bellizzi JJ 3rd, Widom J, Kemp C, Lu JY, Das AK, Hofmann SL, Clardy J. The crystal structure of palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 and the molecular basis of infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 25;97(9):4573-8. PMID:10781062 doi:10.1073/pnas.080508097
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Branneby, Cecilia. "Exploiting Enzyme Promiscuity for Rational Design." KTH Biotechnology (2005): Web. 10 Apr. 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Hofmann SL, Das AK, Yi W, Lu JY, Wisniewski KE. Genotype-phenotype correlations in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis due to palmitoyl-protein thioesterase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab. 1999 Apr;66(4):234-9. PMID:10191107 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/mgme.1999.2803
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Dawson G, Schroeder C, Dawson PE. Palmitoyl:protein thioesterase (PPT1) inhibitors can act as pharmacological chaperones in infantile Batten disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Apr 23;395(1):66-9. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.137. Epub 2010 Mar 25. PMID:20346914 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.137
- ↑ Vines DJ, Warburton MJ. Classical late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis fibroblasts are deficient in lysosomal tripeptidyl peptidase I. FEBS Lett. 1999 Jan 25;443(2):131-5. PMID:9989590
- ↑ Mitchison HM, Taschner PE, Kremmidiotis G, Callen DF, Doggett NA, Lerner TJ, Janes RB, Wallace BA, Munroe PB, O'Rawe AM, Gardiner RM, Mole SE. Structure of the CLN3 gene and predicted structure, location and function of CLN3 protein. Neuropediatrics. 1997 Feb;28(1):12-4. PMID:9151311 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-973656
Similar Proteopedia Pages
Category:Palmitoyl_protein_thioesterase
External Resources
Gauche Effect Wikipedia page
Palmitic acid Wikipedia page
Infantile Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis Wikipedia page
PMSF Wikipedia page
Protein Chaperones Wikipedia page
Endoplasmic reticulum Wikipedia page
Palmitoylation Wikipedia page
Page on Late Infantile neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis
Page on Juvenile neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis
Student Contributors
Andrew Bartels
Nicole Green
Kelly Maddalone
Ryan Mughmaw
Audrey Wright
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
R. Jeremy Johnson, Karsten Theis, Alexander Berchansky, Angel Herraez, Michal Harel