We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ribavirin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| - | Ribavirin, when administered in combination with pegylated interferon alpha, induces an antiviral state in host cells, resulting in reduced virus replication rates and activation of the host immune system. It is thought that Ribavirin acts as an antiviral agent by disrupting viral RNA synthesis, which would impact both transcription and genome replication in the Hepatitis C virus. However, the exact mechanism by which the drug interferes with this process is unknown. Several theories have been proposed to explain the effect of Ribavirin in inhibiting the replication of the Hepatitis C virus <ref name="paesh"/>. | + | Ribavirin, when administered in combination with pegylated interferon alpha, induces an antiviral state in host cells, resulting in reduced virus replication rates and activation of the host immune system. It is thought that Ribavirin acts as an antiviral agent by disrupting viral RNA synthesis, which would impact both transcription and genome replication in the Hepatitis C virus. However, the exact mechanism by which the drug interferes with this process is unknown. jgjhjh Several theories have been proposed to explain the effect of Ribavirin in inhibiting the replication of the Hepatitis C virus <ref name="paesh"/>. |
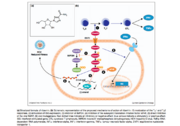
Immunomodulation by Ribavirin may be responsible for the drug’s antiviral properties. It has been suggested that the natural CD4+ helper T cell response may be altered in the presence of Ribavirin. It is thought that ribavirin may enhance the T helper 1 response, resulting in greater clearance of virus <ref>doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01896.x</ref>. However, there is conflicting evidence suggesting that the T helper 2 response may be implicated in this process instead <ref>doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05320.x</ref>. Another possible mechanism involves the enhancement of interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression by Ribavirin. When a cell becomes infected with a virus, it may release interferons. Interferons are signaling molecules that function in a paracrine fashion to induce an antiviral state in neighboring cells, protecting them from infection. Ribavirin is thought to enhance the interferon signaling pathway <ref>doi: 10.1002/hep.21853</ref>, resulting in a wider antiviral response. This theory has been supported in studies using cell culture models <ref>doi: 10.1002/hep.23985</ref>. It has also been suggested that the relationship between Ribavirin and inosine 5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) may impact the virus RNA synthesis. IMPDH plays a significant role in the guanine nucleotide synthesis pathway. It results in the conversion of inosine 5’-monophosphate to xanthine 5’-monophosphate, which is an intermediate for the nucleotide guanosine <ref>doi: 10.1002/chin.200823265</ref>. Therefore, modulation of IMPDH activity affects a cell’s reservoir of guanosine. Ribavirin has been shown to function as a competitive inhibitor for IMPDH <ref>PMID: 4197928</ref>. Because guanosine triphosphate (GTP) plays a critical role in the viral genome replication process, inhibition of IMPDH would result in the prevention of viral replication. | Immunomodulation by Ribavirin may be responsible for the drug’s antiviral properties. It has been suggested that the natural CD4+ helper T cell response may be altered in the presence of Ribavirin. It is thought that ribavirin may enhance the T helper 1 response, resulting in greater clearance of virus <ref>doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01896.x</ref>. However, there is conflicting evidence suggesting that the T helper 2 response may be implicated in this process instead <ref>doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05320.x</ref>. Another possible mechanism involves the enhancement of interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression by Ribavirin. When a cell becomes infected with a virus, it may release interferons. Interferons are signaling molecules that function in a paracrine fashion to induce an antiviral state in neighboring cells, protecting them from infection. Ribavirin is thought to enhance the interferon signaling pathway <ref>doi: 10.1002/hep.21853</ref>, resulting in a wider antiviral response. This theory has been supported in studies using cell culture models <ref>doi: 10.1002/hep.23985</ref>. It has also been suggested that the relationship between Ribavirin and inosine 5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) may impact the virus RNA synthesis. IMPDH plays a significant role in the guanine nucleotide synthesis pathway. It results in the conversion of inosine 5’-monophosphate to xanthine 5’-monophosphate, which is an intermediate for the nucleotide guanosine <ref>doi: 10.1002/chin.200823265</ref>. Therefore, modulation of IMPDH activity affects a cell’s reservoir of guanosine. Ribavirin has been shown to function as a competitive inhibitor for IMPDH <ref>PMID: 4197928</ref>. Because guanosine triphosphate (GTP) plays a critical role in the viral genome replication process, inhibition of IMPDH would result in the prevention of viral replication. | ||
Revision as of 17:41, 16 November 2016
1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- Gish, R. G. Treating HCV with ribavirin analogue and ribavirin-like molecules. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2005, November 17;1-6. doi:10.1093/jac/dki405
- Chung, R.T., Gale, M.J., Polyak, S.J., Lemon, S.M., Liang, T.J., & Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanisms of action of interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008;47 (1), 306-320. doi: 10.1002/hep.22070
- Paeshuyse, J, Dallmeier, K, Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of the proposed mechanisms of action. Current Opinion in Virology. 2011;1(6) 590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Pneumonia. 2016, September 26; Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu
- Foster, G. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Drugs. 2010;70(2):147-165. doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000
- Hofmann WP, Herrmann E, Sarrazin C, Zeuzem S. Ribavirin mode of action in chronic hepatitis C: from clinical use back to molecular mechanisms. Liver Int. 2008, 28:1332-1343. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01896.x
- Fujimoto T, Tomimatsu M, Iga D, Endo H, Otsuka K. Changes in the Th1/Th2 ratio during a 24-week course of an interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin combination therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23:E432- E437. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05320.x
- Feld, JJ, Nanda, S, Huang, Y, Chen, W, Cam, M, Pusek, SN, Schwigler, LM, Theodore, D, Zacks, SL, Liang, TJ, Fried, MW. Hepatic gene expression during treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin: Identifying molecule pathways for treatment response. Hepatol. 2007, 46(5): 1548-1563. doi: 10.1002/hep.21853
- Thomas E, Feld JJ, Li QS, Hu ZY, Fried MW, Liang TJ. Ribavirin potentiates interferon action by augmenting interferon stimulated gene induction in hepatitis C virus cell culture models. Hepatology 2011, 53:32-41. doi: 10.1002/hep.23985
- Shu QN, Nair V. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) as a target in drug discovery. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28:219-232. doi: 10.1002/chin.200823265
- Streeter, DG, Witkowski, JT, Khare, GP, Sidwell, RW, Bauer, RJ, Robins, RK, Simon, LN. Mechanisms of action of 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole) a new broad spectrum antiviral agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1973, 70:1174-1178. PMID: 4197928
- Kentsis, A, Topisirovic, I, Culjkovic, B, Shao, L, Borden, KLB. Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the guanosine mRNA cap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101:18105-18110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406927102
- Graci, JD, Cameron, CE. Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16: 37-48. doi: 10.1002/rmv.483
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Jamie Costa, Edmond R Atalla, Katherine Reynolds, Taylor H. Derby, Shannon Shaughnessy, Alexander Berchansky