We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Carbidopa
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
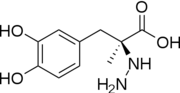
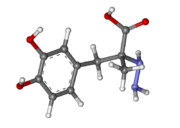
| - | [[Image:512px-Carbidopa.svg.png|thumb|right|2D Structure of Carbidopa]][[Image:800px-Carbidopa ball-and-stick.png|thumb|right|Ball and Stick Model of Carbidopa]]Carbidopa is an inhibitor of DDC. It is a partially water soluble, white, crystalline compound with a molecular weight of 226.232g/mol and a melting point of 208°C. Its empirical formula is C10H14N2O4•H2O and its IUPAC name is (2S)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydrazinyl-2-methylpropanoic acid. Used in conjunction with Levadopa (L-DOPA), a precursor to dopamine, it increases concentrations of L-DOPA in the brain. Due to the fact Carbidopa cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, it inhibits only peripheral DDC thus preventing the conversion of L-DOPA to dopamine outside of neuronal cells. This greatly lessens the side effects caused by dopamine on the periphery, as well as increasing the concentration of L-DOPA and subsequently dopamine in the brain.<ref name="two">https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/carbidopa | + | [[Image:512px-Carbidopa.svg.png|thumb|right|2D Structure of Carbidopa]][[Image:800px-Carbidopa ball-and-stick.png|thumb|right|Ball and Stick Model of Carbidopa]]Carbidopa is an inhibitor of DDC. It is a partially water soluble, white, crystalline compound with a molecular weight of 226.232g/mol and a melting point of 208°C. Its empirical formula is C10H14N2O4•H2O and its IUPAC name is (2S)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydrazinyl-2-methylpropanoic acid. Used in conjunction with Levadopa (L-DOPA), a precursor to dopamine, it increases concentrations of L-DOPA in the brain. Due to the fact Carbidopa cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, it inhibits only peripheral DDC thus preventing the conversion of L-DOPA to dopamine outside of neuronal cells. This greatly lessens the side effects caused by dopamine on the periphery, as well as increasing the concentration of L-DOPA and subsequently dopamine in the brain.<ref name="two">https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/carbidopa</ref> |
== Molecular Mechanism == | == Molecular Mechanism == | ||
Revision as of 20:37, 16 November 2016
Carbidoba ((2S)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydrazinyl-2-methylpropanoic acid)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Gilbert JA, Frederick LM, Ames MM. The aromatic-L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor carbidopa is selectively cytotoxic to human pulmonary carcinoid and small cell lung carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Nov;6(11):4365-72. PMID:11106255
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/carbidopa
- ↑ Opacka-Juffry J, Brooks DJ. L-dihydroxyphenylalanine and its decarboxylase: new ideas on their neuroregulatory roles. Mov Disord. 1995 May;10(3):241-9. PMID:7651438 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mds.870100302
- ↑ Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
- ↑ Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963
- ↑ Ishii S, Mizuguchi H, Nishino J, Hayashi H, Kagamiyama H. Functionally important residues of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase probed by sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 1996 Aug;120(2):369-76. PMID:8889823
- ↑ Feany MB, Bender WW. A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 2000 Mar 23;404(6776):394-8. PMID:10746727 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35006074
- ↑ http://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/treatment/Medications-for-Motor-Symptoms/Carbidopa-levodopa
- ↑ http://www.merck.com/product/home.html
- ↑ Lopez VM, Decatur CL, Stamer WD, Lynch RM, McKay BS. L-DOPA is an endogenous ligand for OA1. PLoS Biol. 2008 Sep 30;6(9):e236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060236. PMID:18828673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060236