We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Carbidopa
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Interactions== | ==Interactions== | ||
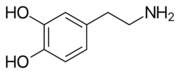
[[Image:Levodopa.png|thumb|left|2D Structure of Levodopa]][[Image:Dopamine.svg.png|thumb|left|2D Structure of Dopamine]] | [[Image:Levodopa.png|thumb|left|2D Structure of Levodopa]][[Image:Dopamine.svg.png|thumb|left|2D Structure of Dopamine]] | ||
| - | Carbidopa only interactions | + | Carbidopa only has interactions with Levodopa (L-DOPA) and dopamine, but there are more interactions between Levodopa and dopamine. Dopamine is essential when it comes to motor, cognitive, behavioral, endocrine functions, and even neuronal retinal development in the central nervous system.<ref name="seven">PMID:18828673</ref><ref name="eight">PMID:22131937</ref> Therefore,understanding the interactions between how Levodopa and dopamine affect the body can help understand why it pairs well with Carbidopa. Carbidopa works by inhibiting the enzyme activity of DDC, when both are working in the body it blocks the Levodopa negative side effects so the lipid soluble drug pair can now pass the blood-brain barrier where Carbidopa cannot. Carbidopa only interaction is to reduce side effects of Levodopa because once Levodopa crosses the blood brain barrier it can help increase levels of dopamine to improve motor, cognitive, behavioral, endocrine functions, etc. Another likely interaction between dopamine and Carbidopa is the human peripheral blood lymphocytes. These blood lymphocytes supposedly synthesize dopamine through the tyrosine-hydroxylase/DOPA-decarboxylase pathway, and express dopamine receptors and dopamine transport on their plasma membrane.<ref name="eight">PMID:22131937</ref> Reports show changes in expression of this dopamine receptors and dopamine transport system in the peripheral blood lymphocytes, but since the Carbidopa can’t pass the blood brain barrier it needs to be paired to a lipid soluble chemical (Levodopa) until a different method is found. |
== Disease in Humans == | == Disease in Humans == | ||
| - | Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive neurological disease whose symptoms include bradykinesia, tremors, postural instability and rigidity. Although the exact cause of the disease is currently unknown, it is | + | Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive neurological disease whose symptoms include bradykinesia, tremors, postural instability and rigidity. Although the exact cause of the disease is currently unknown, it is believed to be caused by the apoptosis of dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra of the brain and subsequent loss of dopamine.<ref name="nine">PMID:10746727</ref> Carbidopa is mostly related to people with Parkinson’s disease. According to the National Parkinson Foundation, Levodopa alone is known to cause nausea and vomiting in Parkinson’s patients, and Carbidopa prevents those side effects.<ref name="ten">http://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/treatment/Medications-for-Motor-Symptoms/Carbidopa-levodopa</ref> Carbidopa can act as an enhancer for Levodopa by decreasing the dosage of Levodopa needed for Parkinson’s patients, up to 80%. It’s a inhibitor that is limited to extracerebral tissue, therefore Carbidopa with Levodopa leaves more Levodopa available for transport to the brain.<ref name="eleven">PMID:10939456</ref> Modern treatments like this are used for Parkinson’s disease today. A combined tablet of Carbidopa and Levodopa (Sinemet)are offered as immediate-release tablets and slow-release tablets, along with dissolvable tablets.<ref name="twelve">http://www.merck.com/product/home.html</ref> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 03:16, 17 November 2016
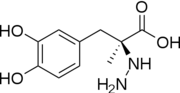
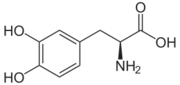
Carbidoba ((2S)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydrazinyl-2-methylpropanoic acid)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Gilbert JA, Frederick LM, Ames MM. The aromatic-L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor carbidopa is selectively cytotoxic to human pulmonary carcinoid and small cell lung carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Nov;6(11):4365-72. PMID:11106255
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/carbidopa
- ↑ Opacka-Juffry J, Brooks DJ. L-dihydroxyphenylalanine and its decarboxylase: new ideas on their neuroregulatory roles. Mov Disord. 1995 May;10(3):241-9. PMID:7651438 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mds.870100302
- ↑ Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
- ↑ Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963
- ↑ Ishii S, Mizuguchi H, Nishino J, Hayashi H, Kagamiyama H. Functionally important residues of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase probed by sequence alignment and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biochem. 1996 Aug;120(2):369-76. PMID:8889823
- ↑ Lopez VM, Decatur CL, Stamer WD, Lynch RM, McKay BS. L-DOPA is an endogenous ligand for OA1. PLoS Biol. 2008 Sep 30;6(9):e236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060236. PMID:18828673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060236
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Buttarelli FR, Fanciulli A, Pellicano C, Pontieri FE. The dopaminergic system in peripheral blood lymphocytes: from physiology to pharmacology and potential applications to neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011 Jun;9(2):278-88. doi: 10.2174/157015911795596612. PMID:22131937 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/157015911795596612
- ↑ Feany MB, Bender WW. A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 2000 Mar 23;404(6776):394-8. PMID:10746727 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35006074
- ↑ http://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/treatment/Medications-for-Motor-Symptoms/Carbidopa-levodopa
- ↑ Fanali S, Pucci V, Sabbioni C, Raggi MA. Quality control of benserazide-levodopa and carbidopa-levodopa tablets by capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2000 Jul;21(12):2432-7. PMID:10939456 doi:<2432::AID-ELPS2432>3.0.CO;2-E http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1522-2683(20000701)21:12<2432::AID-ELPS2432>3.0.CO;2-E
- ↑ http://www.merck.com/product/home.html