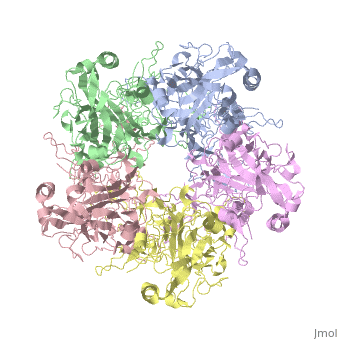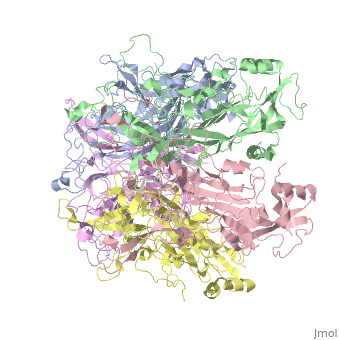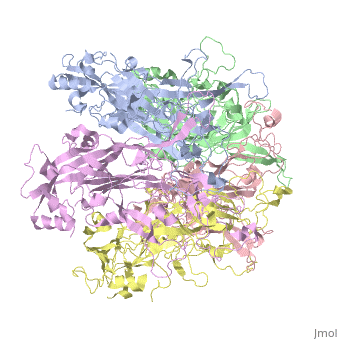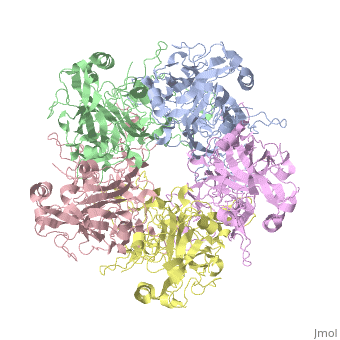Major capsid protein L1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Structural Highlights== | == Structural Highlights== | ||
| - | The main ingredient in Gardasil 9 is L1 Major Capsid Protein<ref name="L1"/>. L1 Major Capsid Protein has 72 pentamers of major capsid proteins that are linked together by <scene name='74/746002/L1_disulfide_bonds_final/1'>disulfide bonds</scene>, indicated | + | The main ingredient in Gardasil 9 is L1 Major Capsid Protein<ref name="L1"/>. L1 Major Capsid Protein has 72 pentamers of major capsid proteins that are linked together by <scene name='74/746002/L1_disulfide_bonds_final/1'>disulfide bonds</scene>, indicated in red on the monomer, that creates an icosahedral capsid with a T=7 symmetry, which is a spherical protein <ref>PMID:12663788</ref>. The disulfide bonds are formed to increase the stability of the pentamers. The disulfide bonds in HPV16 is between <scene name='74/746002/L1_cys_175new/1'>Cys175</scene> and Cys428, which cannot be modeled due to being located in a disordered region<ref>PMID:23800545</ref>. L1 Major Capsid Protein is associated with L2 Minor Capsid Protein. The L1 Major Capsid Protein is built of mainly <scene name='74/746002/L1_beta_sheets/1'>Beta sheets</scene> <ref> http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03101 </ref> shown in orange. Other inactive ingredients in Gardasil 9 are amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate, yeast protein, sodium chloride, L-histidine, polysorbate 80, sodium borate, and water <ref>https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/g/gardasil/gardasil_ppi.pdf</ref>. Amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate is used to increase the antibody response in the body by increasing the ability of the antigen to have a response to the virus <ref>PMID:17581283</ref>. Yeast is used to express the specific protein from each HPV virus type in order to create numerous copies of those proteins <ref>http://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/QuestionsaboutVaccines/ucm096052.htm</ref>. L-histidine is an enzymes used to create histamines that creates an immuno-response against a pathogen <ref>http://www.news-medical.net/health/Histamine-Storage-and-Release.aspx</ref>. Polysorbate 80 is used is vaccines in order to create an even blend of all the ingredients in the vaccine <ref>www.westonaprice.org/health-topics/vaccination/adjuvants-in-vaccines/</ref>. Sodium borate and water are used as a buffer and a solvent, respectively, for the other ingredients ingredients in Gardasil <ref>http://www.immune.org.nz/sites/default/files/resources/ConcernVaccineIngredients20140522V01Final.pdf</ref>. |
== Relevance to Human Health and Disease == | == Relevance to Human Health and Disease == | ||
Revision as of 23:36, 5 December 2016
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zhai L, Tumban E. Gardasil-9: A global survey of projected efficacy. Antiviral Res. 2016 Jun;130:101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.03.016. Epub, 2016 Apr 1. PMID:27040313 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.03.016
- ↑ https://www.gardasil9.com
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 http://www.hpvvaccine.org.au/the-hpv-vaccine/how-does-it-work.aspx
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/19016
- ↑ Harper DM, Vierthaler SL, Santee JA. Review of Gardasil. J Vaccines Vaccin. 2010 Nov 23;1(107). pii: 1000107. PMID:23805398 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2157-7560.1000107
- ↑ http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000703/WC500021140.pdf
- ↑ Finnen RL, Erickson KD, Chen XS, Garcea RL. Interactions between papillomavirus L1 and L2 capsid proteins. J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(8):4818-26. PMID:12663788
- ↑ Buck CB, Day PM, Trus BL. The papillomavirus major capsid protein L1. Virology. 2013 Oct;445(1-2):169-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.038. Epub 2013, Jun 22. PMID:23800545 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.038
- ↑ http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03101
- ↑ https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/g/gardasil/gardasil_ppi.pdf
- ↑ Caulfield MJ, Shi L, Wang S, Wang B, Tobery TW, Mach H, Ahl PL, Cannon JL, Cook JC, Heinrichs JH, Sitrin RD. Effect of alternative aluminum adjuvants on the absorption and immunogenicity of HPV16 L1 VLPs in mice. Hum Vaccin. 2007 Jul-Aug;3(4):139-45. Epub 2007 Apr 5. PMID:17581283
- ↑ http://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/QuestionsaboutVaccines/ucm096052.htm
- ↑ http://www.news-medical.net/health/Histamine-Storage-and-Release.aspx
- ↑ www.westonaprice.org/health-topics/vaccination/adjuvants-in-vaccines/
- ↑ http://www.immune.org.nz/sites/default/files/resources/ConcernVaccineIngredients20140522V01Final.pdf
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Murray, Patrick R., Ken S. Rosenthal, and Michael A. Pfaller. "Papillomavirus and Polyomavirus." Medical Microbiology. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders, 2013. 445-450.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Morgan Smith, Michal Harel, Jessica Troutman., Maximillia Jackson., Jaime Prilusky