Sandbox 45673
From Proteopedia
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
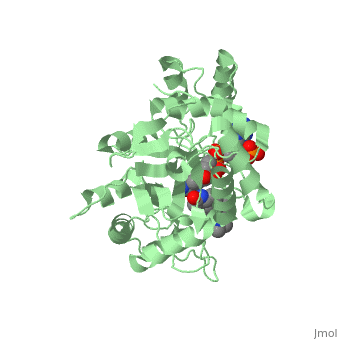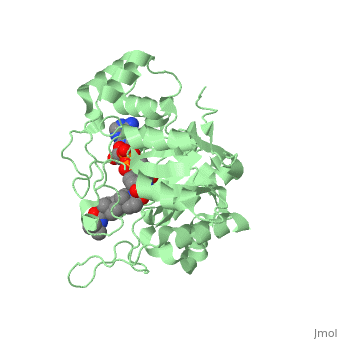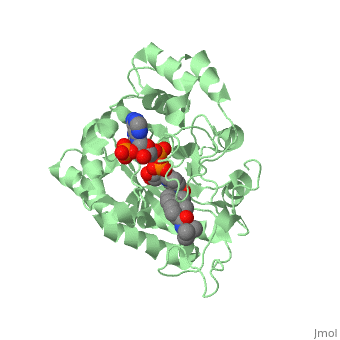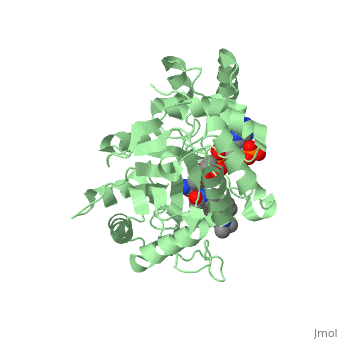
| - | Finasteride is a synthetic 4-azasteroid compound that acts as a 5α-reductase inhibitor <ref name="one"> I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 121, 246. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1 </ref>. The 5α-reductase enzyme is very important in the metabolism of many of the steroids produced by the body, in particular the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT)<ref name="one"> I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 121, 246. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1 </ref>. For this reason, Finasteride is used as a treatment for benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), which is caused by an overproduction of DHT in the male prostate < ref name="two"> Yamana K, Labrie F, Luu-The V (January 2010). | + | Finasteride is a synthetic 4-azasteroid compound that acts as a 5α-reductase inhibitor <ref name="one"> I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 121, 246. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1 </ref>. The 5α-reductase enzyme is very important in the metabolism of many of the steroids produced by the body, in particular the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT)<ref name="one"> I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 121, 246. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1 </ref>. For this reason, Finasteride is used as a treatment for benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), which is caused by an overproduction of DHT in the male prostate <ref name="two"> Yamana K, Labrie F, Luu-The V (January 2010). Human type 3 5α-reductase is expressed in peripheral tissues at higher levels than types 1 and 2 and its activity is potently inhibited by finasteride and dutasteride. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation. 2 (3). doi:10.1515/hmbci.2010.035 </ref>. Pattern hair loss, another condition in men, caused by the build up of DHT, can also be treated with Finasteride. To see what Finasteride looks like unbound, click this link: <scene name='74/745970/Finasteride_unbound/1'>FIT</scene>. |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Revision as of 22:51, 5 December 2016
N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-oxo-(5α,17β)-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 121, 246. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1
- ↑ Yamana K, Labrie F, Luu-The V (January 2010). Human type 3 5α-reductase is expressed in peripheral tissues at higher levels than types 1 and 2 and its activity is potently inhibited by finasteride and dutasteride. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation. 2 (3). doi:10.1515/hmbci.2010.035
Allen, Helen. (2015, March). "Finasteride for prostate gland enlargement. Information. Patient.
Bull, Herbert G.*Garcia-Calvo,Margarita Andersson,Stefan†, Baginsky, Walter F.,Chan,H. Karen,Ellsworth,‡ Dina E., Miller,§ Randall R., Stearns,Ralph A.,Bakshi,Raman K.,Rasmusson, Gary H.,Tolman,Richard L., Myers,Robert W.,Kozarich,John W.,Harris,Georgianna S. (1995, August 6) Mechanism-Based Inhibition of Human Steroid 5R-Reductase by Finasteride: Enzyme-Catalyzed Formation of NADP-Dihydrofinasteride, a Potent Bisubstrate Analog Inhibitor. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja953069t
Leyden, J., Dunlap, F., & Miller, B., et el. (1999, June). Finasteride in the treatment of men with frontal male pattern hair loss.
Olsen, E. A., Hordinsky, M., & Whiting, D., et al. (2006, December). The importance of dual 5α-reductase inhibition in the treatment of male pattern hair loss: Results of a randomized placebo-controlled study of dutasteride versus finasteride.
Schieck, Cynthia L.(1998, August) "Finasteride (Propecia ®)". http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/finasteride/Finasteride%20(Propecia)%20-%20Feature%20Molecule.htm