We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 45673
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
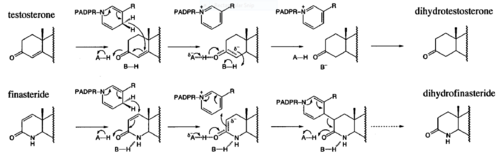
Finasteride can also lead to improvements in Androgenetic alopecia, male pattern baldness (MPB), which is caused by an androgen-dependent miniaturization of scalp hair follicles. Testosterone is the major flow of androgen, but to be maximally active in scalp hair follicles it must be converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5a- reductase. DHT is an important factor in MPB by the absence of the condition in males with a insufficiency of type II 5a-reductase, and by small amounts of hair regrowth in men with MPB (Olsen, et al., 2006). Finasteride acts as an inhibitor for the type II 5a-reductase enzyme, which has shown to reduce both serum and scalp skin dihydrotestosterone levels in balding men (Leyden, et al., 1999). Side effects from Finasteride include but are not limited to, decreased sexual ability and desire. | Finasteride can also lead to improvements in Androgenetic alopecia, male pattern baldness (MPB), which is caused by an androgen-dependent miniaturization of scalp hair follicles. Testosterone is the major flow of androgen, but to be maximally active in scalp hair follicles it must be converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5a- reductase. DHT is an important factor in MPB by the absence of the condition in males with a insufficiency of type II 5a-reductase, and by small amounts of hair regrowth in men with MPB (Olsen, et al., 2006). Finasteride acts as an inhibitor for the type II 5a-reductase enzyme, which has shown to reduce both serum and scalp skin dihydrotestosterone levels in balding men (Leyden, et al., 1999). Side effects from Finasteride include but are not limited to, decreased sexual ability and desire. | ||
| - | |||
| - | *i also might talk about how finasteride can be used to treat prostate cancer, i just haven't found a lot of sourcing talking about it. so thats something i will be working on. | ||
| - | *I plan to do more research on the structure and how it effects within the body for medical uses | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==To do list== | ||
| - | 1.) Hyperlink to other articles | ||
| - | 2.) Go into more depth with each section, especially structure and function | ||
| - | 3.) Add synthesis | ||
| - | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | Allen, Helen. (2015, March). "Finasteride for prostate gland enlargement. Information. Patient. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Bull, Herbert G.*Garcia-Calvo,Margarita Andersson,Stefan†, Baginsky, Walter F.,Chan,H. Karen,Ellsworth,‡ Dina E., Miller,§ Randall R., Stearns,Ralph A.,Bakshi,Raman K.,Rasmusson, Gary H.,Tolman,Richard L., Myers,Robert W.,Kozarich,John W.,Harris,Georgianna S. (1995, August 6) Mechanism-Based Inhibition of Human Steroid 5R-Reductase by Finasteride: Enzyme-Catalyzed Formation of NADP-Dihydrofinasteride, a Potent Bisubstrate Analog Inhibitor. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja953069t | ||
| - | |||
| - | Leyden, J., Dunlap, F., & Miller, B., et el. (1999, June). Finasteride in the treatment of men with frontal male pattern hair loss. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Olsen, E. A., Hordinsky, M., & Whiting, D., et al. (2006, December). The importance of dual 5α-reductase inhibition in the treatment of male pattern hair loss: Results of a randomized placebo-controlled study of dutasteride versus finasteride. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Schieck, Cynthia L.(1998, August) "Finasteride (Propecia ®)". http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/finasteride/Finasteride%20(Propecia)%20-%20Feature%20Molecule.htm | ||
Revision as of 03:45, 6 December 2016
N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-oxo-(5α,17β)-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 121, 246. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Yamana K, Labrie F, Luu-The V (January 2010). Human type 3 5α-reductase is expressed in peripheral tissues at higher levels than types 1 and 2 and its activity is potently inhibited by finasteride and dutasteride. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation. 2 (3). doi:10.1515/hmbci.2010.035
- ↑ Varothai, S; Bergfeld, WF (Jul 2014). "Androgenetic alopecia: an evidence-based treatment update.". American journal of clinical dermatology. 15 (3): 217–30. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0077-5. PMID 24848508
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lednicer D (2011). Steroid Chemistry at a Glance. Hoboken: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-66084-3
- ↑ Burkhard Fugmann; Susanne Lang-Fugmann; Wolfgang Steglich (28 May 2014). RÖMPP Encyclopedia Natural Products, 1st Edition, 2000. Thieme. pp. 1918–. ISBN 978-3-13-179551-9
- ↑ Schieck, Cynthia L.(1998, August) "Finasteride (Propecia ®)". http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/finasteride/Finasteride%20(Propecia)%20-%20Feature%20Molecule.htm
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Bull, Herbert G.*Garcia-Calvo,Margarita Andersson,Stefan†, Baginsky, Walter F.,Chan,H. Karen,Ellsworth,‡ Dina E., Miller,§ Randall R., Stearns,Ralph A.,Bakshi,Raman K.,Rasmusson, Gary H.,Tolman,Richard L., Myers,Robert W.,Kozarich,John W.,Harris,Georgianna S. (1995, August 6) Mechanism-Based Inhibition of Human Steroid 5R-Reductase by Finasteride: Enzyme-Catalyzed Formation of NADP-Dihydrofinasteride, a Potent Bisubstrate Analog Inhibitor. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja953069t