We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Urokinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
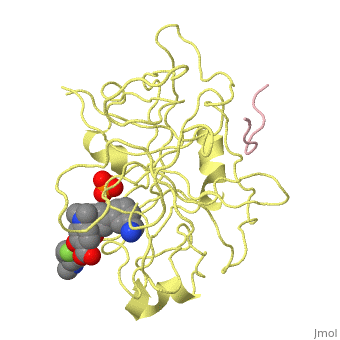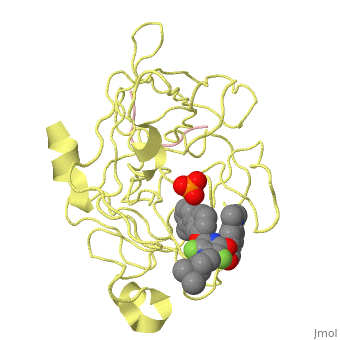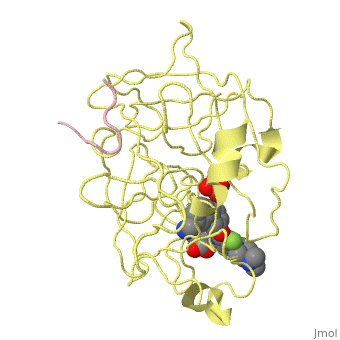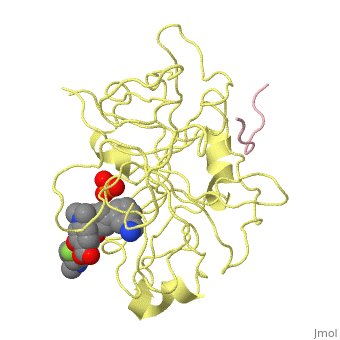
| - | <StructureSection load='3ig6' size='340' side='right' caption='Human urokinase short chain ( | + | <StructureSection load='3ig6' size='340' side='right' caption='Human urokinase short chain (pink) and catalytic domain (yellow) complex with inhibitor and phosphate, [[3ig6]]' scene='' > |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Urokinase''' (UK) is a serine protease whose principal substrate is plasminogen – the inactive zymogen of plasmin<ref>PMID:21711235</ref>. UK consists of 3 domains: ligand-binding domain and kringle and growth factor domains. Prourokinase (PUK) is the inactive zymogen of UK which becomes active by proteolytic cleavage into catalytic domain (residues 179-431) and short chain (residues 156-178). | '''Urokinase''' (UK) is a serine protease whose principal substrate is plasminogen – the inactive zymogen of plasmin<ref>PMID:21711235</ref>. UK consists of 3 domains: ligand-binding domain and kringle and growth factor domains. Prourokinase (PUK) is the inactive zymogen of UK which becomes active by proteolytic cleavage into catalytic domain (residues 179-431) and short chain (residues 156-178). | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Increased levels of UK are associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer and thus is used as prognostic markers for the disease<ref>PMID:15944776</ref>. | Increased levels of UK are associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer and thus is used as prognostic markers for the disease<ref>PMID:15944776</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | The inhibitor of of UK binds in the active site of UK and interacts with the active Ser of the catalytic triad<ref>PMID:19703768</ref>. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of urokinase == | == 3D Structures of urokinase == | ||
Revision as of 10:42, 11 December 2016
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of urokinase
Updated on 11-December-2016
References
- ↑ Carriero MV, Stoppelli MP. The urokinase-type plasminogen activator and the generation of inhibitors of urokinase activity and signaling. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(19):1944-61. PMID:21711235
- ↑ Han B, Nakamura M, Mori I, Nakamura Y, Kakudo K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator system and breast cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 2005 Jul;14(1):105-12. PMID:15944776
- ↑ West CW, Adler M, Arnaiz D, Chen D, Chu K, Gualtieri G, Ho E, Huwe C, Light D, Phillips G, Pulk R, Sukovich D, Whitlow M, Yuan S, Bryant J. Identification of orally bioavailable, non-amidine inhibitors of Urokinase Plasminogen Activator (uPA). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Oct 1;19(19):5712-5. Epub 2009 Aug 7. PMID:19703768 doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.008