User:Charli Barbet/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='1gri' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1gri' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | Grb2 protein: Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein is a cytosolic protein made of 217 amino acids and weighing 25,206 Da. Ubiquitously present in the cell, this protein is involved in signal transduction and especially in the MAP kinase pathway. Grb2 interacts mainly with tyrosine kinase such as [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] once it’s been activated by ligand binding. This specific binding leads to the recruitment of GEF (like SOS1), stimulating the activation of other pathways. Several others interactions have been elucidated like the capacity of the protein to dimerise thus implicated in the growth of malignant cells. | + | Grb2 protein: Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein is a cytosolic protein made of 217 amino acids and weighing 25,206 Da. Ubiquitously present in the cell, this protein is involved in signal transduction and especially in the MAP kinase pathway. Grb2 interacts mainly with tyrosine kinase such as [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] once it’s been activated by ligand binding. This specific binding leads to the recruitment of GEF (like [SOS1 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889]), stimulating the activation of other pathways. Several others interactions have been elucidated like the capacity of the protein to dimerise thus implicated in the growth of malignant cells. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
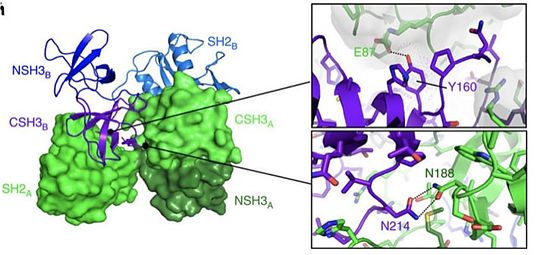
Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the 2 molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (epidermal growth factor receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor, nerve growth factor receptor) but equally in proteins that are not RTK kinases (BCR-Ab1, focal adhesion kinase, insulin receptor substrate-1). | Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the 2 molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (epidermal growth factor receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor, nerve growth factor receptor) but equally in proteins that are not RTK kinases (BCR-Ab1, focal adhesion kinase, insulin receptor substrate-1). | ||
| - | As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding, in turn, leads to the recruitment of SOS-1 via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of SOS-1 protein (Son Of Sevenless). | + | As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding, in turn, leads to the recruitment of [SOS-1 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889] via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of [SOS-1 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889] protein (Son Of Sevenless). |
| - | Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and SOS, the RAS protein is activated. Interestingly, RAS is a g-protein implicated in the activation of Raf-1. The latest activates of the MEK downstream cascade pathway (MEK1/ MEK2 et ERK1/ ERK2) involved in the translocation | + | Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and [SOS http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889], the [RAS http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112] protein is activated. Interestingly, [RAS http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112] is a g-protein implicated in the activation of [Raf-1 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04049]. The latest activates of the MEK downstream cascade pathway ([MEK1 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q02750]/ [MEK2 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36507] et [ERK1 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27361]/ [ERK2 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P28482]) involved in the translocation of ERK factors from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of [Elk-1 http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19419] and [Myc transcription Factor http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01106]. These particular transcription factor participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. |
| - | On the other hand, in T lymphocytes, the simulation of TCRs induces tyrosine phosphorylation on a wide range of of cellular proteins such as p36-38 or LAT. | + | On the other hand, in T lymphocytes, the simulation of TCRs induces tyrosine phosphorylation on a wide range of of cellular proteins such as p36-38 or LAT. As an example, the phosphorylated residues of LAT can bind the SH2 domain of Grb2 while the formation of this complex recruits on the SH3 domain some proteins of the VAV family. VAV proteins are guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) for the GTPase proteins of the Rho family. |
| - | As an example, the phosphorylated residues of LAT can bind the SH2 domain of Grb2 while the formation of this complex recruits on the SH3 domain some proteins of the VAV family. VAV proteins are guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) for the GTPase proteins of the Rho family. | + | |
This complex has for main aim to introduce a Calcium flux and the activation of MAP kinase allowing lymphocytes T proliferation. | This complex has for main aim to introduce a Calcium flux and the activation of MAP kinase allowing lymphocytes T proliferation. | ||
Finally, it was proven that Grb2 in the negative regulation of EGFR. Indeed, c-Cbl is a protein implicated in the E3 complex of EGFR ubiquitination, hence also its degradation. C-Cbl thanks to its SH2 domain can directly bind to EGFR causing its degradation (Grb2 independent regulation). Yet c-Cbl can also indirectly bind to EGFR via its SH3 domain recognition by Grb2 (Dependant Grb2 regulation). The direct or indirect binding of c-Cbl on EGFR induce the recruitment of enzymes that are necessary for the ubiquitination of EGFR. Ubiquitination being a signal for protein degradation. It is important to note that negative regulation is more important when Grb2 is implicated and bound to c-Cbl rather than when c-Cbl is the only protein involved. | Finally, it was proven that Grb2 in the negative regulation of EGFR. Indeed, c-Cbl is a protein implicated in the E3 complex of EGFR ubiquitination, hence also its degradation. C-Cbl thanks to its SH2 domain can directly bind to EGFR causing its degradation (Grb2 independent regulation). Yet c-Cbl can also indirectly bind to EGFR via its SH3 domain recognition by Grb2 (Dependant Grb2 regulation). The direct or indirect binding of c-Cbl on EGFR induce the recruitment of enzymes that are necessary for the ubiquitination of EGFR. Ubiquitination being a signal for protein degradation. It is important to note that negative regulation is more important when Grb2 is implicated and bound to c-Cbl rather than when c-Cbl is the only protein involved. | ||
Revision as of 08:51, 13 January 2017
Grb2 (1gri)
| |||||||||||