User:Charli Barbet/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='1gri' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1gri' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
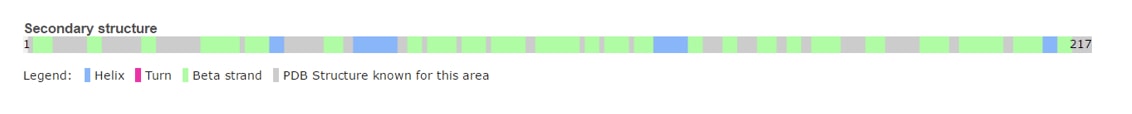
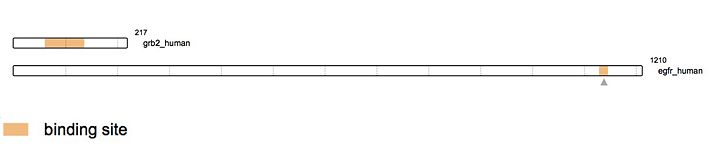
| - | Grb2 protein: Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein is a cytosolic protein made of 217 amino acids and weighing 25,206 Da. Ubiquitously present in the cell, this protein is involved in signal transduction and especially in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MAP kinase pathway]. Grb2 interacts mainly with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tyrosine_kinase tyrosine kinase] such as [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] once it’s been activated by ligand binding. This specific binding leads to the recruitment of GEF (like [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS1]), stimulating the activation of other pathways. Several others interactions have been elucidated like the capacity of the protein to dimerise thus implicated in the growth of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Malignancy malignant cells]. | + | Grb2 protein: Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein is a cytosolic protein made of 217 amino acids and weighing 25,206 Da. Ubiquitously present in the cell, this protein is involved in signal transduction and especially in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MAP kinase pathway]. Grb2 interacts mainly with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tyrosine_kinase tyrosine kinase] such as [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] once it’s been activated by ligand binding. This specific binding leads to the recruitment of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanine_nucleotide_exchange_factor GEF] (like [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS1]), stimulating the activation of other pathways. Several others interactions have been elucidated like the capacity of the protein to dimerise thus implicated in the growth of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Malignancy malignant cells]. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<scene name='75/750264/Sh2/1'>SH2 DOMAIN</scene>: | <scene name='75/750264/Sh2/1'>SH2 DOMAIN</scene>: | ||
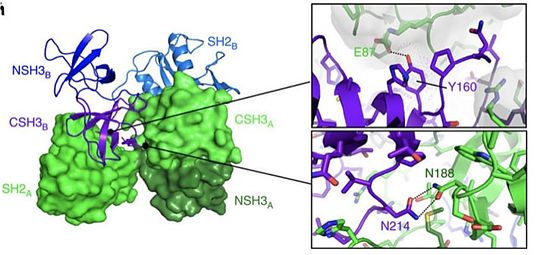
| - | SH2 domain is a domain that is approximately 100 amino acids long and with a very conserved structure. Identified in in several human and rodent proteins such as phosphatases, | + | SH2 domain is a domain that is approximately 100 amino acids long and with a very conserved structure. Identified in in several human and rodent proteins such as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatase phosphatases], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcription_factor transcription factor], or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_transducing_adaptor_protein adaptor] like protein such as Grb2 for instance. This domain is therefore ubiquitous in several cellular signaling pathways.Typically, SH2 domain specifically recognize sites with phosphorylated tyrosine in different types of proteins. SH2 can for instance bind to the intracellular region of EGF leading in turn, to the formation of protein signalization complexes. This binding and the role of SH2 is thus, very important in the conversion of an extra-cellular signal in an intra-cellular signal able to give rise to diversified cellular responses or the expression of specific genes.It is also important to note that the SH2 domain can bind to other SH2 domains.However, a mutation in the specific binding site of SH2 can impede the interaction of two proteins and thus the formation of a protein complex. Therefore, mutations in SH2 can give rise to cellular dysfunction and lead to several diseases. |
<scene name='75/750264/Sh3/1'>SH3 DOMAIN</scene>: | <scene name='75/750264/Sh3/1'>SH3 DOMAIN</scene>: | ||
| - | The SH3 domain is a region of a protein that is approximately 50 amino acid long. Largely present in proteins associated to the membrane. The domain is made of 5 to 6 | + | The SH3 domain is a region of a protein that is approximately 50 amino acid long. Largely present in proteins associated to the membrane. The domain is made of 5 to 6 β-sheets arranged in two antiparallel β-sheets. The linking region between the two β-sheets can contain α helices. This special conformation allows the arrangement of a hydrophobic pocket in which the ligand can bind. Typically, the binding region has a motif rich in Prolines: PXXP. This binding allows the formation of multi-proteins complexes involved in the translation of an extra-cellular signal and its conversion. The binding can thus be largely involved in gene expression and protein concentration. |
ISOFORM: | ISOFORM: | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
- X for a random residue | - X for a random residue | ||
| - | Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the 2 molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (epidermal growth factor receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor | + | Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the 2 molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 epidermal growth factor receptor], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P11362 fibroblast growth factor receptor]) but equally in proteins that are not [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q05397 focal adhesion kinase], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 insulin receptor substrate-1]). |
As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding, in turn, leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] protein (Son Of Sevenless). | As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding, in turn, leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] protein (Son Of Sevenless). | ||
Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS], the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] protein is activated. Interestingly, [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] is a g-protein implicated in the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04049 RAF-1]. The latest activates of the MEK downstream cascade pathway ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q02750 MEK1]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36507 MEK2] et [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27361 ERK1 ]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P28482 ERK2]) involved in the translocation of ERK factors from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19419 Elk-1] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01106 Myc transcription Factor]. These particular transcription factor participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. | Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS], the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] protein is activated. Interestingly, [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] is a g-protein implicated in the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04049 RAF-1]. The latest activates of the MEK downstream cascade pathway ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q02750 MEK1]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36507 MEK2] et [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27361 ERK1 ]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P28482 ERK2]) involved in the translocation of ERK factors from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19419 Elk-1] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01106 Myc transcription Factor]. These particular transcription factor participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8WU20 '''Frs2''']: Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 can link to [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P09769 FGR] and NGF activated receptor. They play an important role in the activation of MAPK kinase for example, or the phosphorylation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27986 PIK3R1]. | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8WU20 '''Frs2''']: Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 can link to [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P09769 FGR] and NGF activated receptor. They play an important role in the activation of MAPK kinase for example, or the phosphorylation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27986 PIK3R1]. | ||
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 '''Irs1'' | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 '''Irs1''']: Insulin receptor substrate 1 may mediate the control of various cellular processes by insulin. It can activate the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase when it bounds to the regulatory [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27986 p85 subunit]. |
[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13480 '''Gab1''']: GRB2 associated binding protein 1, is implicated in many signalling cascades triggered by activated receptor type kinases. It is also probably involved in signalling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13480 '''Gab1''']: GRB2 associated binding protein 1, is implicated in many signalling cascades triggered by activated receptor type kinases. It is also probably involved in signalling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. | ||
Revision as of 13:25, 13 January 2017
Grb2 (1gri)
| |||||||||||