User:Charli Barbet/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The Grb2 isoform has a non-functional SH2 domain, unable to link the phosphorylated tyrosine of its targeted protein (EGFR for instance). This inability of the molecule to transmit signal is traduce by apoptosis of the cell, thus regulating the growth signal. | The Grb2 isoform has a non-functional SH2 domain, unable to link the phosphorylated tyrosine of its targeted protein (EGFR for instance). This inability of the molecule to transmit signal is traduce by apoptosis of the cell, thus regulating the growth signal. | ||
| - | The functional isoform Grb2 is involved in several cellular functions detailed below. On one hand, the SH2 domain recognizes phosphorylated residues which are mainly tyrosines. The recognized tyrosines present a caracteristic motif for recognition : NH2-pYXNX-COOH. | + | The functional isoform Grb2 is involved in several cellular functions detailed below. On one hand, the SH2 domain recognizes phosphorylated residues which are mainly tyrosines. The recognized tyrosines present a caracteristic motif for recognition: NH2-pYXNX-COOH. |
- pY representing the phosphorylated tyrosine. | - pY representing the phosphorylated tyrosine. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
- X for a random residue | - X for a random residue | ||
| - | Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the | + | Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the two molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 epidermal growth factor receptor], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P11362 fibroblast growth factor receptor]) but equally in proteins that are not [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q05397 focal adhesion kinase], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 insulin receptor substrate-1]). |
As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding, in turn, leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] protein (Son Of Sevenless). | As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding, in turn, leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] protein (Son Of Sevenless). | ||
Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS], the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] protein is activated. Interestingly, [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] is a g-protein implicated in the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04049 RAF-1]. The latest activates of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MEK downstream cascade pathway] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q02750 MEK1]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36507 MEK2] et [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27361 ERK1 ]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P28482 ERK2]) involved in the translocation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extracellular_signal–regulated_kinases ERK factors] from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19419 Elk-1] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01106 Myc transcription Factor]. These particular [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcription_factor transcription factor] participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. | Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS], the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] protein is activated. Interestingly, [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] is a g-protein implicated in the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04049 RAF-1]. The latest activates of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MEK downstream cascade pathway] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q02750 MEK1]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36507 MEK2] et [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27361 ERK1 ]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P28482 ERK2]) involved in the translocation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extracellular_signal–regulated_kinases ERK factors] from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19419 Elk-1] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01106 Myc transcription Factor]. These particular [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcription_factor transcription factor] participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 '''Sos1''']: Promotes the exchange of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 Ras]-bound [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanosine_diphosphate GDP] into [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanosine_triphosphate GTP], by promoting the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 Ras] specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity. | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 '''Sos1''']: Promotes the exchange of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 Ras]-bound [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanosine_diphosphate GDP] into [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanosine_triphosphate GTP], by promoting the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 Ras] specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity. | ||
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P29353 '''Shc''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P29353 Shc] is important in the regulation of apoptosis and drug resistance in mammalian cells. She is implicated in the EGFR pathway. | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P29353 '''Shc''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P29353 Shc] is important in the regulation of apoptosis and drug resistance in mammalian cells. She is implicated in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epidermal_growth_factor_receptor EGFR pathway]. |
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P22681 '''Cbl''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P22681 Cbl] is a pronto oncogene protein which serves as an adaptor and a negative regulator of many signalling pathways implicated in cell surface receptors activation. | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P22681 '''Cbl''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P22681 Cbl] is a pronto oncogene protein which serves as an adaptor and a negative regulator of many signalling pathways implicated in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_surface_receptor cell surface receptors] activation. |
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UQC2 '''Gab2''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UQC2 Gab2] acts downstream of several | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UQC2 '''Gab2''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UQC2 Gab2] acts downstream of several [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_surface_receptor cell surface receptors] such as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytokine cytokine], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hormone hormone], cell matrix or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_factor_receptor growth factor receptor]. Thus, it is implicated in many different pathways. |
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13094 '''LCP2''']: Involved in T cell antigen receptor mediated signaling | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13094 '''LCP2''']: Involved in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T-cell_receptor T cell antigen receptor] mediated signaling. |
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04626 '''Erbb2''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04626 Erbb2] is a kinase involved in several surface receptor complexes, but need a co receptor for ligand binding. For example, it participates in neuregulin receptor complex but it can’t bind with it alone. | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04626 '''Erbb2''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04626 Erbb2] is a kinase involved in several surface receptor complexes, but need a co-receptor for ligand binding. For example, it participates in neuregulin receptor complex but it can’t bind with it alone. |
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8WU20 '''Frs2''']: Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 can link to [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P09769 FGR] and NGF activated receptor. They play an important role in the activation of MAPK kinase for example, or the phosphorylation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27986 PIK3R1]. | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8WU20 '''Frs2''']: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P21802 Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2] can link to [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P09769 FGR] and NGF activated receptor. They play an important role in the activation of MAPK kinase for example, or the phosphorylation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27986 PIK3R1]. |
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 '''Irs1''']: Insulin receptor substrate 1 may mediate the control of various cellular processes by insulin. It can activate the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase when it bounds to the regulatory [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27986 p85 subunit]. | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 '''Irs1''']: [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 Insulin receptor substrate 1] may mediate the control of various cellular processes by insulin. It can activate the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase when it bounds to the regulatory [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27986 p85 subunit]. |
[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13480 '''Gab1''']: GRB2 associated binding protein 1, is implicated in many signalling cascades triggered by activated receptor type kinases. It is also probably involved in signalling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13480 '''Gab1''']: GRB2 associated binding protein 1, is implicated in many signalling cascades triggered by activated receptor type kinases. It is also probably involved in signalling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. | ||
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 '''EGFR''']: The epidermal growth factor receptor has a Tyrosine kinase activity and can be recognize by Grb2 thanks to its Tyrosine domains. This receptor is implicated in many pathways, such as antigen fixation on B cells. | + | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 '''EGFR''']: The epidermal growth factor receptor has a Tyrosine kinase activity and can be recognize by Grb2 thanks to its Tyrosine domains. This receptor is implicated in many pathways, such as antigen fixation on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B_cell B cells]. |
== EGFR interaction == | == EGFR interaction == | ||
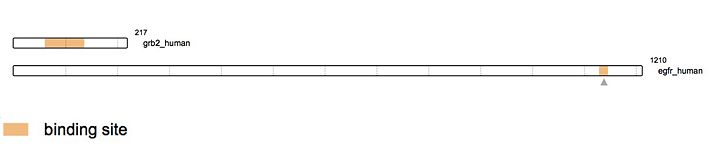
[[Image:EGFR Grb2.jpg|thumb|upright=4]] | [[Image:EGFR Grb2.jpg|thumb|upright=4]] | ||
| - | As stated earlier, Grb2 is made of an SH2 domain able to bind to tyrosine kinase receptors. Thus, Grb2 is able to bind to the activated form of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR]). [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] activation mainly comes from the binding of a ligand. There is a wide range of ligands that are able to bind [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR], yet the majority of the ligands come from the ErbB family. The most known ligands are [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01137 TGF-β] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01133 EGF]. The binding of these latest induces [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] dimerization. This dimerization activates the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain characterized by the autophosphorylation of tyrosines (Y992, Y1045, Y1068, Y1086 and Y1173). The activated form of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] then recruits Grb2. Indeed, the SH2 domain of Grb2 (from the 60th to the 152nd amino acid) binds the phosphorylated tyrosines of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] (Y1068 & Y1086). This interaction leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] (Son Of Sevenless) via the SH3 domain of Grb2. As this example demonstrates, Grb2 is an adapting protein able to conduct a signal between two different proteins via its different domains. [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] is a GEF protein activating [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] and therefore in turn the MAPK pathway. | + | As stated earlier, Grb2 is made of an SH2 domain able to bind to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase tyrosine kinase receptors]. Thus, Grb2 is able to bind to the activated form of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR]). [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] activation mainly comes from the binding of a ligand. There is a wide range of ligands that are able to bind [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR], yet the majority of the ligands come from the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ErbB ErbB family]. The most known ligands are [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01137 TGF-β] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01133 EGF]. The binding of these latest induces [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] dimerization. This dimerization activates the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain characterized by the autophosphorylation of tyrosines (Y992, Y1045, Y1068, Y1086 and Y1173). The activated form of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] then recruits Grb2. Indeed, the SH2 domain of Grb2 (from the 60th to the 152nd amino acid) binds the phosphorylated tyrosines of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 EGFR] (Y1068 & Y1086). This interaction leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] (Son Of Sevenless) via the SH3 domain of Grb2. As this example demonstrates, Grb2 is an adapting protein able to conduct a signal between two different proteins via its different domains. [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanine_nucleotide_exchange_factor GEF protein] activating [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] and therefore in turn the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MAPK pathway]. |
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| - | == | + | == Diseases == |
| - | '''Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)''': It seems like Grb2 is implicated in the simulation of AD. Phenotypic | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer's_disease '''Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)''']: It seems like Grb2 is implicated in the simulation of AD. Phenotypic changes have been identified in cortical and hippocampal neurons characteristic of AD. Indeed, the proteins implicated in the transduction of the signal from Grb2 to [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] are altered in AD. This modifications would be at the heart at the transduction of a “derived” signal stimulating AD. <ref>PMID: 9878757</ref> |
| - | '''HIV-1''': Grb2 isoform could have a simulatory effect in the retro viral infection of HIV-1. By its essential role in the MAPK pathway, Grb3 can have effects on HIV-1 infections. Indeed, the replication of the virus is activated by Lymphocytes T replication. Yet | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer's_disease '''HIV-1''']: Grb2 isoform could have a simulatory effect in the retro viral infection of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer's_disease HIV-1]. By its essential role in the MAPK pathway, Grb3 can have effects on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer's_disease HIV-1] infections. Indeed, the replication of the virus is activated by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell Lymphocytes T] replication. Yet [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell Lymphocytes T]’s activation depend on the activation of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MAPK pathway] dictated by the presence or not of grb3 in the cell. This pathway finally activates [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q14934 NFAT], a transcription factor enhancing the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Long_terminal_repeat LTR promotor] of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer's_disease HIV-1] leading to its replication. |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
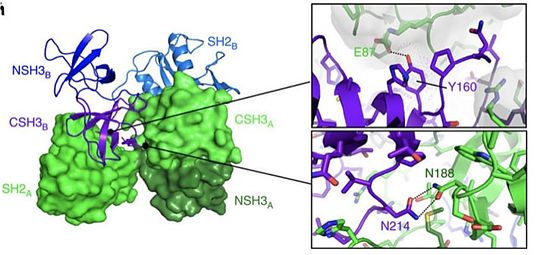
[[Image:Y160.jpg|thumb|upright=3|test]] | [[Image:Y160.jpg|thumb|upright=3|test]] | ||
| - | Grb2 protein is especially involved in the setting up of cellular oncognesis in prostate, colon and lung cancers. This role is mainly due to its essential role in signal transduction in the MAP kinase pathway known to induce mitosis. In this pathway, Grb2 binds to the oncogenic protein [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] under its monomeric form. Yet [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] can also be found in its dimeric form in the cell. Dimerization of Grb2 is dependent upon several factors like the phosphorylation of <scene name='75/750264/Y160/1'>tyrosine 160</scene> or the binding of ligand on the SH2 domain of the same protein. Mainly, phosphorylation | + | Grb2 protein is especially involved in the setting up of cellular oncognesis in prostate, colon and lung cancers. This role is mainly due to its essential role in signal transduction in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitogen-activated_protein_kinase MAP kinase pathway] known to induce [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitosis mitosis]. In this pathway, Grb2 binds to the oncogenic protein [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] under its monomeric form. Yet [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS] can also be found in its dimeric form in the cell. Dimerization of Grb2 is dependent upon several factors like the phosphorylation of <scene name='75/750264/Y160/1'>tyrosine 160</scene> or the binding of ligand on the SH2 domain of the same protein. Mainly, phosphorylation induces the dissociation of the Grb2 dimer induce an increase in the MAP kinase pathway activation by the binding of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS]. The phosphorylated state of <scene name='75/750264/Y160/1'>Y160</scene> has been discovered in severa pre-metastatis cancers. This highly suggest that pY160 could be a oncogenic marker in humans. A new therapeutic way could therefore be considered by stabilizing Grb2 in its dimeric form. This could be achieve with a protein acting as an irreversible cross-link at the interface between the two units. |
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 13 January 2017
Grb2 (1gri)
| |||||||||||