is a serine/threonine phosphatase that is activated by calmodulin in a calcium-dependant manner. Calcineurin is the only known calmodulin-activated protein phosphatase. Calcineurin is responsible mainly for dephosphorylating several member of the NFAT transcription factor family (including NFATc1 through NFATc4).
Localisation and expression:
Calcineurin is a cytoplasmic protein. The catalytic subunit calcineurin A, posses two major isoforms called calcineurin Aα and Aβ. Calcineurin Aα is widely expressed among tissues especially in the Central Nervous System (CNS). Calcineurin Aβ is rather found in the lymphoid cells.Calcineurin Aβ is therefore involved in the mediation of the immune response (PMID:16888030).
Function
General structure
is a heterodimeric Protein that consits of two subunits. They are called catalytic and regulatory subunit. Four molecules of Calcineurin form an asymmetric complex which leads to a total molecular weight of 370 kDa.
The structure presented in this article is the catalytic subunit isoform of the serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2B in rattus norvegicus (rat). It consists of 521 (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329) aminoacids and has a molecular weight of 57 kDa (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329).
The calatytic subunit is subdivided into functional domains which are a , a , a and an .
The catalytic side includes a residue (green) at position 151 that acts as proton donor and metal binding sites. (shown in brown) binds at the position 118, 150, 199 and 281. Iron (blue) interacts at the positions 90, 92 and 118.
are modified with a serine or a tyrosine. At position 2, a N-acetylserine has been found by similarity, as well as a nitrated tyrosine at position 224, and phosphoserine at position 469 and 492.
Discovery of the structure:
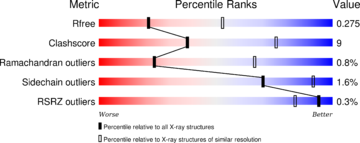
The structure have been published in the year 2013 by Qilu Ye et al. (PMID:24018048) in Cellular Signaling. For their experiments they used x-ray diffraction. The PDB validation obtained a Resolutionof 3.0 Å, a free R-value of 0.273 and a work R-value of 0.241 (http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=4IL1).
secondary structure:

The secondary structure mostly includes helical structures
UniprotBesides, there are six turns reported in the structure of one chain.
The Ramachandran blot of Calcineurin
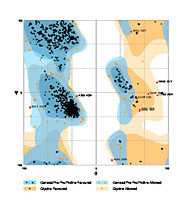
Ramachandran Plot of 4il1
has been obtained by
MolProbity of the DUke University. It plots the torsional angles phi (φ)and psi (ψ)of the molecule and thereby represents the secondary structure. Further information about the Interpretation of this plot can be found at
Ramachandran Plot.
Principle of action
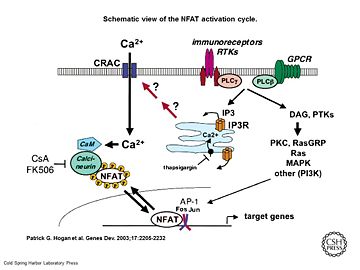
Schematic view of the NFAT activation cycle (PMID:12975316)
As a response of receptor tyrosine kinase [1] activation as well as G protein-coupled receptor (GCPR) activation the Phospholipase C (PLC) catalyse the hydrolysis of PIP2 to IP3 and DAG. IP3 activates the Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor and therby leads to an increasing amount of the second Messenger Ca2+ in the cytoplasma.
Calcineurin is activated by Calmodulin, a calcium-binding protein. Calmodulin interacts with the calmodulin-binding/regulatory region of Calcineurin. That binding leads to a conformational change in the autoinhibitory domain and remove it from the active site (doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.008).
It has been reported that Calcineurin activates the transcription factor NFAT by forming a complex and dephosporylation (PMID:17502104). Following, the factor enters the nucleus and activates the expression of Interleukin-2.
Binding Partners
The main partners of interaction are Calmodulin,NFATc1, NFATc2 and NFATc3.
Many of the calcineurin substrates’ contain a PxIxIT motif. Among them, beside the phosphorylated forms of NFAT we can also mentioned; cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), PP1, microtubule-associated protein tau and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK- 3)(PMID: 17666045)(PMID: 22676853)(PMID: 14701880)(PMID: 7515479).
Calcineurin is inhibited by the immunosuppressive drugs tacrolismus (FK506) or cyclosporine A (CsA). CsA and FK506 conduct their therapeutic role thought binding to the immunophilins cyclophilin and FK506 binding protein (FK506BP) respectively. The complexes CsA-cyclophilin and FK506-FK506BP bind then to calcineurin in a calcium-dependent manner thus inhibiting its phosphatase activity. Therefore the addition of these drugs to lymphocytes T prevent NFAT translocation to the nucleus and the subsequent activation its target gene.That's why FK506 and CsA are use in the treatment of various immune-mediated diseases. However since calcineurin is is widely expressed in non-haemopoietic tissues like the kidney and the hearth, both drugs present a long term toxicity and can lead to deleterious effect to these Organs (PMID: 8811062), (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus).
Cofactors:
Calcineurin belong to the family of metalloprotein. To conduct its activity it requires the presence of Fe3+ and Zn2+ ions in the active site (one per subunit).Superoxide dismutase has been shown to protect calcineurin from inactivation by preventing Fe3+ from oxidation. Thus after activation of calcineurin by calmodulin, the AID is displaced from the catalytic core exposing Fe3+ to oxidation (PMID: 8837775)(Calmodulin and Signal Transduction (p184), Linda J. Van Eldik,D. Martin Watterson (1998)).
Related health defects
Calcineurin hyperactivation thought dysregulation of the Ca2+ dynamic have been show to play a critical role in several diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Schizophrenia ,Diabetes, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as well as Alzheimer diseases (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus)(PMID: 12851457)(PMID: 16988714)(PMID: 20421909)(PMID: 22654726).In order to fight those health defects calmodulin inhibitors can be administrated.