User:Charli Barbet/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
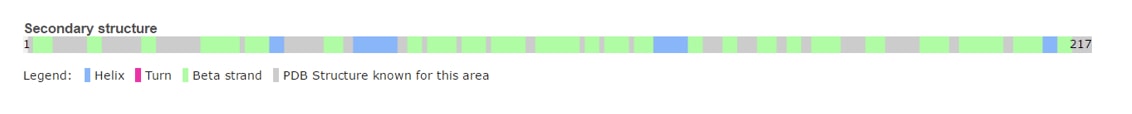
| - | The Grb2 isoform has a non-functional SH2 domain, unable to bind the phosphorylated tyrosine of its targeted protein (EGFR for instance). The inability of the molecule to transmit signal is translated by apoptosis of the cell, thus regulating growth signal. | + | The Grb2 isoform has a non-functional SH2 domain, unable to bind the phosphorylated tyrosine of its targeted protein (EGFR for instance). The inability of the molecule to transmit signal is translated by apoptosis of the cell, thus regulating growth signal. |
The functional isoform: Grb2, is involved in several cellular functions detailed below: | The functional isoform: Grb2, is involved in several cellular functions detailed below: | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
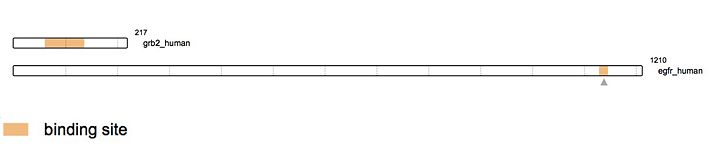
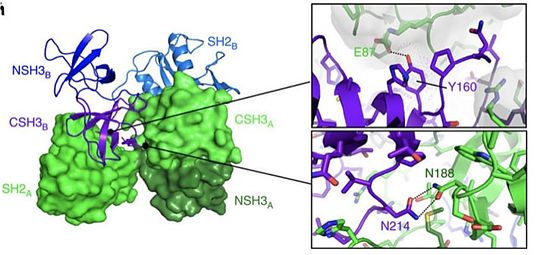
Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the two molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 epidermal growth factor receptor], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P11362 fibroblast growth factor receptor]) but equally in proteins that are not [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q05397 focal adhesion kinase], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 insulin receptor substrate-1]). | Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the two molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00533 epidermal growth factor receptor], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P11362 fibroblast growth factor receptor]) but equally in proteins that are not [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_tyrosine_kinase Receptor Tyrosine Kinase] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q05397 focal adhesion kinase], [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P35568 insulin receptor substrate-1]). | ||
As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] protein (Son Of Sevenless). | As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding leads to the recruitment of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS-1] protein (Son Of Sevenless). | ||
| - | Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS], the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] protein is activated. Interestingly, [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] is a g-protein implicated in the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04049 RAF-1]. The latest activates of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MEK downstream cascade pathway] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q02750 MEK1]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36507 MEK2] et [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27361 ERK1 ]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P28482 ERK2]) involved in the translocation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extracellular_signal–regulated_kinases ERK factors] from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19419 Elk-1] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01106 Myc transcription Factor]. These particular [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcription_factor transcription factor] participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. | + | Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q07889 SOS], the [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] protein is activated. Interestingly, [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01112 RAS] is a g-protein implicated in the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P04049 RAF-1]. The latest activates of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAPK/ERK_pathway MEK downstream cascade pathway] ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q02750 MEK1]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36507 MEK2] et [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27361 ERK1 ]/ [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P28482 ERK2]) involved in the translocation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extracellular_signal–regulated_kinases ERK factors] from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P19419 Elk-1] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P01106 Myc transcription Factor]. These particular [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcription_factor transcription factor] participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. <ref> PMID: 12006650</ref> |
On the other hand, in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell T lymphocytes], the simulation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T-cell_receptor TCRs] induces tyrosine phosphorylation on a wide range of of cellular proteins such as [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P07355 p36]-[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16539 p38] or [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O43561 LAT]. As an example, the phosphorylated residues of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O43561 LAT] can bind the SH2 domain of Grb2 while the formation of this complex recruits on the SH3 domain some proteins of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vav_(protein) VAV family]. [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P15498 VAV proteins] are guanine nucleotide exchange factors ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanine_nucleotide_exchange_factor GEF]) for the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GTPase GTPase proteins] of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rho_family_of_GTPases Rho family]. This complex has for main aim to introduce a Calcium flux and the activation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitogen-activated_protein_kinase MAP kinase] allowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell T lymphocyte] proliferation. | On the other hand, in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell T lymphocytes], the simulation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T-cell_receptor TCRs] induces tyrosine phosphorylation on a wide range of of cellular proteins such as [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P07355 p36]-[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q16539 p38] or [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O43561 LAT]. As an example, the phosphorylated residues of [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O43561 LAT] can bind the SH2 domain of Grb2 while the formation of this complex recruits on the SH3 domain some proteins of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vav_(protein) VAV family]. [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P15498 VAV proteins] are guanine nucleotide exchange factors ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guanine_nucleotide_exchange_factor GEF]) for the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GTPase GTPase proteins] of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rho_family_of_GTPases Rho family]. This complex has for main aim to introduce a Calcium flux and the activation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitogen-activated_protein_kinase MAP kinase] allowing [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell T lymphocyte] proliferation. | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 15 January 2017
Grb2 (1gri)
| |||||||||||