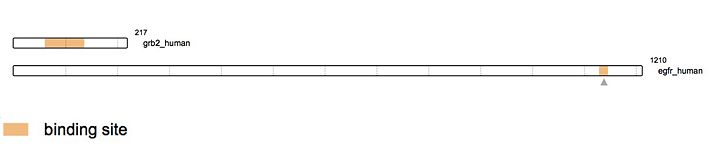
Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein (Grb2) is a cytosolic protein made of 217 amino acids and weighing 25,206 Da. Ubiquitously present in the cell, the protein is involved in signal transduction and has a major role in the MAP kinase pathway. Grb2 interacts mainly with tyrosine kinases such as EGFR. When EGFR is activated by ligand binding, a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor GEF is recruited (like SOS1), stimulating the activation of other pathways.
Several others interactions have been elucidated like the capacity of the protein to dimerise proving its potential implication in the growth of malignant cells.
Structure
Grb2 protein has a very well characterized structure. Composed of 217 amino acids organized in two chains structured in β sheets and α helices.
The protein has three main domains:
-
-
-
:
SH2 domain is a domain that is approximately 100 amino acids long with a very conserved structure. Identified in several human and rodent proteins such as phosphatases, transcription factor, or adaptor like protein as Grb2 for instance.
This domain is ubiquitous in several protein implicated in cellular signaling pathways.Typically, the SH2 domain specifically recognizes sites with phosphorylated tyrosine in different types of proteins. SH2 can, for instance bind to the intracellular region of EGF leading in turn, to the formation of protein signalization complexes. This binding and the role of SH2 is very important in the conversion of an extra-cellular signal in an intra-cellular signal giving rise to diversified cellular responses or the expression of specific genes. It is also important to note that the SH2 domain can bind to other SH2 domains. Nevertheless, a mutation in the specific binding site of SH2 can impede the interaction of two proteins and thus the formation of a protein complex. Therefore, mutations in SH2 can give rise to cellular dysfunction and lead to several diseases. [1]
:
The SH3 domain is approximately 50 amino acid long. Largely expressed in proteins associated to the membrane. The domain is made of 5 to 6 β-sheets arranged in two antiparallel β-sheets. The linking region between the two β-sheets os made of α helices. This special conformation allows the arrangement of a hydrophobic pocket in which the ligand can bind. Typically, the binding region has a motif rich in Prolines: PXXP. This binding allows the formation of multi-proteins complexes involved in the translation and conversion of extra-cellular signals. The binding is thus largely involved in gene expression and protein concentration. [2]
ISOFORM:
Grb2 posses an isoform, known as Grb3.3.
Grb3.3 is present in cells but it induces apoptosis. The isoform has a very similar structure to Grb2 but is truncated from an SH3 domain (from the 60th to the 100th amino) resulting in a degradation of its SH2 domain and a loss of functionality. [3]
Function
The Grb2 isoform has a non-functional SH2 domain, unable to bind the phosphorylated tyrosine of its targeted protein (EGFR for instance). The inability of the molecule to transmit signal is translated by apoptosis of the cell, thus regulating growth signal.
The functional isoform: Grb2, is involved in several cellular functions detailed below:
On one hand, the SH2 domain recognizes phosphorylated residues which are mainly tyrosines. The recognized tyrosines present a caracteristic motif for recognition: NH2-pYXNX-COOH.
- pY representing the phosphorylated tyrosine.
- N for Asparagine
- X for a random residue
Thus by the special recognition of this motif, the binding of the two molecules is very specific. These motifs are highly expressed in several cellular proteins like Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (epidermal growth factor receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor) but equally in proteins that are not Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (focal adhesion kinase, insulin receptor substrate-1).
As an example, the SH2 domain of Grb2 recognizes an intracellular phosphorylated tyrosine. This binding leads to the recruitment of SOS-1 via the SH3 domain of Grb2. Indeed, Grb2 is also made of two SH3 domains. These domains are able to recognize Proline rich region like the one of SOS-1 protein (Son Of Sevenless).
Following this pathway and the formation of a complex between Grb2 and SOS, the RAS protein is activated. Interestingly, RAS is a g-protein implicated in the activation of RAF-1. The latest activates of the MEK downstream cascade pathway (MEK1/ MEK2 et ERK1 / ERK2) involved in the translocation of ERK factors from the cytosol to the nucleus for the activation of Elk-1 and Myc transcription Factor. These particular transcription factor participate in the activation of SRE containing gene leading to cellular growth. [4]
On the other hand, in T lymphocytes, the simulation of TCRs induces tyrosine phosphorylation on a wide range of of cellular proteins such as p36-p38 or LAT. As an example, the phosphorylated residues of LAT can bind the SH2 domain of Grb2 while the formation of this complex recruits on the SH3 domain some proteins of the VAV family. VAV proteins are guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) for the GTPase proteins of the Rho family. This complex has for main aim to introduce a Calcium flux and the activation of MAP kinase allowing T lymphocyte proliferation.[5]
Finally, it was proven that Grb2 in the negative regulation of EGFR. Indeed, c-Cbl is a protein implicated in the E3 complex of EGFR ubiquitination, hence also its degradation C-Cbl thanks to its SH2 domain can directly bind to EGFR causing its degradation (Grb2 independent regulation). Yet c-Cbl can also indirectly bind to EGFR via its SH3 domain recognition by Grb2 (Dependant Grb2 regulation). The direct or indirect binding of c-Cbl on EGFR induce the recruitment of enzymes that are necessary for the ubiquitination of EGFR. Ubiquitination being a signal for protein degradation. It is important to note that negative regulation is more important when Grb2 is implicated and bound to c-Cbl rather than when c-Cbl is the only protein involved. [6] [7]
Interactions
Sos1: Promotes the exchange of Ras-bound GDP into GTP, by promoting the Ras specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity. [8]
Shc: Shc is important in the regulation of apoptosis and drug resistance in mammalian cells. She is implicated in the EGFR pathway. [9]
Cbl: Cbl is a pronto oncogene protein which serves as an adaptor and a negative regulator of many signalling pathways implicated in cell surface receptors activation. [10]
Gab2: Gab2 acts downstream of several cell surface receptors such as cytokine, hormone, cell matrix or growth factor receptor. Thus, it is implicated in many different pathways. [11]
LCP2: Involved in T cell antigen receptor mediated signaling. [12]
Erbb2: Erbb2 is a kinase involved in several surface receptor complexes, but need a co-receptor for ligand binding. For example, it participates in neuregulin receptor complex but it can’t bind with it alone. [13]
Frs2: Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 can link to FGR and NGF activated receptor. They play an important role in the activation of MAPK kinase for example, or the phosphorylation of PIK3R1. [14]
Irs1: [Insulin receptor substrate 1 may mediate the control of various cellular processes by insulin. It can activate the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase when it bounds to the regulatory p85 subunit. [15]
Gab1: GRB2 associated binding protein 1, is implicated in many signalling cascades triggered by activated receptor type kinases. It is also probably involved in signalling by the epidermal growth factor receptor. [16]
EGFR: The epidermal growth factor receptor has a Tyrosine kinase activity and can be recognize by Grb2 thanks to its Tyrosine domains. This receptor is implicated in many pathways, such as antigen fixation on B cells. [17]
EGFR interaction
As stated earlier, Grb2 is made of an SH2 domain able to bind to tyrosine kinase receptors. Thus, Grb2 is able to bind to the activated form of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR). EGFR activation mainly comes from the binding of a ligand. There is a wide range of ligands that are able to bind EGFR, yet the majority of the ligands come from the ErbB family. The most known ligands are TGF-β and EGF. The binding of these latest induces EGFR dimerization. This dimerization activates the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain characterized by the autophosphorylation of tyrosines (Y992, Y1045, Y1068, Y1086 and Y1173). The activated form of EGFR then recruits Grb2. Indeed, the SH2 domain of Grb2 (from the 60th to the 152nd amino acid) binds the phosphorylated tyrosines of EGFR (Y1068 & Y1086). This interaction leads to the recruitment of SOS (Son Of Sevenless) via the SH3 domain of Grb2. As this example demonstrates, Grb2 is an adapting protein able to conduct a signal between two different proteins via its different domains. SOS is a GEF protein activating RAS and therefore in turn the MAPK pathway. [18]
Diseases
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD): It seems like Grb2 is implicated in the simulation of AD. Phenotypic changes have been identified in cortical and hippocampal neurons characteristic of AD. Indeed, the proteins implicated in the transduction of the signal from Grb2 to SOS are altered in AD. This modifications would be at the heart at the transduction of a “derived” signal stimulating AD.
[19]
HIV-1: Grb2 isoform could have a simulatory effect in the retro viral infection of HIV-1. By its essential role in the MAPK pathway, Grb3 can have effects on HIV-1 infections. Indeed, the replication of the virus is activated by Lymphocytes T replication. Yet Lymphocytes T’s activation depend on the activation of the MAPK pathway dictated by the presence or not of grb3 in the cell. This pathway finally activates NFAT, a transcription factor enhancing the LTR promotor of HIV-1 leading to its replication. [20]
Relevance
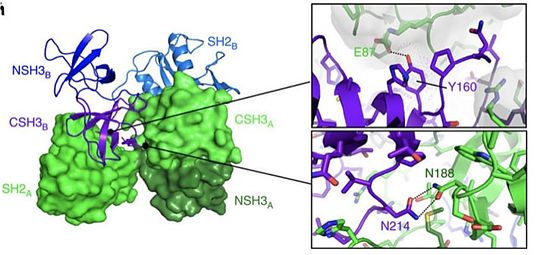
Grb2 protein is especially involved in the setting up of cellular oncognesis in prostate, colon and lung cancers. This role is mainly due to its essential role in signal transduction in the MAP kinase pathway known to induce mitosis. In this pathway, Grb2 binds to the oncogenic protein SOS under its monomeric form. Yet SOS can also be found in its dimeric form in the cell. Dimerization of Grb2 is dependent upon several factors like the phosphorylation of or the binding of ligand on the SH2 domain of the same protein. Mainly, phosphorylation induces the dissociation of the Grb2 dimer induce an increase in the MAP kinase pathway activation by the binding of SOS. The phosphorylated state of has been discovered in severa pre-metastatis cancers. This highly suggest that pY160 could be a oncogenic marker in humans. A new therapeutic way could therefore be considered by stabilizing Grb2 in its dimeric form. This could be achieve with a protein acting as an irreversible cross-link at the interface between the two units. [21]
References
- ↑ Gan W, Roux B. Binding specificity of SH2 domains: insight from free energy simulations. Proteins. 2009 Mar;74(4):996-1007. doi: 10.1002/prot.22209. PMID:18767163 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/prot.22209
- ↑ Musacchio A, Noble M, Pauptit R, Wierenga R, Saraste M. Crystal structure of a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):851-5. PMID:1279434 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/359851a0
- ↑ Fath I, Schweighoffer F, Rey I, Multon MC, Boiziau J, Duchesne M, Tocque B. Cloning of a Grb2 isoform with apoptotic properties. Science. 1994 May 13;264(5161):971-4. PMID:8178156
- ↑ Jiang X, Sorkin A. Coordinated traffic of Grb2 and Ras during epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis visualized in living cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002 May;13(5):1522-35. PMID:12006650 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.01-11-0552
- ↑ Tybulewicz VL. Vav-family proteins in T-cell signalling. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005 Jun;17(3):267-74. PMID:15886116 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2005.04.003
- ↑ Yokouchi M, Kondo T, Houghton A, Bartkiewicz M, Horne WC, Zhang H, Yoshimura A, Baron R. Ligand-induced ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor involves the interaction of the c-Cbl RING finger and UbcH7. J Biol Chem. 1999 Oct 29;274(44):31707-12. PMID:10531381
- ↑ Waterman H, Katz M, Rubin C, Shtiegman K, Lavi S, Elson A, Jovin T, Yarden Y. A mutant EGF-receptor defective in ubiquitylation and endocytosis unveils a role for Grb2 in negative signaling. EMBO J. 2002 Feb 1;21(3):303-13. PMID:11823423 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/21.3.303
- ↑ Park RK, Erdreich-Epstein A, Liu M, Izadi KD, Durden DL. High affinity IgG receptor activation of Src family kinases is required for modulation of the Shc-Grb2-Sos complex and the downstream activation of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced) oxidase. J Immunol. 1999 Dec 1;163(11):6023-34. PMID:10570290
- ↑ Oksvold MP, Skarpen E, Wierod L, Paulsen RE, Huitfeldt HS. Re-localization of activated EGF receptor and its signal transducers to multivesicular compartments downstream of early endosomes in response to EGF. Eur J Cell Biol. 2001 Apr;80(4):285-94. PMID:11370743 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1078/0171-9335-00160
- ↑ Buchse T, Horras N, Lenfert E, Krystal G, Korbel S, Schumann M, Krause E, Mikkat S, Tiedge M. CIN85 interacting proteins in B cells-specific role for SHIP-1. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Oct;10(10):M110.006239. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M110.006239., Epub 2011 Jul 1. PMID:21725061 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M110.006239
- ↑ Lynch DK, Daly RJ. PKB-mediated negative feedback tightly regulates mitogenic signalling via Gab2. EMBO J. 2002 Jan 15;21(1-2):72-82. PMID:11782427
- ↑ Erdreich-Epstein A, Liu M, Kant AM, Izadi KD, Nolta JA, Durden DL. Cbl functions downstream of Src kinases in Fc gamma RI signaling in primary human macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Apr;65(4):523-34. PMID:10204582
- ↑ Schulze WX, Deng L, Mann M. Phosphotyrosine interactome of the ErbB-receptor kinase family. Mol Syst Biol. 2005;1:2005.0008. Epub 2005 May 25. PMID:16729043 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/msb4100012
- ↑ Wong A, Lamothe B, Lee A, Schlessinger J, Lax I. FRS2 alpha attenuates FGF receptor signaling by Grb2-mediated recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase Cbl. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 May 14;99(10):6684-9. Epub 2002 May 7. PMID:11997436 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.052138899
- ↑ Morrison KB, Tognon CE, Garnett MJ, Deal C, Sorensen PH. ETV6-NTRK3 transformation requires insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling and is associated with constitutive IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation. Oncogene. 2002 Aug 22;21(37):5684-95. PMID:12173038 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205669
- ↑ Holgado-Madruga M, Emlet DR, Moscatello DK, Godwin AK, Wong AJ. A Grb2-associated docking protein in EGF- and insulin-receptor signalling. Nature. 1996 Feb 8;379(6565):560-4. PMID:8596638 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/379560a0
- ↑ Sorkin A, McClure M, Huang F, Carter R. Interaction of EGF receptor and grb2 in living cells visualized by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) microscopy. Curr Biol. 2000 Nov 2;10(21):1395-8. PMID:11084343
- ↑ Jones RB, Gordus A, Krall JA, MacBeath G. A quantitative protein interaction network for the ErbB receptors using protein microarrays. Nature. 2006 Jan 12;439(7073):168-74. Epub 2005 Nov 6. PMID:16273093 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature04177
- ↑ McShea A, Zelasko DA, Gerst JL, Smith MA. Signal transduction abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease: evidence of a pathogenic stimuli. Brain Res. 1999 Jan 9;815(2):237-42. PMID:9878757
- ↑ Li X, Multon MC, Henin Y, Schweighoffer F, Venot C, Josef J, Zhou C, LaVecchio J, Stuckert P, Raab M, Mhashilkar A, Tocque B, Marasco WA. Grb3-3 is up-regulated in HIV-1-infected T-cells and can potentiate cell activation through NFATc. J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):30925-33. PMID:10906142 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M005535200
- ↑ Ahmed Z, Timsah Z, Suen KM, Cook NP, Lee GR 4th, Lin CC, Gagea M, Marti AA, Ladbury JE. Grb2 monomer-dimer equilibrium determines normal versus oncogenic function. Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 24;6:7354. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8354. PMID:26103942 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8354