This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
IGF1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Biological structures and interactions == | == Biological structures and interactions == | ||
In the pituitary gland inside the brain, Growth Hormone (GH) is secreted and its release enable transcription of IGF-1 in liver and depending on the nutritional state, a paracrine or autocrine activation IGF-1 occurs. IGF-1 then acts as a ligand and can interact with Insulin Receptor protein and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein. | In the pituitary gland inside the brain, Growth Hormone (GH) is secreted and its release enable transcription of IGF-1 in liver and depending on the nutritional state, a paracrine or autocrine activation IGF-1 occurs. IGF-1 then acts as a ligand and can interact with Insulin Receptor protein and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein. | ||
| + | |||
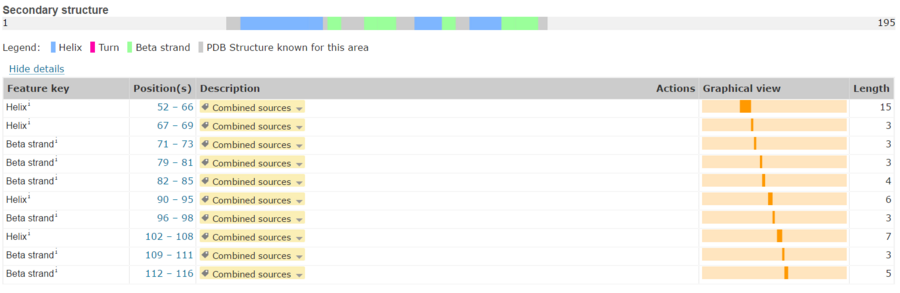
=== Structures === | === Structures === | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
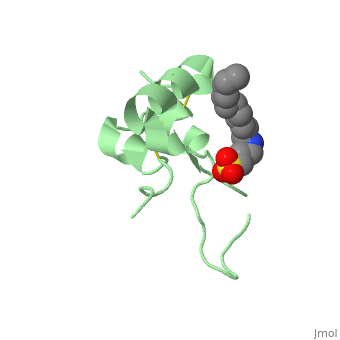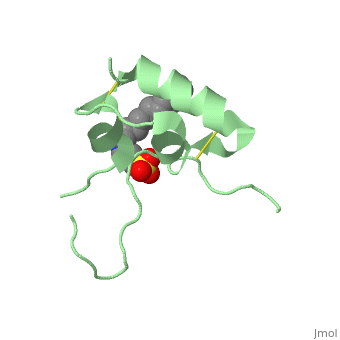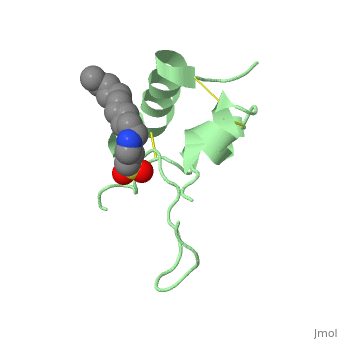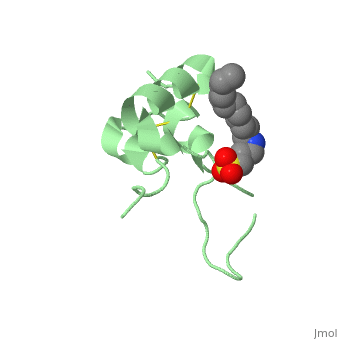
Its 3D structure is shown on the right. | Its 3D structure is shown on the right. | ||
| + | |||
=== Stimulating interaction : IGF1 - IGF1R === | === Stimulating interaction : IGF1 - IGF1R === | ||
| Line 49: | Line 51: | ||
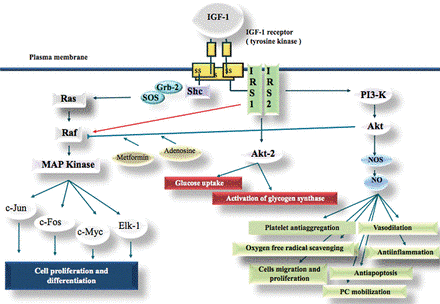
Secretion of GH induces IGF1 transcription but IGF1 can also be secreted by the liver without GH stimulation. After binding to its receptors (IGF1R and | Secretion of GH induces IGF1 transcription but IGF1 can also be secreted by the liver without GH stimulation. After binding to its receptors (IGF1R and | ||
insulin receptor), IGF1 activates a signalling cascade by autocrine or paracrine way resulting in cell growth, proliferation and survival against apoptose. | insulin receptor), IGF1 activates a signalling cascade by autocrine or paracrine way resulting in cell growth, proliferation and survival against apoptose. | ||
| - | However IGFBPs can activate or inhibate IGF1 actions on their target cells.<ref>http://www.hal.inserm.fr/tel-00932409/,26/01/2017</ref> <ref>Elena Conti, Maria Beatrice Musumeci, et all, IGF-1 and atherothrombosis: relevance to pathophysiology and therapy,Clinical Science, May 01, 2011, 120 (9) 377-402</ref> | + | However IGFBPs can activate or inhibate IGF1 actions on their target cells.<ref>http://www.hal.inserm.fr/tel-00932409/, 26/01/2017</ref> <ref>Elena Conti, Maria Beatrice Musumeci, et all, IGF-1 and atherothrombosis: relevance to pathophysiology and therapy,Clinical Science, May 01, 2011, 120 (9) 377-402</ref> |
If IGF1 is lacking, it reduces cell growth and can also induce dysfunctions or even apoptose of cells, thus creating diseases. | If IGF1 is lacking, it reduces cell growth and can also induce dysfunctions or even apoptose of cells, thus creating diseases. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 60: | ||
Knowing that IGF1 leads to cell proliferation with apoptose inhibition, if DNA undergoes alterations or mutations, those alterated cells will proliferate and survive even though it should result in their elimination by apoptose. Hence inducing cancer proliferation. <ref>R. Kaaks, Médecine Nucléaire - Imagerie fonctionnelle et métabolique, 2003, vol.27, n°1</ref> | Knowing that IGF1 leads to cell proliferation with apoptose inhibition, if DNA undergoes alterations or mutations, those alterated cells will proliferate and survive even though it should result in their elimination by apoptose. Hence inducing cancer proliferation. <ref>R. Kaaks, Médecine Nucléaire - Imagerie fonctionnelle et métabolique, 2003, vol.27, n°1</ref> | ||
| - | The Laron syndrom, caused by mutation of GH genes, features growth failure and high insulin sensibility. Thus reducing concentration of GH receptors and inducing an IGF1 low level. Treatment is based on biosynthetic IGF1 carry out in mecasermin (a drug developed by Genentech) with IGFBP3 and recombinant human IGF1. One main side effect is hypoglycemia due to IGF1 activity. <ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laron_syndrome,26/01/2017</ref> | + | The Laron syndrom, caused by mutation of GH genes, features growth failure and high insulin sensibility. Thus reducing concentration of GH receptors and inducing an IGF1 low level. Treatment is based on biosynthetic IGF1 carry out in mecasermin (a drug developed by Genentech) with IGFBP3 and recombinant human IGF1. One main side effect is hypoglycemia due to IGF1 activity. <ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laron_syndrome, 26/01/2017</ref> |
Revision as of 19:47, 26 January 2017
Insulin-like growth factor 1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Patrick Jouandin. Rôle de la voie de signalisation Insuline dans le couplage des informations nutritionnelles et développementales au cours de l'ovogenèse chez la drosophile. Sciences agricoles.Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, 2013. Français.<NNT : 2013NICE4102>.<tel-00932409>
- ↑ http://www.hal.inserm.fr/tel-00932409/, 26/01/2017
- ↑ Elena Conti, Maria Beatrice Musumeci, et all, IGF-1 and atherothrombosis: relevance to pathophysiology and therapy,Clinical Science, May 01, 2011, 120 (9) 377-402
- ↑ R. Kaaks, Médecine Nucléaire - Imagerie fonctionnelle et métabolique, 2003, vol.27, n°1
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laron_syndrome, 26/01/2017
- ↑ Richard Holt, Diabetes Voice, Septembre 2003, Volume 48, Numéro 2
- ↑ Srinivas Teppala, Anoop Shankar, Diabetes Care, Octobre 2010, Volume 33, Number 10
- ↑ Westwood AJ, Beiser A, et all, Neurology, 2014 May, 6;82(18):1613-9
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Maxime Julliot, Alexia Kindler, Virginie Nakad, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky