We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Ophelie Lefort/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Neutrophil Serine 4 or Serine Protease 57 (4Q7X)== | ==Neutrophil Serine 4 or Serine Protease 57 (4Q7X)== | ||
<StructureSection load='4Q7X' size='350' side='right' caption='[[4Q7X]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.55Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4Q7X' size='350' side='right' caption='[[4Q7X]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.55Å' scene=''> | ||
| - | |||
NSP4 also called Neutrophil Serine 4 (NSP4) or Serine Protease 57 (PRSS57),is member of the peptidase S1 family of proteins. It is one of the neutrophil serine protease in the cytoplasmic granules of neutrophils. This enzyme is expressed in bone marrow and takes part of the immune response against pathogens. NSP4 is located in the telomeric region of the chromosome 19. The protein cleaves preferentially after Arg residues but also after citrulline and methylarginie residues. | NSP4 also called Neutrophil Serine 4 (NSP4) or Serine Protease 57 (PRSS57),is member of the peptidase S1 family of proteins. It is one of the neutrophil serine protease in the cytoplasmic granules of neutrophils. This enzyme is expressed in bone marrow and takes part of the immune response against pathogens. NSP4 is located in the telomeric region of the chromosome 19. The protein cleaves preferentially after Arg residues but also after citrulline and methylarginie residues. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
== Interaction == | == Interaction == | ||
| - | N terminus of NSP4 has been shown to be cleaved off by Cathepsin C in | + | Like in other trypsin-like proteases D226 is inaccessible to the substrate but helps stabilize the closed S1 pocket by forming an H-bond with the F190 amide. The 99-loop which forms the S2 and S4 substrate interaction sites, is weak and may be implicated in NSP4 allosteric regulation. |
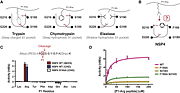
| - | Natural serine protease inhibitors of NSP4 are present in human plasma and can form covalent NSP4-serpin complexes in vitro ( | + | NSP4 compared to the other trypsin-like proteases has some specificity as the arginine side chain movement from the canonical "down" to the noncanonical "up" position in NSP4, which is accomplished by a rotation of the Chi2 angle by 160°, this is possible thanks to F190 which provides a hydrophobic platform that interacts with the aliphatic portion of the P1-arginine side chain. All other residue positions are preserved. The specificity for P1-arginine is conferred by H-bonds between guanidinium group and three H-bonds acceptors (S216, S192, G217). This specificity allows NSP4 to cleave citrulline, which is not cleaved by other trypsin-like proteases because of its non-charged propriety, and the impossibility to do salt-bridges. Other trypsin-like proteases are not able to cleave methylarginine neither because of a steric clash with the methyl group, which is not an issue for NSP4 since the methyl group is exposed to the solvent. |
| + | The capacity to cleave these post-translationally modified arginine utility may be to act against microbial and virulence factors containing modified arginine or to interact with chemokines. | ||
| + | |||
| + | N terminus of NSP4 has been shown to be cleaved off by Cathepsin C and occurs during the translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum before the enzyme is stored in cytoplasmic granules. Natural serine protease inhibitors of NSP4 are present in human plasma and can form covalent NSP4-serpin complexes in vitro (antithrombin for example which act as a suicide substrate with NSP4). However, in vivo, antithrombin can not trap NSP4 because of the presence of other neutrophil proteases. | ||
Revision as of 07:53, 27 January 2017
Neutrophil Serine 4 or Serine Protease 57 (4Q7X)
| |||||||||||
References
[1] NSP4 is stored in azurophil granules and released by activated neutrophils as active endoprotease with restricted specificity, NCBI
[2] NSP4, an elastase-related protease in human neutrophils with arginine specificity, NCBI
[3] Tailor-made inflammation: how neutrophil serine proteases modulate the inflammatory response, NCBI
[4] Role of neutrophils in innate immunity: a systems biology-level approach, NCBI
[5] Neutrophils: Their Role in Innate and Adaptive Immunity, NCBI
[6] Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria, NCBI
[7] Tailor-made inflammation: how neutrophil serine proteases modulate the inflammatory response, NCBI
- ↑ S.. Jack Lin, Ken C. Dong, Charles Eigenbrot, Menno van Lookeren Campagne, Daniel Kirchhofer Structures of Neutrophil Serine Protease 4 Reveal an Unusual Mechanism of Substrate Recognition by a Trypsin-Fold Protease DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.07.008
- ↑ Natascha C. Perera, Karl-Heinz Wiesmüller, Maria Torp Larsen, Beate Schacher, Peter Eickholz, Niels Borregaard and Dieter E. Jenne NSP4 Is Stored in Azurophil Granules and Released by Activated Neutrophils as Active Endoprotease with Restricted Specificity DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1301293