This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Aldolase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
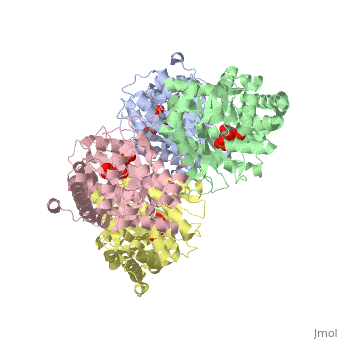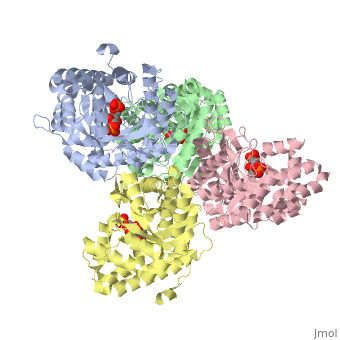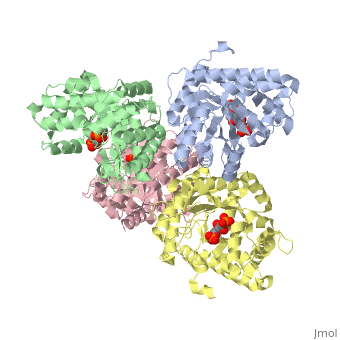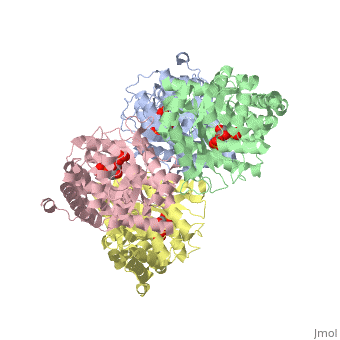
<StructureSection load='3mmt' size='340' side='right' caption='Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase tetramer complex with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, [[3mmt]]|' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3mmt' size='340' side='right' caption='Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase tetramer complex with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, [[3mmt]]|' scene=''> | ||
| + | =Aldolase= | ||
| + | '''Fructose-6-phosphate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of fructose-6-phosphate<ref>PMID:11120740</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase''' cconverts 2-deoxy-D-ribose-5-phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and acetaldehyde<ref>PMID:25229427</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Dihydroneopterin aldolase''' catalyzes the conversion of 7,8-dihydropterin to 6-hydroxymethyl-7,8-dihydropterin. It is part of the folate synthesis <ref>PMID:15107504</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase''' catalyzes the condensation of dihydroxyacetone phosphate with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to produce tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate<ref>PMID:11940603</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''Fuculose-1-phosphate aldolase''' catalyzes the cleavage of fuculose-1-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and lactaldehyde<ref>PMID:10821675</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | '''HpcH/HpaI aldolase''' catalyzes the conversion of 4-hydroxy-2-oxo-heptane-1,7-dioate intu pyruvate and succinate. It is part of the aromatic compounds degradation<ref>PMID:17881002</ref>.<br /> | ||
= Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase = | = Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase = | ||
==Introduction and Structure== | ==Introduction and Structure== | ||
| Line 106: | Line 113: | ||
**[[4s1f]] – EcF6PA 1 <br /> | **[[4s1f]] – EcF6PA 1 <br /> | ||
**[[4rz4]], [[4rxg]], [[4rxf]] – EcF6PA 1 (mutant)<br /> | **[[4rz4]], [[4rxg]], [[4rxf]] – EcF6PA 1 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Tagatose–1,6-bisphosphate aldolase | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3myo]], [[3myp]], [[3mhf]], [[3jrk]] – SpTBPA – ''Streptococcus pyogenes''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5f2i]] – SpDERA2 (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ff7]] – SpDERA + glycerol-3-phosphate + glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5f4w]] – SpDERA2 + phosphonotagatose <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5f4s]] – SpDERA2 + phosphonofructose <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5f2g]] – SpDERA2 (mutant) + phosphonofructose <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5f2m]], [[5f2l]] – SpDERA2 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3iv3]] - TBPA – ''Streptococcus mutans''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3mhg]] - SpTBPA + reaction intermediate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3kao]] – SaTBPA – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1gvf]] - EcTBPA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5hjl]] - TBPA – ''Streptococcus porcinus''<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Fuculose–1-phosphate aldolase | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2opi]] – FPA – ''Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2flf]], [[2fk5]] – TtFPA - ''Thermus thermophilus''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1fua]], [[2fua]], [[3fua]] – EcFPA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1e46]], [[1e47]], [[1e48]], [[1e49]], [[1e4a]], [[1e4b]], [[1e4c]], [[1dzu]], [[1dzw]], [[1dzx]], [[1dzy]], [[1dzz]], [[1dzv]] – EcFPA (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4fua]] – EcFPA + oxamate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4c24]] ,[[4c25]] – SpFPA - ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4xxf]] – FPA – ''Glaciozyma antarctica''<br /> | ||
*Deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase | *Deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase | ||
| Line 261: | Line 243: | ||
**[[4to8]] – SsFBPA <br /> | **[[4to8]] – SsFBPA <br /> | ||
**[[5u7s]] – ALD – ''Acinetobacter baumannii''<br /> | **[[5u7s]] – ALD – ''Acinetobacter baumannii''<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Tagatose–1,6-bisphosphate aldolase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[3myo]], [[3myp]], [[3mhf]], [[3jrk]] – SpTBPA – ''Streptococcus pyogenes''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5f2i]] – SpDERA2 (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5ff7]] – SpDERA + glycerol-3-phosphate + glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5f4w]] – SpDERA2 + phosphonotagatose <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5f4s]] – SpDERA2 + phosphonofructose <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5f2g]] – SpDERA2 (mutant) + phosphonofructose <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5f2m]], [[5f2l]] – SpDERA2 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3iv3]] - TBPA – ''Streptococcus mutans''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3mhg]] - SpTBPA + reaction intermediate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3kao]] – SaTBPA – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1gvf]] - EcTBPA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5hjl]] - TBPA – ''Streptococcus porcinus''<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Fuculose–1-phosphate aldolase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[2opi]] – FPA – ''Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2flf]], [[2fk5]] – TtFPA - ''Thermus thermophilus''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1fua]], [[2fua]], [[3fua]] – EcFPA<br /> | ||
| + | **[[1e46]], [[1e47]], [[1e48]], [[1e49]], [[1e4a]], [[1e4b]], [[1e4c]], [[1dzu]], [[1dzw]], [[1dzx]], [[1dzy]], [[1dzz]], [[1dzv]] – EcFPA (mutant)<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4fua]] – EcFPA + oxamate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4c24]] ,[[4c25]] – SpFPA - ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4xxf]] – FPA – ''Glaciozyma antarctica''<br /> | ||
*Sphingosin-1-phosphate aldolase | *Sphingosin-1-phosphate aldolase | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 28 February 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Aldolase
Updated on 28-February-2017
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Schurmann M, Sprenger GA. Fructose-6-phosphate aldolase is a novel class I aldolase from Escherichia coli and is related to a novel group of bacterial transaldolases. J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 6;276(14):11055-61. Epub 2000 Dec 18. PMID:11120740 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008061200
- ↑ Salleron L, Magistrelli G, Mary C, Fischer N, Bairoch A, Lane L. DERA is the human deoxyribose phosphate aldolase and is involved in stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1843(12):2913-25. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.007. Epub 2014 Sep 16. PMID:25229427 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.007
- ↑ Goyer A, Illarionova V, Roje S, Fischer M, Bacher A, Hanson AD. Folate biosynthesis in higher plants. cDNA cloning, heterologous expression, and characterization of dihydroneopterin aldolases. Plant Physiol. 2004 May;135(1):103-11. Epub 2004 Apr 23. PMID:15107504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.038430
- ↑ Hall DR, Bond CS, Leonard GA, Watt CI, Berry A, Hunter WN. Structure of tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Insight into chiral discrimination, mechanism, and specificity of class II aldolases. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):22018-24. Epub 2002 Apr 8. PMID:11940603 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M202464200
- ↑ Joerger AC, Gosse C, Fessner WD, Schulz GE. Catalytic action of fuculose 1-phosphate aldolase (class II) as derived from structure-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 2000 May 23;39(20):6033-41. PMID:10821675
- ↑ Rea D, Fulop V, Bugg TD, Roper DI. Structure and mechanism of HpcH: a metal ion dependent class II aldolase from the homoprotocatechuate degradation pathway of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 2;373(4):866-76. Epub 2007 Jun 26. PMID:17881002 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.048
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Voet, D, Voet, J, & Pratt, C. (2008). Fundamentals of biochemistry, third edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- ↑ Protein: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from human (homo sapiens), muscle isozyme. (2009). Retrieved from http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Gefflaut, T., B. Casimir, J. Perie, and M. Willson. "Class I Aldolases: Substrate Specificity, Mechanism, Inhibitors and Structural Aspects." Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol.. 63. (1995): 301-340.
- ↑ Dalby A, Dauter Z, Littlechild JA. Crystal structure of human muscle aldolase complexed with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate: mechanistic implications. Protein Sci. 1999 Feb;8(2):291-7. PMID:10048322
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Sygusch, J., and Beaudry, D. "Allosteric communication in mammalian muscle aldolase." Biochem. J.. 327. (1997): 717-720.
- ↑ Paolella, G, Buono, P, Mancini, F P, Izzo, P, and Salvatore, F. "Structure and expression of mouse aldolase genes." Eur. J. Biochem.. 156. (1986): 229-235.
- ↑ Buono, P, Cassano, S, Alfieri, A, Mancini, A, and Salvatore, F. "Human aldolase C gene expression is regulated by adenosine 30,50-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) in PC12 cells." Gene. 291. (2002): 115-121.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Sophie Mullinix, Jaime Prilusky, Austin Drake, David Canner