We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1053
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Biological Function == | == Biological Function == | ||
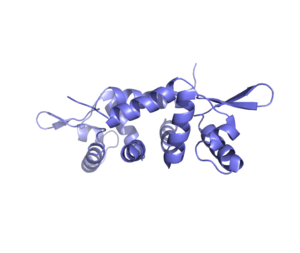
| - | Czr A is a transcriptional repressor protein responsible for the regulation of the Chromosome Determined Zinc Responsible (Czr) operon. The Czr operon contains genes for the proteins Czr A and Czr B. Czr B is a Zinc transport protein which moves | + | Czr A is a transcriptional repressor protein responsible for the regulation of the Chromosome Determined Zinc Responsible (Czr) operon. The Czr operon contains genes for the proteins Czr A and Czr B. Czr B is a Zinc transport protein which moves Zn 2+ out of a cell. Czr A regulates this process by controlling the degree to which Czr B is expressed. When relatively low amounts of zinc are present in the cell Czr A will bind to DNA,preventing the progression of RNA polymerase and thus inhibiting expression of Czr B. Decreased expression of Czr B results in the ability of the cell to retain Zn 2+ more readily. Because Czr A and Czr B are transcribed as part of the same operon, there must be a way that Czr A is inhibited to allow full transcription of Czr B. Czr A is inhibited by the binding of two Zn 2+ ions, which is ideal considering that this mechanism allows for Zn 2+ concentration inside the cell to determine the need for Zn 2+ transport out of the cell. Zn 2+ competitively inhibits the binding of DNA to Czr A. Czr A has two distinct conformations, one of which binds Zn 2+ with very high affinity that has virtually no affinity towards DNA binding, the other having a high affinity for DNA binding but very little affinity for Zn 2+. |
| - | + | ||
===DNA Binding === | ===DNA Binding === | ||
===Zinc Binding === | ===Zinc Binding === | ||
Revision as of 13:31, 14 March 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Czr A Staphylococcus aureus
| |||||||||||