This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Madelyn Smith/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(rough intro, mechanism and pdb pic added) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
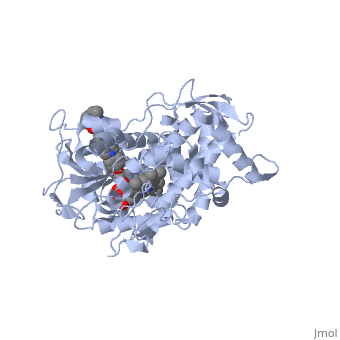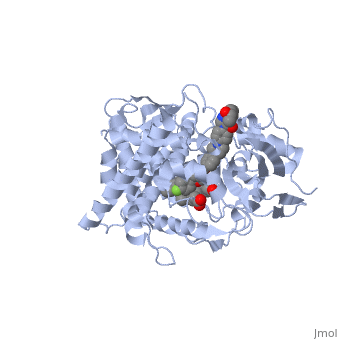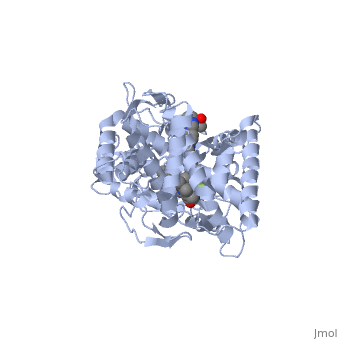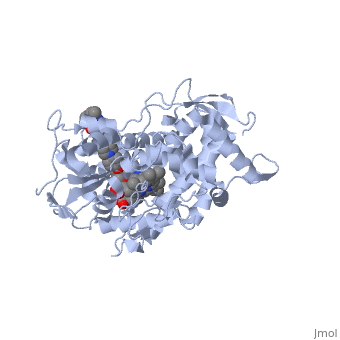
| + | <Structure load='5FSA' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Crystal structure of sterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51) from a pathogenic yeast Candida albicans in complex with the antifungal drug posaconazole' /> | ||
When administered, Posaconazole acts as an antifungal by blocking Lanosterol 14α-demethylase, a P-450 dependant fungal enzyme containing heme as a cofactor. Posaconazole binds to the heme cofactor that the enzyme contains, which prevents the fungus from creating ergosterol, an essential component of the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol performs in fungal cells how cholesterol does in animal cells, making the cell membrane less permeable. Without it, the cells can no longer proliferate and eventually die because the cell membranes become “leaky”, releasing essential organic components from the cell’s interior and preventing it from performing normal cellular functions. In this way, Posaconazole acts both as fungicidal and fungistatic. | When administered, Posaconazole acts as an antifungal by blocking Lanosterol 14α-demethylase, a P-450 dependant fungal enzyme containing heme as a cofactor. Posaconazole binds to the heme cofactor that the enzyme contains, which prevents the fungus from creating ergosterol, an essential component of the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol performs in fungal cells how cholesterol does in animal cells, making the cell membrane less permeable. Without it, the cells can no longer proliferate and eventually die because the cell membranes become “leaky”, releasing essential organic components from the cell’s interior and preventing it from performing normal cellular functions. In this way, Posaconazole acts both as fungicidal and fungistatic. | ||
Revision as of 18:14, 27 March 2017
|
Contents |
Introduction
Noxafil, also known as Posaconazole, is an antifungal drug used to treat fungal infections caused by Candida and Aspergillus species, as well as treat other fungal infections such as chromoblastomycosis, mycetoma, and coccidioidomycosis. Noxafil is also often used when other antifungal medicines are tolerated or if the patient is immunocompromised. Noxafil is under the triazole class of antifungal drugs and works by inhibiting the production of ergosterol, an important factor in fungi cell membranes, leading to prevention of cell growth and ultimately death.
Structure
- Chemical Formula: C37H42F2N8O4
- Molecular Weight: 700.792 g/mol
- IUPAC name: 4-[4-[4-[4-[[(3R,5R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)oxolan-3-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-2-[(2S,3S)-2-hydroxypentan-3-yl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
Function
Relevance
Mechanism
|
When administered, Posaconazole acts as an antifungal by blocking Lanosterol 14α-demethylase, a P-450 dependant fungal enzyme containing heme as a cofactor. Posaconazole binds to the heme cofactor that the enzyme contains, which prevents the fungus from creating ergosterol, an essential component of the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol performs in fungal cells how cholesterol does in animal cells, making the cell membrane less permeable. Without it, the cells can no longer proliferate and eventually die because the cell membranes become “leaky”, releasing essential organic components from the cell’s interior and preventing it from performing normal cellular functions. In this way, Posaconazole acts both as fungicidal and fungistatic.