Found at high concentrations in the brain and bordering tissues, Caspase-6 has been implicated in several neurological diseases including Alzheimer's and dementia[1][1]. It's primarily involved in apoptosis through a largely ambiguous mechanism. It is classified as an [2]endopeptidase as it cleaves an internal peptide bond of its substrate. It has relatively low specificity in the binding site which allows for a variety of substrates, including other caspase enzymes and neuronal proteins to bind[2]. Furthermore, it is a part of the cysteine-aspartate family[3], which have these critical amino acid residues in the active site of the enzyme. Caspase-6 has both an inactive zinc-bound conformation and an active ligand-bound conformation, which are largely regulated by variations in zinc concentration[2].
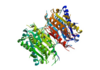
This is the figure legend of the thumbnail
Structure
Active Site
In order to function as an endoprotease, Caspase-6 binds a , which can include neuronal proteins and tubulins
[4], in its active site. This binding groove contains three critical amino acid residues necessary to perform cleavage of the peptide bonds. Together,, , and form a
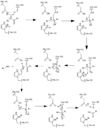
Cystine Aspartase mechanism
. In the theorized mechanism, His-121 acts as an acid catalyst, Glu-123 acts as a base catalyst to deprotonate Cys-163, which then acts as covalent catalyst.
Zinc Exosite
Caspase-6 function is inhibited by the binding of a ion, which binds to an instead of the . This allosteric site is located on the outside of the protein and it is distal to the active site. The Zinc ion is bound to , Lys-36, Glu-244, and His-287, once the ion is bound to the protein it is then stabilized by a single water molecule. The binding of Zinc at the exosite is suggested to cause a conformational change to the protein, which then causes a change in the active site, which inhibits Caspase-6's ability to bind to substrate. Zinc binding to the exosite is tightly regulated, because it inhibits Caspase-6's ability to inititate apoptosis.
Activation of Caspase-6
Structural Units involved in autoactivation
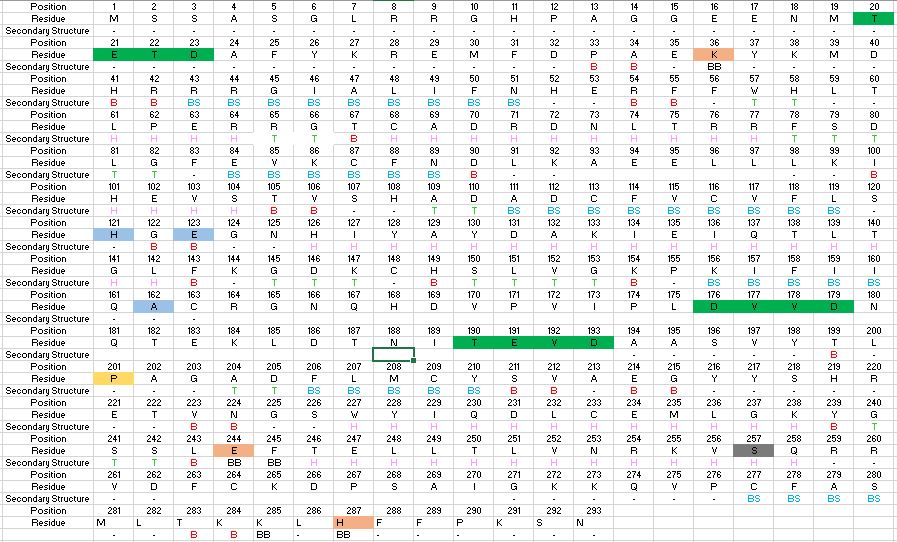
Before Caspase-6 is a functional and active dimer, the enzyme exists as a procaspase. This precursor enzyme is modified by self-processing, a characteristic unique to Caspase-6. The unprocessed enzyme contains a small and large subunit, a pro domain, as well as a intersubunit linker. To become active, the intersubunit linker binds to the active site, where it is then cleaved. Other cleavages must occur as well for the enzyme to become active, specifically at TETD23 of the pro-domain, DVVD179, and TEVD193 amino acid sequences. Cleavage at these sites occurs in a specific sequence. To begin, the site within the pro-domain, TETD23, must be cleaved. This cleavage is then followed by either DVVD179 or TEVD193. It has been proposed that this sequence of cleavage is due to the structure of Caspase-6, which allows the pro-domain to be more readily available to enter the active site. To some extent, the pro-domain inhibits Caspase-6's ability to cleave the intersubunit loop and self-activate, but this also happens in a currently unknown mechanism. The pro-domain is released after the cleavage at TETD23, which then allows the two subunits to interact to form the active dimer.
Caspase-6 can also be activated by other caspases as an alternate to auto-activation.
It has been found that Caspase-6 can undergo activation without any other caspases, so there is a suggested self-cleavage mechanism for Caspase-6. The intramolecular cleavage of TEVD193 is essential for the initiation caspase-6 activation without Caspase-3 present. As mentioned above the pro-domain somehow inhibits the intramolecular cleavage of TEVD193, but currently the mechanism is not known. The TETD23 and TEVD193 cleavage sites are extremly similar to one another, but the TETD23 cleavage site is always cleaved before TEVD193. This indicates that the TETD23 cleavage site is more readily available for cleavage. The result of the TETD23 cleavage site priority is that the prodomain acts as a “suicide protector”, which protects the TEVD193 cleavage site from self-cleavage[5]. This protection is useful when there are low levels of protein it also helps explain why the pro-domain inhibits self-activation.
Inhibition
Zinc Inhibition
Primary inhibition of Caspase-6 occurs when a zinc ion binds to the exosite containing Lys-36, Glu-244, and His-287 of the active dimer. In addition to these residues, the zinc interacts with one water molecule from the cytoplasm. It has been proposed that helices of the active dimer must rotate or move in some other way to provide these ideal interactions with zinc. This subtle shift is most likely the cause for allosteric inhibition. As the helices move to bind zinc, the amino acids of the active site become misaligned. The altered positions of the amino acids no longer provide ideal interactions for incoming substrates. After zinc binds, no new substrates enter the active site. Thus, Caspase-6 is effectively inhibited.
Phosphorylation
The function of Caspase-6 can be inhibited by phosphorylation of Ser-257. The exact mechanism of this reaction remains unidentified at the time of publication, but proceeds when ARK5 kinase is present. This modification can occur before and after zymogen activation or auto-processing. The phosphoryl group inhibits Caspase-6 through steric interference. When Ser-257 is phosphorylated, the amino acid residue interacts with Pro-201, causing a shift in the helices of Caspase-6. The shift misaligns and disrupts residues found in the active site. This conformational difference prevents the inter-subunit loop from entering during zymogen activation and the self-cleaved active dimer cannot be formed. Additionally, no new substrate is able to enter the active site.
Function
Caspase-6 involvement in Alzheimer's Disease
Caspase-6 activity is associated with the formation of lesions within the Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and they can become present very early on during the disease's progression. Proapoptotic protein p53 is present at increased levels within AD brains, which seems to directly increase the transcription of Caspase-6. Treatments of Alzheimer's include targeting active Caspase-6 proteins because staining has found active Caspase-6 within the hippocampus and cortex of the Brain within in mild, moderate, and severe cases of AD, which indicates that Caspase-6 plays a predominate role in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's. There has been research conducted that shows activation of Caspase-6 in AD could cause disruption of the cytoskeleton network of neurons, which then causes handicapped synaptic plasticity.
Luke's free space
If is , the activity of this protein is inhibited.
 If binds to the protein, the activity of the active site is inhibited.
If binds to the protein, the activity of the active site is inhibited.
Inactive state of caspase 6:
Relevance





