We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1072
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structural Overview == | == Structural Overview == | ||
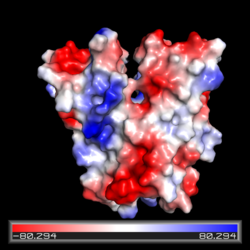
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:DgcZ full molecule all sites and ligands labeled.png|250 px|left|thumb|Diguanylate cyclase DgcZ from “E. Coli” with Domains Labeled]] |
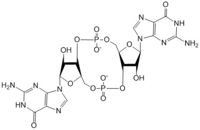
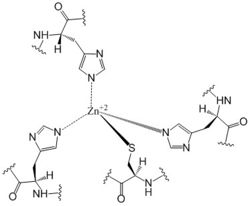
The DgcZ protein has C2 symmetry composed of two domains. The catalytic glycine-glycine-glutamate-glutamate-phenylalanine (GGEEF) domain responsible for synthesizing c-di-GMP and the regulatory chemoreceptor zinc binding (CZB) domain comprising two zinc binding sites. DgcZ binds zinc with sub-femtomolar affinity. When zinc is bound, the CZB and GGEEF domains adopt conformations that inhibit DgcZ function <sup>[1]</sup>. Enzyme DgcZ was co-crystallized with Zinc fixing the structure in its inactivate conformation. The CZB domain is common to many bacterial lineages, appearing most commonly in bacterial chemoreceptors involved in <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemotaxis chemotaxis]</span>. The second most common group of CZB domains is that of DgcZ homologs. The domain has an important role in signal transduction of bacteria. Many bacterial proteins from differing strands of ''E. coli'' contain CZB and GGDEF domains<sup>[2]</sup>. The GGEEF domain of DgcZ is common to this family of enzymes containing the GGDEF domain. ''E. coli'' DgcZ is a protein made of two domains each of which is a symmetric homodimer. It exhibits <scene name='69/694239/C2_symmetry/6'>C2</scene> symmetry down its central axis. The GGEEF domain is catalytic in that it contains the active sites used for cyclizing GTP into c-di-GMP. The CZB domain is used for ligand-mediated regulation of c-di-GMP production. Zinc binds as an allosteric inhibitor in coordination with four residues to shift the protein into an inactive conformation<sup>[1]</sup>. | The DgcZ protein has C2 symmetry composed of two domains. The catalytic glycine-glycine-glutamate-glutamate-phenylalanine (GGEEF) domain responsible for synthesizing c-di-GMP and the regulatory chemoreceptor zinc binding (CZB) domain comprising two zinc binding sites. DgcZ binds zinc with sub-femtomolar affinity. When zinc is bound, the CZB and GGEEF domains adopt conformations that inhibit DgcZ function <sup>[1]</sup>. Enzyme DgcZ was co-crystallized with Zinc fixing the structure in its inactivate conformation. The CZB domain is common to many bacterial lineages, appearing most commonly in bacterial chemoreceptors involved in <span class="plainlinks">[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemotaxis chemotaxis]</span>. The second most common group of CZB domains is that of DgcZ homologs. The domain has an important role in signal transduction of bacteria. Many bacterial proteins from differing strands of ''E. coli'' contain CZB and GGDEF domains<sup>[2]</sup>. The GGEEF domain of DgcZ is common to this family of enzymes containing the GGDEF domain. ''E. coli'' DgcZ is a protein made of two domains each of which is a symmetric homodimer. It exhibits <scene name='69/694239/C2_symmetry/6'>C2</scene> symmetry down its central axis. The GGEEF domain is catalytic in that it contains the active sites used for cyclizing GTP into c-di-GMP. The CZB domain is used for ligand-mediated regulation of c-di-GMP production. Zinc binds as an allosteric inhibitor in coordination with four residues to shift the protein into an inactive conformation<sup>[1]</sup>. | ||
Revision as of 18:12, 14 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Diguanylate Cyclase DgcZ from Escherichia coli
| |||||||||||