This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox 123456
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
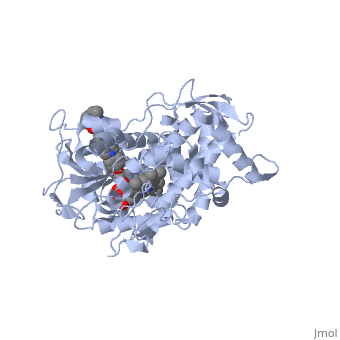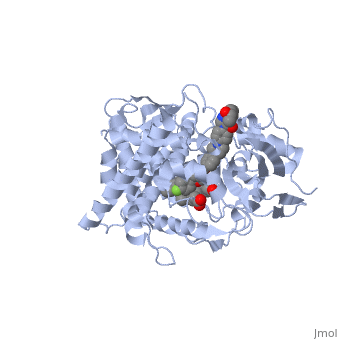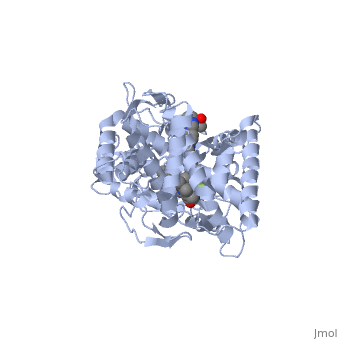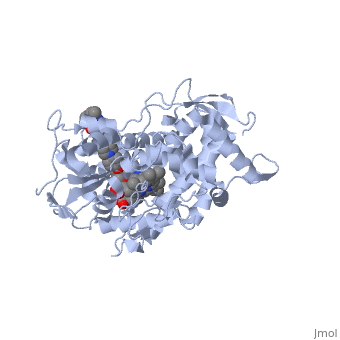
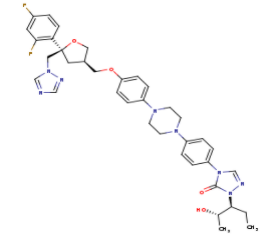
The primary component of Noxafil, posaconazole (green link) is a potent, broad-spectrum antifungal drug. It was derived from a similar triazole antifungal agent, Itraconazole. The differences in structure are that the chlorine substituents in the aromatic ring on the left-hand side of the images are replaces with fluorines and that the triazolone sidechain is hydroxylated in the posaconazole structure<ref name="drugbank">Posaconazole. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01263 | The primary component of Noxafil, posaconazole (green link) is a potent, broad-spectrum antifungal drug. It was derived from a similar triazole antifungal agent, Itraconazole. The differences in structure are that the chlorine substituents in the aromatic ring on the left-hand side of the images are replaces with fluorines and that the triazolone sidechain is hydroxylated in the posaconazole structure<ref name="drugbank">Posaconazole. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01263 | ||
| - | Accession Number: DB01263 </ref>. The extended side chain residues and hydrophobic contacts enhances antifungal activity by allowing tighter binding affinities to the <scene name='75/756730/Hemegroup/1'>heme cofactor</scene> in the active site of the CYP450-dependent enzyme lanosterol alpha-demthylase (CYP51) <ref name="groll">doi:10.1586/14787210.3.4.467</ref><ref>doi: 10.1086/523576</ref>. The tighter binding affinity of posaconazole makes it less susceptible to be affected by mutations in the enzyme resulting in resistance of fungi <ref name="formularyjournal">Sircar-Ramsewak,, F., Nicolau, D. P., & Kuti, J. L. (2005). Focus on posaconazole: A novel triazole antifungal for the treatment of invasive fungal infections. Formulary Journal - Modern Medicine Network </ref>. The scene shows the crystal <scene name='75/756730/ | + | Accession Number: DB01263 </ref>. The extended side chain residues and hydrophobic contacts enhances antifungal activity by allowing tighter binding affinities to the <scene name='75/756730/Hemegroup/1'>heme cofactor</scene> in the active site of the CYP450-dependent enzyme lanosterol alpha-demthylase (CYP51) <ref name="groll">doi:10.1586/14787210.3.4.467</ref><ref>doi: 10.1086/523576</ref>. The tighter binding affinity of posaconazole makes it less susceptible to be affected by mutations in the enzyme resulting in resistance of fungi <ref name="formularyjournal">Sircar-Ramsewak,, F., Nicolau, D. P., & Kuti, J. L. (2005). Focus on posaconazole: A novel triazole antifungal for the treatment of invasive fungal infections. Formulary Journal - Modern Medicine Network </ref>. The scene shows the crystal <scene name='75/756730/Structure/1'>structure</scene> of sterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51) from a pathogenic yeast Candida albicans in complex with the antifungal drug posaconazole |
Revision as of 20:52, 19 April 2017
| |||||||||||