We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1072
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
===Catalytic GGEEF Domain=== | ===Catalytic GGEEF Domain=== | ||
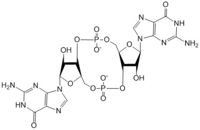
| - | The <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_dgcz/5'>GGEEF</scene> domain of DgcZ is part of the GGDEF family of proteins that includes a conserved sequence, GG[DE][DE]F<sup>[3]</sup>.The GGEEF domain is a homodimer consisting of a central five-stranded β-sheet surrounded by five α-helices. The GGEEF domain contains two catalytic half sites that, when combined together in a productive conformation, form the entire <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_dgcz/6'>active site</scene>. Residues Gly-206, Gly-207, Glu-208, Glu-209, and Phe-210 form the active site. Each <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_half_site_dgcz/1'>half-site</scene> binds one GTP molecule. DgcZ binds the guanine base of GTP through hydrogen bonds to <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_guanine_bonds_asn_asp_dgcz/4'>Asn173 and Asp 182</scene>. The ribose of each guanosine triphosphate, and subsequent product c-di-GMP riboses, are held only loosely by the enzyme, while the phosphate groups are not bound at all<sup>[1]</sup>. | + | The <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_dgcz/5'>GGEEF</scene> domain of DgcZ is part of the GGDEF family of proteins that includes a conserved sequence, GG[DE][DE]F<sup>[3]</sup>.The GGEEF domain is a homodimer consisting of a central five-stranded β-sheet surrounded by five α-helices. The GGEEF domain contains two catalytic half sites that, when combined together in a productive conformation, form the entire <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_dgcz/6'>active site</scene>. Residues Gly-206, Gly-207, Glu-208, Glu-209, and Phe-210 form the active site. Each <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_half_site_dgcz/1'>half-site</scene> binds one GTP molecule. DgcZ binds the guanine base of GTP through hydrogen bonds to <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_guanine_bonds_asn_asp_dgcz/4'>Asn173 and Asp 182</scene>. This scene depicts an inactive form of the protein because it was crystallized with zinc bound. The ribose of each guanosine triphosphate, and subsequent product c-di-GMP riboses, are held only loosely by the enzyme, while the phosphate groups are not bound to the active site at all<sup>[1]</sup>. |
The alpha phosphate is available for attack by the 3 prime hydroxyl group on another GTP. A <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_magnesium_cofactors_dgcz/1'>Magnesium ion</scene> (Mg<sup>2+</sup>) stabilizes the negative charges on the phosphate groups. When in the productive conformation, each GTP is held in close proximity with the α-phosphate groups overlapping C3 of the ribose ring. This conformation allows the α-phospate of one GTP to react with the alcohol group attached to C3 of the ribose on the second GTP, resulting in a cyclization of the two molecules into c-di-GMP. | The alpha phosphate is available for attack by the 3 prime hydroxyl group on another GTP. A <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_magnesium_cofactors_dgcz/1'>Magnesium ion</scene> (Mg<sup>2+</sup>) stabilizes the negative charges on the phosphate groups. When in the productive conformation, each GTP is held in close proximity with the α-phosphate groups overlapping C3 of the ribose ring. This conformation allows the α-phospate of one GTP to react with the alcohol group attached to C3 of the ribose on the second GTP, resulting in a cyclization of the two molecules into c-di-GMP. | ||
Revision as of 02:16, 21 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Diguanylate Cyclase DgcZ from Escherichia coli
| |||||||||||